How to implement Redis7.0 deployment cluster
Redis7.0 Deployment Cluster Detailed Version
The cluster architecture is a way to connect multiple computers through the network and use a unified management method to externally appear as a single computer providing services
The role of the cluster:
Distribute the access pressure of a single server and achieve load balancing
Distribute the storage of a single server Pressure and achieve scalability
Reduce the business disaster caused by the downtime of a single server
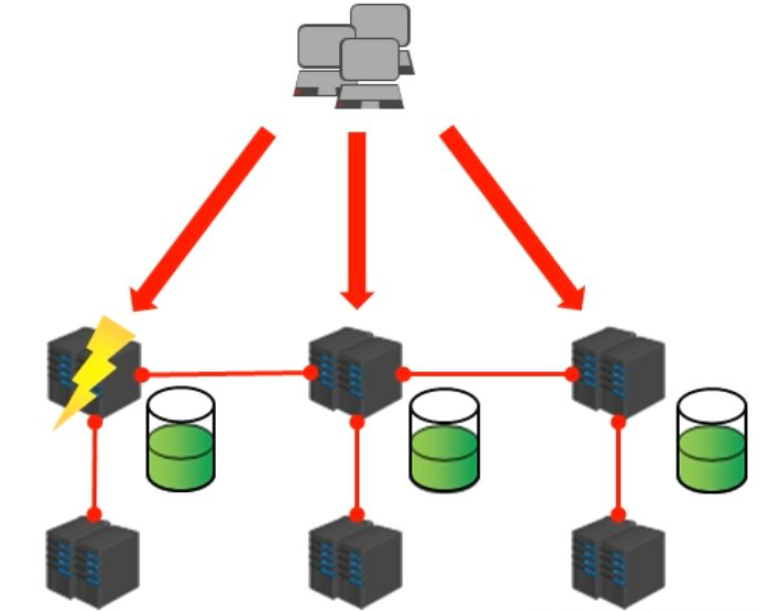
1 , Redis cluster internal structure design
Data storage design
Through algorithm design, calculate the location where the key should be saved
All storage spaces are planned to be cut into 16384 parts, and each host saves a part. Each part represents a storage space, not a key storage space.
The key is calculated according to the The results are placed in the corresponding storage space
Enhance scalability (new storage space is added, officially called
slot)
Internal communication design of the cluster
Each database communicates with each other and saves the numbered data of the slot in each library
Once hit, return directly
Once a miss, inform the specific location
2. Building the internal structure of the cluster
In the virtual machine Start multiple windows for cluster construction demonstration

The main command is executed on the
main command operation client
Modifyredis.confConfiguration file
Add the following content
cluster-enabled yes # 启动为节点 cluster-config-file nodes-6379.conf # cluster配置文件名,该文件属于自动生成,仅用于快速查找文件并查询文件内容 cluster-node-timeout 10000 # 节点服务响应超时时间,用于判定该节点是否下线或切换为从节点 cluster-migration-barrier <count> # master连接的slave最小数量
Quickly copy 5 points of the configuration file and replace the ports inside
[root@localhost conf]# sed "s/6379/6380/g" redis-6379.conf > redis-6380.conf [root@localhost conf]# sed "s/6379/6381/g" redis-6379.conf > redis-6381.conf [root@localhost conf]# sed "s/6379/6382/g" redis-6379.conf > redis-6382.conf [root@localhost conf]# sed "s/6379/6383/g" redis-6379.conf > redis-6383.conf [root@localhost conf]# sed "s/6379/6384/g" redis-6379.conf > redis-6384.conf [root@localhost conf]# sed "s/6379/6385/g" redis-6379.conf > redis-6385.conf
After all execution, you can check the content through the
catcommand to ensure it has been modified
Start the redis service cluster
# 在第一个窗口执行6379服务 redis-server redis-6379.conf # 在第二个窗口执行6380服务 redis-server redis-6380.conf # 在第三个窗口执行6381服务 redis-server redis-6381.conf # 下面的代码依次类推到6385
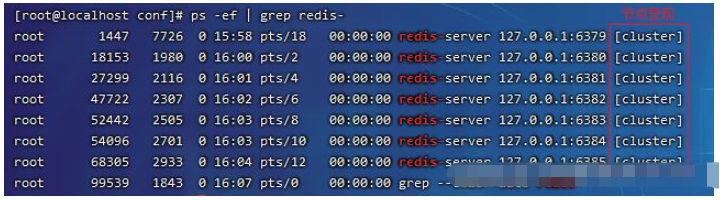
Execute the command to view redis Process and port
ps -ef | grep redis-
View in the src directoryThe execution results are as followsredis-trib.rb
In higher versions, the startup operation has been moved toredis-cli
Startup requires two downloads of two files, namelyruby
andgem# 下载命令也会将gem一起 yum -y install rubygemsCopy after login# --cluster create 创建集群 # --cluster-replicas 1 指定集群的内部结构(1代表一个master连接1个slave,2代表一个master连接两个save) # 后面的连接端口按数量实现master连接哪一个slave,1对1,1对2 redis-cli --cluster create 127.0.0.1:6379 127.0.0.1:6380 127.0.0.1:6381 127.0.0.1:6382 127.0.0.1:6383 127.0.0.1:6384 --cluster-replicas 1Copy after login

yes command is as follows
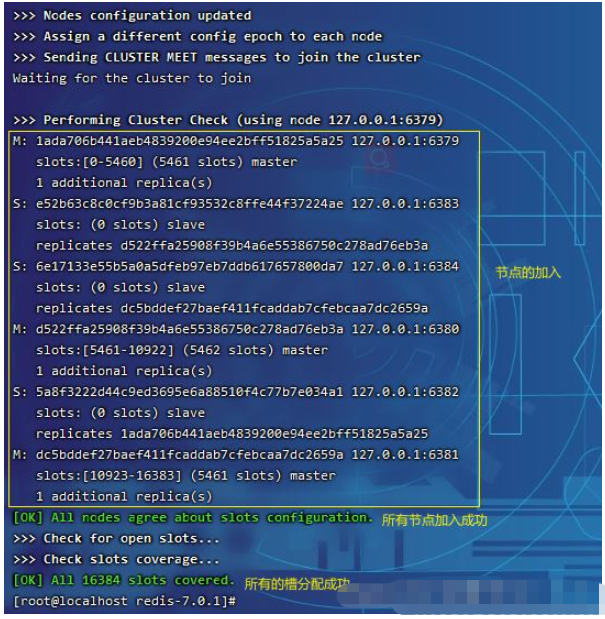
Check the configuration file information again, which is recorded All cluster informationStart the client to store data
Because cluster deployment is used, the cluster can be operated through theSpecify the port to connect the client-c
Note:parameter, if not specified What is more, when operating the redis command, the prompt(error) MOVED 5798 127.0.0.1:6380-c
Operation clusterredis-cli -c # 创建key,通过返回信息可以知道key存储到6380下了 127.0.0.1:6379> set name 123 -> Redirected to slot [5798] located at 127.0.0.1:6380 OKCopy after login
# 连接指定的集群客户端 [root@localhost data]# redis-cli -c -p 6382 # 获取key 127.0.0.1:6382> get name -> Redirected to slot [5798] located at 127.0.0.1:6380 "123" 127.0.0.1:6380>
Cluster node operation command
View cluster node informationcluster nodes
cluster replicate <master-id>
cluster meet ip:port
cluster forget <id>
cluster failover
redis- trib command
Add noderedis-trib.rb add-node
redis-trib.rb del-node
redis-trib.rb reshard
Execute on the slave serverObserve the status of the connected host , the host will mark the slave as failed if it cannot connect to the slave within 10 seconds. Other cluster services will fail to connect, and other services will receive the message Start the slave again, and the host will reconnect. On the slave machineCtrl C
Download service
If the master machine goes offline, the slave machine will switch to a certain slot. When the master machine comes back online, the original master machine will become the slave machine
The above is the detailed content of How to implement Redis7.0 deployment cluster. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear Redis data: Use the FLUSHALL command to clear all key values. Use the FLUSHDB command to clear the key value of the currently selected database. Use SELECT to switch databases, and then use FLUSHDB to clear multiple databases. Use the DEL command to delete a specific key. Use the redis-cli tool to clear the data.
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
Using the Redis directive requires the following steps: Open the Redis client. Enter the command (verb key value). Provides the required parameters (varies from instruction to instruction). Press Enter to execute the command. Redis returns a response indicating the result of the operation (usually OK or -ERR).
 How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
Using Redis to lock operations requires obtaining the lock through the SETNX command, and then using the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time. The specific steps are: (1) Use the SETNX command to try to set a key-value pair; (2) Use the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time for the lock; (3) Use the DEL command to delete the lock when the lock is no longer needed.
 How to configure Lua script execution time in centos redis
Apr 14, 2025 pm 02:12 PM
How to configure Lua script execution time in centos redis
Apr 14, 2025 pm 02:12 PM
On CentOS systems, you can limit the execution time of Lua scripts by modifying Redis configuration files or using Redis commands to prevent malicious scripts from consuming too much resources. Method 1: Modify the Redis configuration file and locate the Redis configuration file: The Redis configuration file is usually located in /etc/redis/redis.conf. Edit configuration file: Open the configuration file using a text editor (such as vi or nano): sudovi/etc/redis/redis.conf Set the Lua script execution time limit: Add or modify the following lines in the configuration file to set the maximum execution time of the Lua script (unit: milliseconds)
 How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
Use the Redis command line tool (redis-cli) to manage and operate Redis through the following steps: Connect to the server, specify the address and port. Send commands to the server using the command name and parameters. Use the HELP command to view help information for a specific command. Use the QUIT command to exit the command line tool.
 How to set the redis expiration policy
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:03 PM
How to set the redis expiration policy
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:03 PM
There are two types of Redis data expiration strategies: periodic deletion: periodic scan to delete the expired key, which can be set through expired-time-cap-remove-count and expired-time-cap-remove-delay parameters. Lazy Deletion: Check for deletion expired keys only when keys are read or written. They can be set through lazyfree-lazy-eviction, lazyfree-lazy-expire, lazyfree-lazy-user-del parameters.






