How SpringBoot integrates Redis to serialize and store Java objects
1. Background
1. Thinking
Through our previous study, we can already store strings in Redis, so what should we do to store Java objects in Redis? What to do?
2. Solution
We can convert Java objects into JSON objects, then into JSON strings, and store them in Redis. Then when we take out the data from Redis, we only Can take out a string and convert it into a Java object. Does this series of operations seem a bit troublesome?
2. Source code analysis
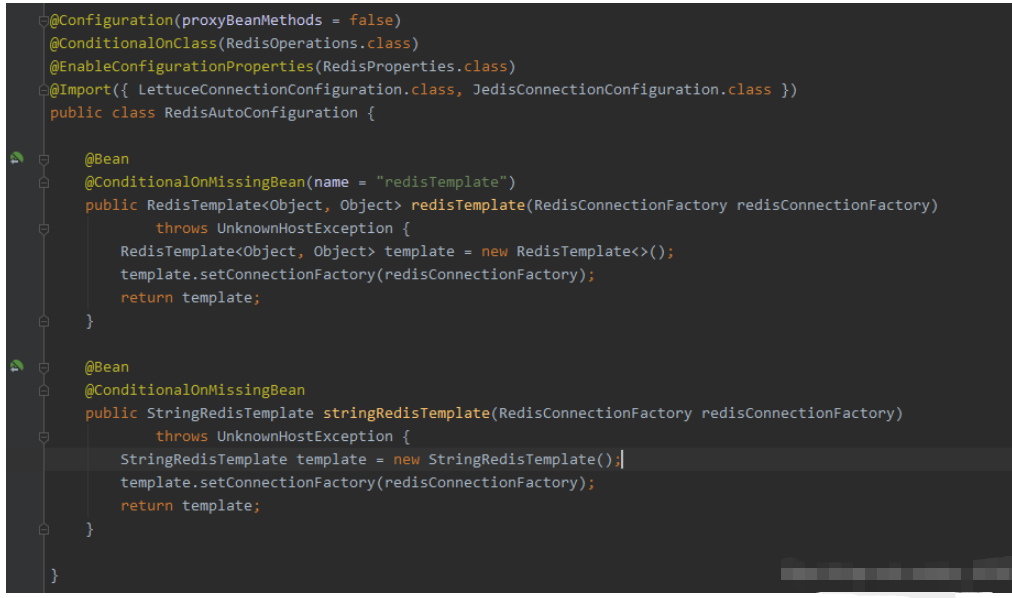
The above is the source code fragment in the RedisAutoConfiguration class. It can be seen that SpringBoot automatically configures Redis. At that time, redisTemplate and stringRedisTemplate
were injected into the container. RedisTemplate
After seeing this @ConditionalOnMissingBean annotation, you know that if there is a RedisTemplate object in the Spring container, this automatically configured RedisTemplate will not be instantiated. Therefore, we have the ability to write custom configuration classes to configure RedisTemplate.
3. Inject RedisTemplate
1. Introduce dependencies
<!-- redis -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>The above has introduced the dependency of redis, please add the other dependencies by yourself
2. Redis connection information
spring:
# Redis配置
redis:
host: 127.0.0.1
port: 6379
database: 10
jedis:
pool:
# 连接池最大连接数(使用负值表示没有限制)
max-active: 50
# 连接池最大阻塞等待时间(使用负值表示没有限制)
max-wait: 3000ms
# 连接池中的最大空闲连接数
max-idle: 20
# 连接池中的最小空闲连接数
min-idle: 5
# 连接超时时间(毫秒)
timeout: 5000ms3. Redis core configuration class
We place the core configuration of Redis in the RedisConfig.java file
package com.zyxx.redistest.common;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonAutoDetect;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.PropertyAccessor;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;
/**
* @ClassName RedisConfig
* @Description
* @Author Lizhou
* @Date 2020-10-22 9:48:48
**/
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {
/**
* RedisTemplate配置
*/
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) {
// 配置redisTemplate
RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>();
redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
// 设置序列化
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Object> jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<>(Object.class);
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
om.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
om.activateDefaultTyping(LaissezFaireSubTypeValidator.instance, ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL, JsonTypeInfo.As.PROPERTY);
jackson2JsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(om);
// key序列化
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
// value序列化
redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
// Hash key序列化
redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
// Hash value序列化
redisTemplate.setHashValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
redisTemplate.afterPropertiesSet();
return redisTemplate;
}
}We inject a file named redisTemplate, a Bean of type RedisTemplate
4, Redis tool class
We will conduct a series of Redis The series of operations are placed in the RedisUtils.java file
package com.zyxx.redistest.common;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @ClassName RedisUtils
* @Description
* @Author Lizhou
* @Date 2020-10-22 10:10:10
**/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class RedisUtils {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate;
/**
* 根据key读取数据
*/
public Object get(final String key) {
if (StringUtils.isBlank(key)) {
return null;
}
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
/**
* 写入数据
*/
public boolean set(final String key, Object value) {
if (StringUtils.isBlank(key)) {
return false;
}
try {
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, value);
log.info("存入redis成功,key:{},value:{}", key, value);
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("存入redis失败,key:{},value:{}", key, value);
e.printStackTrace();
}
return false;
}
}We wrote the get and set methods for testing
4. Test
1. Create a Java entity class UserInfo
package com.zyxx.redistest.common;
import lombok.Data;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* @ClassName UserInfo
* @Description
* @Author Lizhou
* @Date 2020-10-22 10:12:12
**/
@Data
public class UserInfo implements Serializable {
/**
* id
*/
private Integer id;
/**
* 姓名
*/
private String name;
/**
* 创建时间
*/
private Date createTime;
}2. Test case
package com.zyxx.redistest;
import com.zyxx.redistest.common.RedisUtils;
import com.zyxx.redistest.common.UserInfo;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import java.util.Date;
@SpringBootTest
class RedisTestApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private RedisUtils redisUtil;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
UserInfo userInfo = new UserInfo();
userInfo.setId(1);
userInfo.setName("jack");
userInfo.setCreateTime(new Date());
// 放入redis
redisUtil.set("user", userInfo);
// 从redis中获取
System.out.println("获取到数据:" + redisUtil.get("user"));
}
}We store a data with key "user" and value as UserInfo object into Redis, and then obtain the data based on key
3. Test results
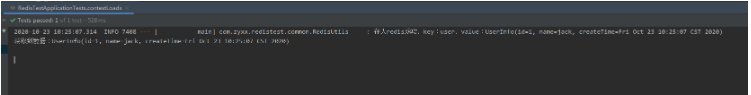
It can be seen that we successfully stored Java object data in Redis and successfully obtained the object.
The above is the detailed content of How SpringBoot integrates Redis to serialize and store Java objects. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 PHP: A Key Language for Web Development
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP: A Key Language for Web Development
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP is a scripting language widely used on the server side, especially suitable for web development. 1.PHP can embed HTML, process HTTP requests and responses, and supports a variety of databases. 2.PHP is used to generate dynamic web content, process form data, access databases, etc., with strong community support and open source resources. 3. PHP is an interpreted language, and the execution process includes lexical analysis, grammatical analysis, compilation and execution. 4.PHP can be combined with MySQL for advanced applications such as user registration systems. 5. When debugging PHP, you can use functions such as error_reporting() and var_dump(). 6. Optimize PHP code to use caching mechanisms, optimize database queries and use built-in functions. 7
 PHP vs. Python: Understanding the Differences
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP vs. Python: Understanding the Differences
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages, and the choice should be based on project requirements. 1.PHP is suitable for web development, with simple syntax and high execution efficiency. 2. Python is suitable for data science and machine learning, with concise syntax and rich libraries.
 PHP vs. Other Languages: A Comparison
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP vs. Other Languages: A Comparison
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP is suitable for web development, especially in rapid development and processing dynamic content, but is not good at data science and enterprise-level applications. Compared with Python, PHP has more advantages in web development, but is not as good as Python in the field of data science; compared with Java, PHP performs worse in enterprise-level applications, but is more flexible in web development; compared with JavaScript, PHP is more concise in back-end development, but is not as good as JavaScript in front-end development.
 How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear Redis data: Use the FLUSHALL command to clear all key values. Use the FLUSHDB command to clear the key value of the currently selected database. Use SELECT to switch databases, and then use FLUSHDB to clear multiple databases. Use the DEL command to delete a specific key. Use the redis-cli tool to clear the data.
 PHP vs. Python: Core Features and Functionality
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:16 AM
PHP vs. Python: Core Features and Functionality
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:16 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages and are suitable for different scenarios. 1.PHP is suitable for web development and provides built-in web servers and rich function libraries. 2. Python is suitable for data science and machine learning, with concise syntax and a powerful standard library. When choosing, it should be decided based on project requirements.
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 PHP: The Foundation of Many Websites
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP: The Foundation of Many Websites
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
The reasons why PHP is the preferred technology stack for many websites include its ease of use, strong community support, and widespread use. 1) Easy to learn and use, suitable for beginners. 2) Have a huge developer community and rich resources. 3) Widely used in WordPress, Drupal and other platforms. 4) Integrate tightly with web servers to simplify development deployment.






