How Springboot uses Redis to implement interface idempotent interception
Text
How to use custom annotations:
①Mark which interface requires idempotent interception
②Every Each interface can require different idempotent range times. For example: it can be within 2 seconds, it can be within 3 seconds, and the time is transmitted by itself.
③ Once triggered, the prompts can be different. For example: VIP interface, ordinary The user interface and prompts are different (just kidding)
Effect:
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* @Author: JCccc
* @Date: 2022-6-13 9:04
* @Description: 自定义注解,防止重复提交
*/
@Target({ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface RepeatDaMie {
/**
* 时间ms限制
*/
public int second() default 1;
/**
* 提示消息
*/
public String describe() default "重复提交了,兄弟";
}import com.example.repeatdemo.annotation.RepeatDaMie;
import com.example.repeatdemo.util.ContextUtil;
import com.example.repeatdemo.util.Md5Encrypt;
import com.example.repeatdemo.util.RedisUtils;
import com.example.repeatdemo.wrapper.CustomHttpServletRequestWrapper;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.method.HandlerMethod;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerInterceptor;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Objects;
/**
* @Author: JCccc
* @Date: 2022-6-15 9:11
* @Description: 接口幂等性校验拦截器
*/
@Component
public class ApiRepeatInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
private final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
private static final String POST="POST";
private static final String GET="GET";
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
try {
if (handler instanceof HandlerMethod) {
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = (HandlerMethod) handler;
// 获取RepeatDaMie注解
RepeatDaMie repeatDaMie = handlerMethod.getMethodAnnotation(RepeatDaMie.class);
if (null==repeatDaMie) {
return true;
}
//限制的时间范围
int seconds = repeatDaMie.second();
//这个用户唯一标识,可以自己细微调整,是userId还是token还是sessionId还是不需要
String userUniqueKey = request.getHeader("userUniqueKey");
String method = request.getMethod();
String apiParams = "";
if (GET.equals(method)){
log.info("GET请求来了");
apiParams = new ObjectMapper().writeValueAsString(request.getParameterMap());
}else if (POST.equals(method)){
log.info("POST请求来了");
CustomHttpServletRequestWrapper wrapper = (CustomHttpServletRequestWrapper) request;
apiParams = wrapper.getBody();
}
log.info("当前参数是:{}",apiParams);
// 存储key
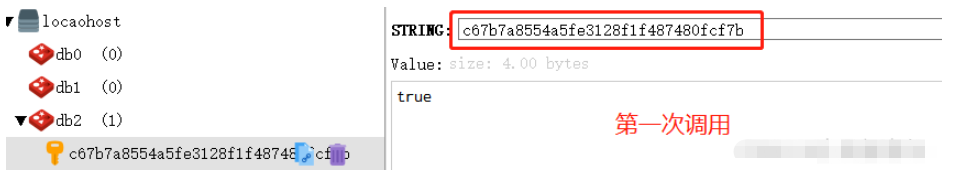
String keyRepeatDaMie = Md5Encrypt.md5(userUniqueKey+request.getServletPath()+apiParams) ;
RedisUtils redisUtils = ContextUtil.getBean(RedisUtils.class);
if (Objects.nonNull(redisUtils.get(keyRepeatDaMie))){
log.info("重复请求了,重复请求了,拦截了");
returnData(response,repeatDaMie.describe());
return false;
}else {
redisUtils.setWithTime(keyRepeatDaMie, true,seconds);
}
}
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
log.warn("请求过于频繁请稍后再试");
e.printStackTrace();
}
return true;
}
public void returnData(HttpServletResponse response,String msg) throws IOException {
response.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
response.setContentType("application/json; charset=utf-8");
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
//这里传提示语可以改成自己项目的返回数据封装的类
response.getWriter().println(objectMapper.writeValueAsString(msg));
return;
}
}import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.InterceptorRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;
/**
* @Author: JCccc
* @Date: 2022-6-15 9:24
* @Description:
*/
@Configuration
public class WebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(new ApiRepeatInterceptor()).addPathPatterns("/**");
}
}import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @Author: JCccc
* @Date: 2022-6-15 9:24
* @Description:
*/
@Component
public final class ContextUtil implements ApplicationContextAware {
protected static ApplicationContext applicationContext ;
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext arg0) throws BeansException {
if (applicationContext == null) {
applicationContext = arg0;
}
}
public static Object getBean(String name) {
//name表示其他要注入的注解name名
return applicationContext.getBean(name);
}
/**
* 拿到ApplicationContext对象实例后就可以手动获取Bean的注入实例对象
*/
public static <T> T getBean(Class<T> clazz) {
return applicationContext.getBean(clazz);
}
}import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
import java.security.MessageDigest;
import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;
/**
* @Author: JCccc
* @CreateTime: 2018-10-30
* @Description:
*/
public class Md5Encrypt {
private static final char[] DIGITS = {'0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9', 'a',
'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f'};
/**
* 对字符串进行MD5加密
*
* @param text 明文
* @return 密文
*/
public static String md5(String text) {
MessageDigest msgDigest = null;
try {
msgDigest = MessageDigest.getInstance("MD5");
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException("System doesn't support MD5 algorithm.");
}
try {
// 注意该接口是按照指定编码形式签名
msgDigest.update(text.getBytes("UTF-8"));
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException("System doesn't support your EncodingException.");
}
byte[] bytes = msgDigest.digest();
String md5Str = new String(encodeHex(bytes));
return md5Str;
}
private static char[] encodeHex(byte[] data) {
int l = data.length;
char[] out = new char[l << 1];
// two characters form the hex value.
for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < l; i++) {
out[j++] = DIGITS[(0xF0 & data[i]) >>> 4];
out[j++] = DIGITS[0x0F & data[i]];
}
return out;
}
}import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@Component
public class RedisUtils {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
/**
* 写入String型 [ 键,值]
*
* @param key
* @param value
* @return
*/
public boolean set(final String key, Object value) {
boolean result = false;
try {
ValueOperations<Serializable, Object> operations = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
operations.set(key, value);
result = true;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return result;
}
/**
* 写入String型,顺便带有过期时间 [ 键,值]
*
* @param key
* @param value
* @return
*/
public boolean setWithTime(final String key, Object value,int seconds) {
boolean result = false;
try {
ValueOperations<Serializable, Object> operations = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
operations.set(key, value,seconds, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
result = true;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return result;
}
/**
* 批量删除对应的value
*
* @param keys
*/
public void remove(final String... keys) {
for (String key : keys) {
remove(key);
}
}
/**
* 批量删除key
*
* @param pattern
*/
public void removePattern(final String pattern) {
Set<Serializable> keys = redisTemplate.keys(pattern);
if (keys.size() > 0)
redisTemplate.delete(keys);
}
/**
* 删除对应的value
*
* @param key
*/
public void remove(final String key) {
if (exists(key)) {
redisTemplate.delete(key);
}
}
/**
* 判断缓存中是否有对应的value
*
* @param key
* @return
*/
public boolean exists(final String key) {
return redisTemplate.hasKey(key);
}
/**
* 读取缓存
*
* @param key
* @return
*/
public Object get(final String key) {
Object result = null;
ValueOperations<Serializable, Object> operations = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
result = operations.get(key);
return result;
}
/**
* 哈希 添加
* hash 一个键值(key->value)对集合
*
* @param key
* @param hashKey
* @param value
*/
public void hmSet(String key, Object hashKey, Object value) {
HashOperations<String, Object, Object> hash = redisTemplate.opsForHash();
hash.put(key, hashKey, value);
}
/**
* Hash获取数据
*
* @param key
* @param hashKey
* @return
*/
public Object hmGet(String key, Object hashKey) {
HashOperations<String, Object, Object> hash = redisTemplate.opsForHash();
return hash.get(key, hashKey);
}
/**
* 列表添加
* list:lpush key value1
*
* @param k
* @param v
*/
public void lPush(String k, Object v) {
ListOperations<String, Object> list = redisTemplate.opsForList();
list.rightPush(k, v);
}
/**
* 列表List获取
* lrange: key 0 10 (读取的个数 从0开始 读取到下标为10 的数据)
*
* @param k
* @param l
* @param l1
* @return
*/
public List<Object> lRange(String k, long l, long l1) {
ListOperations<String, Object> list = redisTemplate.opsForList();
return list.range(k, l, l1);
}
/**
* Set集合添加
*
* @param key
* @param value
*/
public void add(String key, Object value) {
SetOperations<String, Object> set = redisTemplate.opsForSet();
set.add(key, value);
}
/**
* Set 集合获取
*
* @param key
* @return
*/
public Set<Object> setMembers(String key) {
SetOperations<String, Object> set = redisTemplate.opsForSet();
return set.members(key);
}
/**
* Sorted set :有序集合添加
*
* @param key
* @param value
* @param scoure
*/
public void zAdd(String key, Object value, double scoure) {
ZSetOperations<String, Object> zset = redisTemplate.opsForZSet();
zset.add(key, value, scoure);
}
/**
* Sorted set:有序集合获取
*
* @param key
* @param scoure
* @param scoure1
* @return
*/
public Set<Object> rangeByScore(String key, double scoure, double scoure1) {
ZSetOperations<String, Object> zset = redisTemplate.opsForZSet();
return zset.rangeByScore(key, scoure, scoure1);
}
/**
* 根据key获取Set中的所有值
*
* @param key 键
* @return
*/
public Set<Integer> sGet(String key) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForSet().members(key);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* 根据value从一个set中查询,是否存在
*
* @param key 键
* @param value 值
* @return true 存在 false不存在
*/
public boolean sHasKey(String key, Object value) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForSet().isMember(key, value);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
}
}import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonAutoDetect;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.PropertyAccessor;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import org.springframework.cache.CacheManager;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheManager;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializationContext;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;
import static org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig;
/**
* @Author: JCccc
* @CreateTime: 2018-09-11
* @Description:
*/
@Configuration
@EnableCaching
public class RedisConfig {
@Bean
public CacheManager cacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
RedisCacheConfiguration cacheConfiguration =
defaultCacheConfig()
.disableCachingNullValues()
.serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class)));
return RedisCacheManager.builder(connectionFactory).cacheDefaults(cacheConfiguration).build();
}
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory factory) {
RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>();
redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(factory);
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
om.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
om.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
jackson2JsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(om);
//序列化设置 ,这样为了存储操作对象时正常显示的数据,也能正常存储和获取
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setHashValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
return redisTemplate;
}
@Bean
public StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory factory) {
StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate = new StringRedisTemplate();
stringRedisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(factory);
return stringRedisTemplate;
}
}import com.example.repeatdemo.dto.PayOrderApply;
import com.example.repeatdemo.annotation.RepeatDaMie;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
/**
* @Author: JCccc
* @Date: 2022-6-05 9:44
* @Description:
*/
@RestController
public class TestController {
private final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
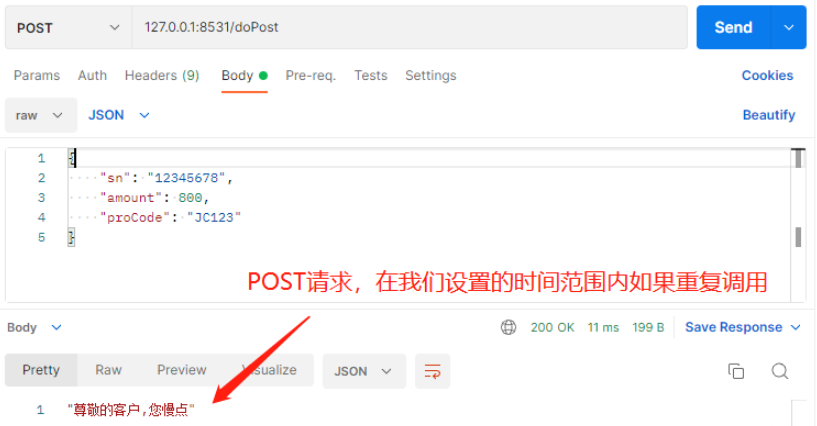
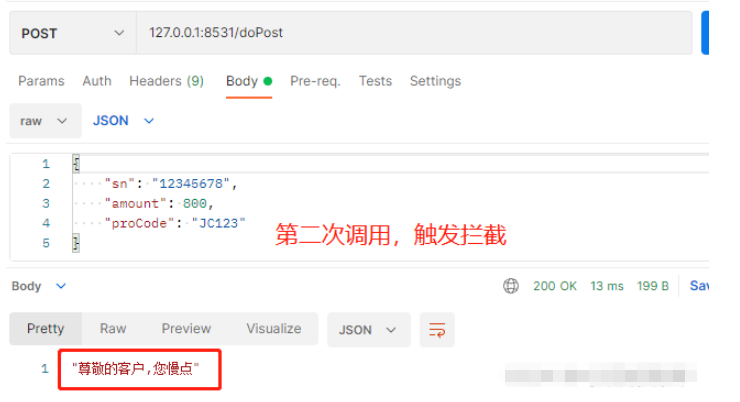
@RepeatDaMie(second = 1000,describe = "尊敬的客户,您慢点")
@PostMapping(value = "/doPost")
@ResponseBody
public void test(@RequestBody PayOrderApply payOrderApply) {
log.info("Controller POST请求:"+payOrderApply.toString());
}
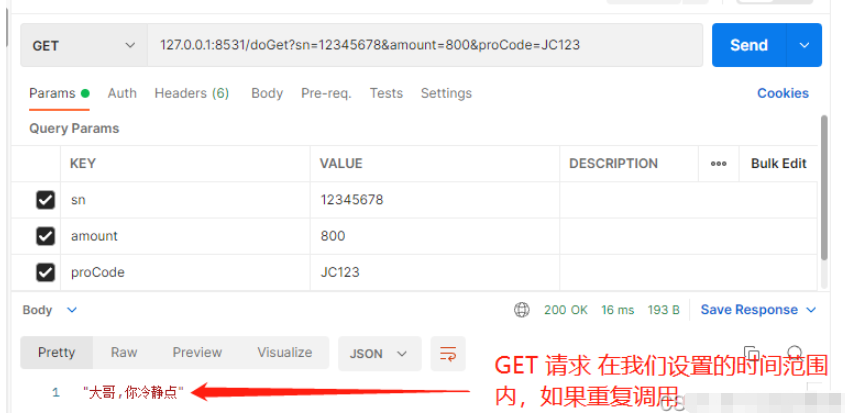
@RepeatDaMie(second = 1000,describe = "大哥,你冷静点")
@GetMapping(value = "/doGet")
@ResponseBody
public void doGet( PayOrderApply payOrderApply) {
log.info("Controller GET请求:"+payOrderApply.toString());
}
}/**
* @Author: JCccc
* @Date: 2022-6-12 9:46
* @Description:
*/
public class PayOrderApply {
private String sn;
private Long amount;
private String proCode;
public String getSn() {
return sn;
}
public void setSn(String sn) {
this.sn = sn;
}
public Long getAmount() {
return amount;
}
public void setAmount(Long amount) {
this.amount = amount;
}
public String getProCode() {
return proCode;
}
public void setProCode(String proCode) {
this.proCode = proCode;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "PayOrderApply{" +
"sn='" + sn + '\'' +
", amount=" + amount +
", proCode='" + proCode + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
The above is the detailed content of How Springboot uses Redis to implement interface idempotent interception. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear Redis data: Use the FLUSHALL command to clear all key values. Use the FLUSHDB command to clear the key value of the currently selected database. Use SELECT to switch databases, and then use FLUSHDB to clear multiple databases. Use the DEL command to delete a specific key. Use the redis-cli tool to clear the data.
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
Using the Redis directive requires the following steps: Open the Redis client. Enter the command (verb key value). Provides the required parameters (varies from instruction to instruction). Press Enter to execute the command. Redis returns a response indicating the result of the operation (usually OK or -ERR).
 How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
Using Redis to lock operations requires obtaining the lock through the SETNX command, and then using the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time. The specific steps are: (1) Use the SETNX command to try to set a key-value pair; (2) Use the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time for the lock; (3) Use the DEL command to delete the lock when the lock is no longer needed.
 How to configure Lua script execution time in centos redis
Apr 14, 2025 pm 02:12 PM
How to configure Lua script execution time in centos redis
Apr 14, 2025 pm 02:12 PM
On CentOS systems, you can limit the execution time of Lua scripts by modifying Redis configuration files or using Redis commands to prevent malicious scripts from consuming too much resources. Method 1: Modify the Redis configuration file and locate the Redis configuration file: The Redis configuration file is usually located in /etc/redis/redis.conf. Edit configuration file: Open the configuration file using a text editor (such as vi or nano): sudovi/etc/redis/redis.conf Set the Lua script execution time limit: Add or modify the following lines in the configuration file to set the maximum execution time of the Lua script (unit: milliseconds)
 How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
Use the Redis command line tool (redis-cli) to manage and operate Redis through the following steps: Connect to the server, specify the address and port. Send commands to the server using the command name and parameters. Use the HELP command to view help information for a specific command. Use the QUIT command to exit the command line tool.
 How to optimize the performance of debian readdir
Apr 13, 2025 am 08:48 AM
How to optimize the performance of debian readdir
Apr 13, 2025 am 08:48 AM
In Debian systems, readdir system calls are used to read directory contents. If its performance is not good, try the following optimization strategy: Simplify the number of directory files: Split large directories into multiple small directories as much as possible, reducing the number of items processed per readdir call. Enable directory content caching: build a cache mechanism, update the cache regularly or when directory content changes, and reduce frequent calls to readdir. Memory caches (such as Memcached or Redis) or local caches (such as files or databases) can be considered. Adopt efficient data structure: If you implement directory traversal by yourself, select more efficient data structures (such as hash tables instead of linear search) to store and access directory information






