How to configure the master-slave mode of Redis cluster

1. Why is a cluster needed?
In our actual development, it is not possible to use only one Redis in engineering projects for the following reasons:
(1) In terms of structure, a single Redis server has the risk of a single point of failure, and one server needs to bear the load of all requests, which puts a relatively high pressure
(2) From In terms of capacity, the memory capacity of a single Redis server is limited. Even if the memory capacity of a Redis server is 256G, all the memory cannot be used as Redis storage memory. Generally speaking, the maximum memory used by a single Redis server should not exceed 20G.
(3) The read and write performance of a single Redis server is limited, and the read and write capabilities can be improved by using a cluster.
2. Master-slave mode
Introduction
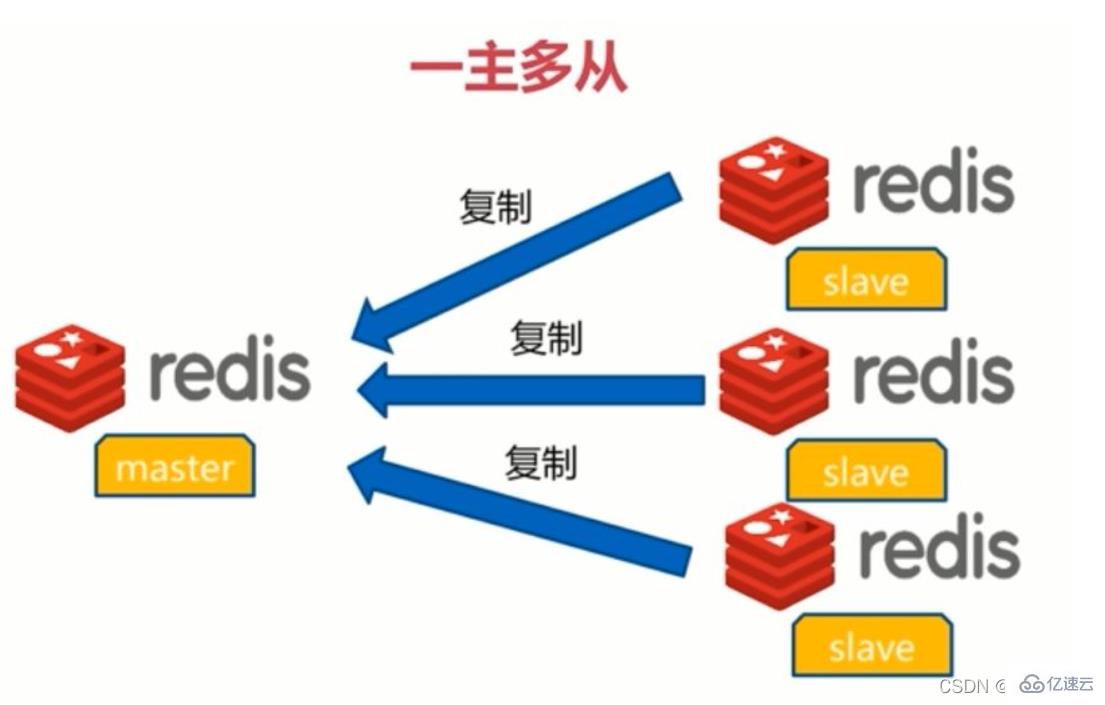
Currently, Redis has three cluster modes, namely: master-slave mode , Sentinel mode, Cluster mode; master-slave mode is the simplest of the three modes. In master-slave replication, it refers to copying the data of one Redis server to other Redis servers. The first one is called the master node (master/leader), while the second one is called the slave node (slave/follower).
Note:
(1) Data replication is one-way, only from the master node to the slave node node. Master is mainly for writing, and Slave is mainly for reading.
(2) By default, each Redis server is a master node;
(3) A master node can have multiple slave nodes (or no slave nodes), but a slave node can only have one master node. node.
Function
1.Data redundancy: Master-slave replication realizes data redundancy Hot backup is a data redundancy method other than persistence.
2. Failure recovery: When a problem occurs on the master node, the slave node can provide services to achieve rapid failure recovery; it is actually a kind of service redundancy.
3. Cornerstone of high availability (cluster) : Master-slave replication is still the basis for the implementation of sentinels and clusters. Therefore, master-slave replication is the basis of Redis high availability.
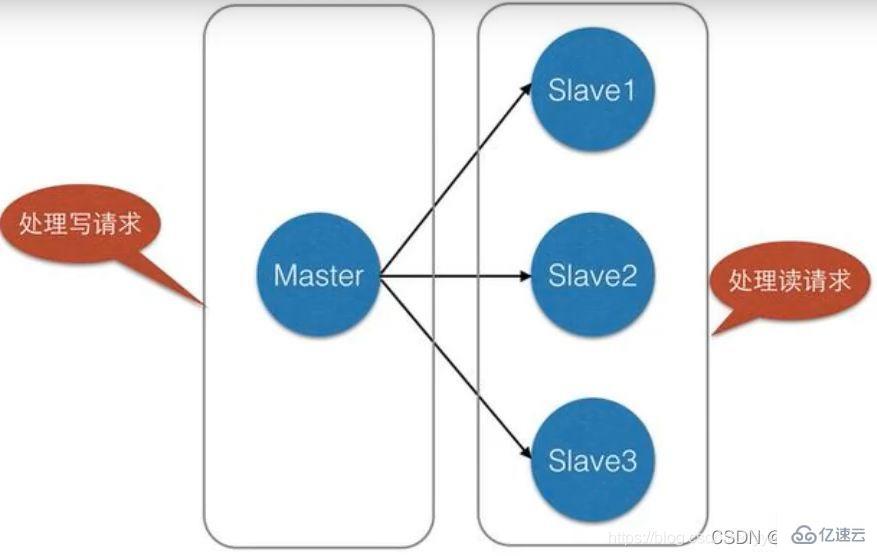
4. Load balancing: On the basis of master-slave replication, combined with read-write separation, the master node can provide write services and the slave nodes can provide read services (that is, when writing Redis data, the application connects to the master Node, when reading Redis data, the application connects to the slave node) to share the server load; especially in the scenario of less writing and more reading, sharing the read load through multiple slave nodes can greatly increase the concurrency of the Redis server.
For example, you can find on our e-commerce website that a product only needs to be uploaded once, but it can be viewed multiple times by the user, that is, "write Read less and read more" In this case, we can use master-slave replication to separate reading and writing,reduce the pressure on the server:
3. Build the master-slave cluster
3.1. Preparation work
1. Copy Three configuration files (original name: redis.conf) were renamed to: redis79.conf, redis80.conf, redis81.conf.
2. Modify the configuration file
(1) Modify redis79.conf
Modify the port number
port 6379
Set to run in the background
daemonize:yes
Set the name of the log file
logfile “6379.log"
Set the db file name
dbfilename dump6379.rdb
(2) Modify redis80.conf
##Modify the port number
port 6380
Set to run in the background
daemonize:yes
Set the recording process Id file name
pidfile /var/run/redis_6380.pid
Set the log file Name
logfile “6380.log"
Set the db file name
dbfilename dump6380.rdb
(3) Modify redis81.conf
Modify the port number
port 6381
Set to run in the background
daemonize:yes
Set the recording process ID file name
pidfile /var/run/redis_6381.pid
Set the name of the log file
logfile “6381.log"
Set the name of the db file
dbfilename dump6381.rdb
The functions of these attributes are as follows:
pid(port ID): The ID of the process is recorded, and the file has a lock. Prevents the program from being started multiple times. logfile: Clear the location of the log file
dbfilename: dumpxxx.file #Persistent file location
port: The port number occupied by the process
3.2、搭建一主二从
启动Redis服务器
注意:默认情况下,每台Reids服务器都是主节点,而我们要搭建主从只需要在从机那本搭建即可。
现在分别启动redis79,redis80,redis81服务器。
redis-server redis79.conf redis-server redis80.conf redis-server redis81.conf
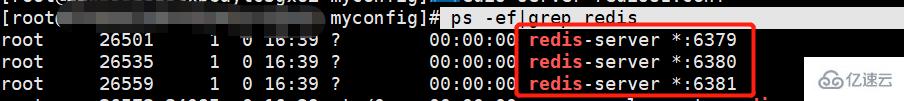
使用以下命令,查看是否启动成功:
ps -ef|grep redis
打开三个客户端窗口,分别对应操作三个Redis服务器。
输入命令:
注意要指定端口,才知道我们要打开哪一个Redis。
窗口一:
redis-cli -p 6379
窗口二:
redis-cli -p 6380
窗口三:
redis-cli -p 6381
设置主从关系
我们将redis79设置为主节点,而将redis80和redis81设置为从结点。
配置主机的IP地址和端口号,相当于想认其为自己的老大。
redis80:
#SLAVEOF IP地址 端口 127.0.0.1:6380> slaveof 127.0.0.1 6379 OK
redis81:
#SLAVEOF IP地址 端口 127.0.0.1:6381> slaveof 127.0.0.1 6379 OK
这个时候,我们在从机使用INFO命令就可以查看主从关系了:
info replication
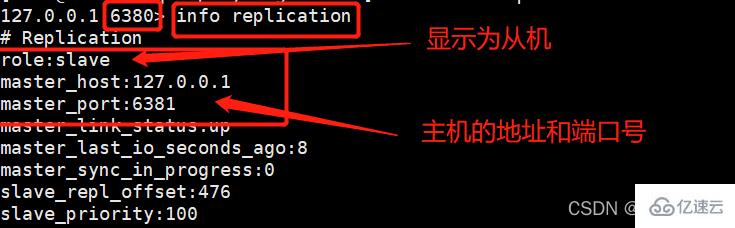
而此时我们去主机redis79中使用同样的命令进行查看:
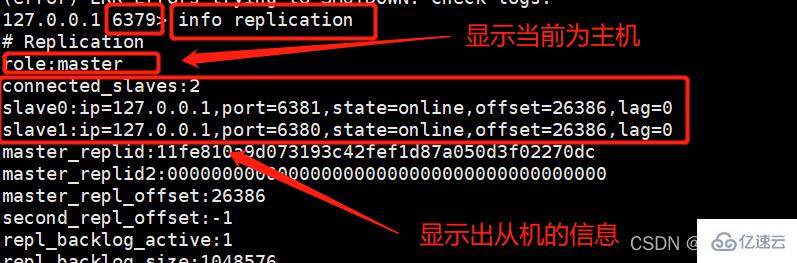
现在我们的一主二从的关系就成功搭建好了!
提示:如果要将从机变成主机,我们只需要在从机执行以下命令,即可让自己变为主机。
SLAVEOF no one
四、知识讲解
知识一
主机可以进行读写操作,而从机只能读操作。
注意:主机中的所有信息和数据,都会自动被从机保存。
主机:
127.0.0.1:6379> set key1 v1 OK 127.0.0.1:6379> get key1 "v1"
从机:
127.0.0.1:6380> get key1 "v1" 127.0.0.1:6380> set key2 v2 #进行写操作就会报错,提示从机只能进行读操作 (error) READONLY You can't write against a read only replica.
知识二
主机如果宕机了,从机依旧可以读取到主机宕机前的数据,但仍然没有写操作,如果主机恢复过来了,从机依旧可以获取到主机写的数据。
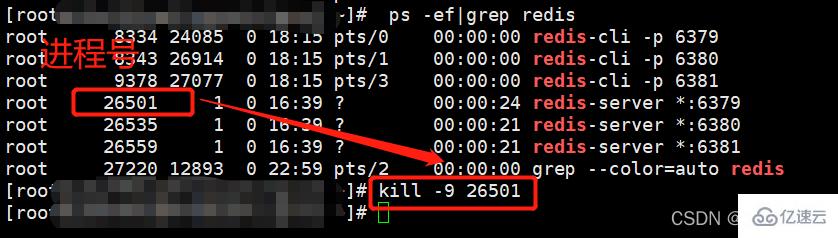
(1)停止主机进程(演示主机宕机了)
停止进程的命令:
kill -9 pid #pid为redis进程号
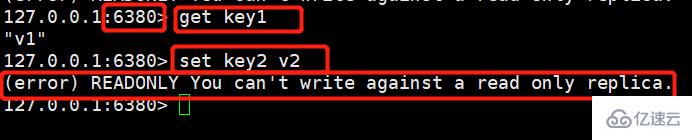
(2)从机获取宕机前主机写入的数据
可以发现,能够顺利拿到,但仍然是无法进行写操作的。
(3)恢复主机
redis-server redis79.conf
(4)主机重新写入数据,从机获取最新数据。
主机写入数据:
127.0.0.1:6379> set k2 yixin OK
从机读取最新数据:
127.0.0.1:6380> get k2 "yixin"
知识三
两种配置方式下的从机断开情况
a、命令行设置主从关系
从机断开了,其重新连接后变为主机,能拿到断开之前的数据,但拿不到主机新写入的值,如果重新设置主从关系,就可以拿到主机全部的数据了。
(1)停止从机进程。
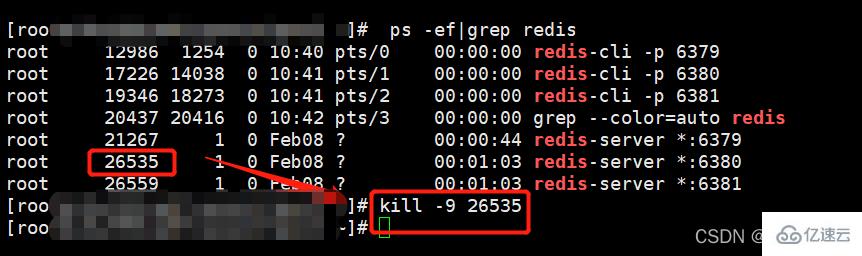
(2)主机写入新数据。
127.0.0.1:6379> set k3 new OK
(3)重新启动从机服务器。
redis-server redis80.conf
(4)尝试获取从机宕机前主机写入的数据,发现可以拿到。
127.0.0.1:6380> get k1 "v1"
(5)尝试获取从机宕机期间主机写入的数据,发现无法拿到了。
127.0.0.1:6380> get k3 (nil)
此次我们可以进行查看主从关系,由于是命令行配置的,所以重启之后又变回主机了。
127.0.0.1:6380> info replication # Replication role:master connected_slaves:0
(6)如果要拿到主机的所有数据,只要执行以下命令重新配置主从关系就可以了。
slaveof 127.0.0.1 6379
b、配置文件设置的主从关系
从机断开后,重新连接,也是可以拿到主机的全部数据的。
(1)修改配置文件redis80.conf,添加主从关系。
#指定主机的ip与port slaveof 127.0.0.1 6379
(2)主机添加新数据
127.0.0.1:6379> set k5 hello OK
(3)重新启动redis80服务器。
redis-server redis80.conf
(4)获取从机宕机期间主机新写入的数据,发现现在可以顺利拿到了。
127.0.0.1:6380> get k5 "hello"
我们来查看6380的主从关系,可以发现在重启的时候就已经设置好主从关系了。
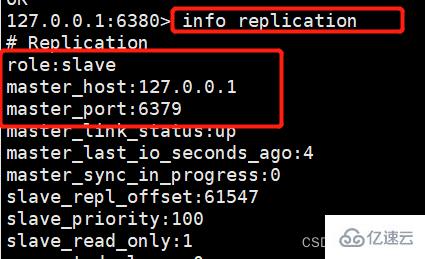
五、复制原理
(1)Slave 启动成功连接到 Master 后会发送一个sync同步命令
(2)Master 接到命令,启动后台的存盘进程,同时收集所有接收到的用于修改数据集命令,在后台进程执行完毕之后,master将传送整个数据文件到slave,并完成一次完全同步。
(3)全量复制:而slave服务在接收到数据库文件数据后,将其存盘并加载到内存中。
(4)增量复制:Master 继续将新的所有收集到的修改命令依次传给slave,完成同步。
注意:只要是重新连接master,一次完全同步(全量复制)将被自动执行! 我们的数据一定可以在从机中看到。
六、主从模式的优缺点
优点
(1)同一个Master可以同步多个Slaves。
(2)Slave同样可以接受其它Slaves的连接和同步请求,这样可以有效的分载Master的同步压力。因此我们可以将Redis的Replication架构视为图结构。
(3)Master Server是以非阻塞的方式为Slaves提供服务。所以在Master-Slave同步期间,客户端仍然可以提交查询或修改请求。
(4)Slave Server同样是以非阻塞的方式完成数据同步。在同步期间,如果有客户端提交查询请求,Redis则返回同步之前的数据。
(5)为了分载Master的读操作压力,Slave服务器可以为客户端提供只读操作的服务,写服务仍然必须由Master来完成。即便如此,系统的伸缩性还是得到了很大的提高。
(6)Master可以将数据保存操作交给Slaves完成,从而避免了在Master中要有独立的进程来完成此操作。
(7)支持主从复制,主机会自动将数据同步到从机,可以进行读写分离。
缺点
(1) Redis 主从模式不具备自动容错和恢复功能,如果主节点宕机,Redis 集群将无法工作,此时需要人为干预,将从节点提升为主节点。
(2) 如果主机宕机前有一部分数据未能及时同步到从机,即使切换主机后也会造成数据不一致的问题,从而降低了系统的可用性。
(3) 因为只有一个主节点,所以其写入能力和存储能力都受到一定程度地限制。
(4) 在进行数据全量同步时,若同步的数据量较大可能会造卡顿的现象。
The above is the detailed content of How to configure the master-slave mode of Redis cluster. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear Redis data: Use the FLUSHALL command to clear all key values. Use the FLUSHDB command to clear the key value of the currently selected database. Use SELECT to switch databases, and then use FLUSHDB to clear multiple databases. Use the DEL command to delete a specific key. Use the redis-cli tool to clear the data.
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
Using the Redis directive requires the following steps: Open the Redis client. Enter the command (verb key value). Provides the required parameters (varies from instruction to instruction). Press Enter to execute the command. Redis returns a response indicating the result of the operation (usually OK or -ERR).
 How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
Using Redis to lock operations requires obtaining the lock through the SETNX command, and then using the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time. The specific steps are: (1) Use the SETNX command to try to set a key-value pair; (2) Use the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time for the lock; (3) Use the DEL command to delete the lock when the lock is no longer needed.
 How to configure Lua script execution time in centos redis
Apr 14, 2025 pm 02:12 PM
How to configure Lua script execution time in centos redis
Apr 14, 2025 pm 02:12 PM
On CentOS systems, you can limit the execution time of Lua scripts by modifying Redis configuration files or using Redis commands to prevent malicious scripts from consuming too much resources. Method 1: Modify the Redis configuration file and locate the Redis configuration file: The Redis configuration file is usually located in /etc/redis/redis.conf. Edit configuration file: Open the configuration file using a text editor (such as vi or nano): sudovi/etc/redis/redis.conf Set the Lua script execution time limit: Add or modify the following lines in the configuration file to set the maximum execution time of the Lua script (unit: milliseconds)
 How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
Use the Redis command line tool (redis-cli) to manage and operate Redis through the following steps: Connect to the server, specify the address and port. Send commands to the server using the command name and parameters. Use the HELP command to view help information for a specific command. Use the QUIT command to exit the command line tool.
 How to optimize the performance of debian readdir
Apr 13, 2025 am 08:48 AM
How to optimize the performance of debian readdir
Apr 13, 2025 am 08:48 AM
In Debian systems, readdir system calls are used to read directory contents. If its performance is not good, try the following optimization strategy: Simplify the number of directory files: Split large directories into multiple small directories as much as possible, reducing the number of items processed per readdir call. Enable directory content caching: build a cache mechanism, update the cache regularly or when directory content changes, and reduce frequent calls to readdir. Memory caches (such as Memcached or Redis) or local caches (such as files or databases) can be considered. Adopt efficient data structure: If you implement directory traversal by yourself, select more efficient data structures (such as hash tables instead of linear search) to store and access directory information






