MySQL performance indicator TPS+QPS+IOPS stress test example analysis
1. Overview of performance indicators
QPS (Queries Per Second) is the number of queries per second. For the database, it is the number of SQLs executed by the database per second (including insert, select, update, delete etc.).
TPS (Transactions Per Second) is the number of transactions per second. For a database, TPS is the number of transactions executed by the database per second, based on the number of successful commits.
IOPS The number of I/O operations performed by the disk per second
2. Indicator calculation method
2.1 TPS
Applicable to innodb Transactions Per Second (The number of transactions transmitted per second), that is, the number of transactions processed by the server per second
Generally, the performance of the evaluation system is measured by the number of technical transactions completed per second. The overall processing capacity of the system depends on the TPS value of the module with the lowest processing capacity
mysql> SHOW GLOBAL STATUS LIKE 'Com_commit';
+---------------+-------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+---------------+-------+
| Com_commit | 22402 |
+---------------+-------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> SHOW GLOBAL STATUS LIKE 'Com_rollback';
+---------------+-------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+---------------+-------+
| Com_rollback | 0 |
+---------------+-------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> SHOW GLOBAL STATUS LIKE 'Uptime'
-> ;
+---------------+-------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+---------------+-------+
| Uptime | 3319 |
+---------------+-------+
1 row in set (0.01 sec)
TPS=(Com_commit + Com_rollback)/Uptime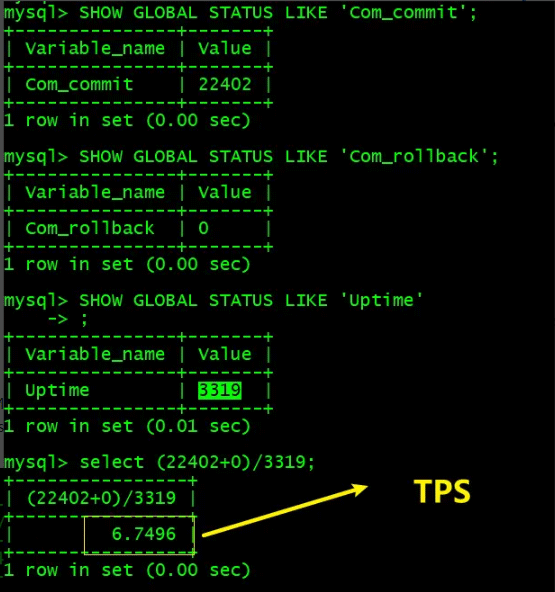
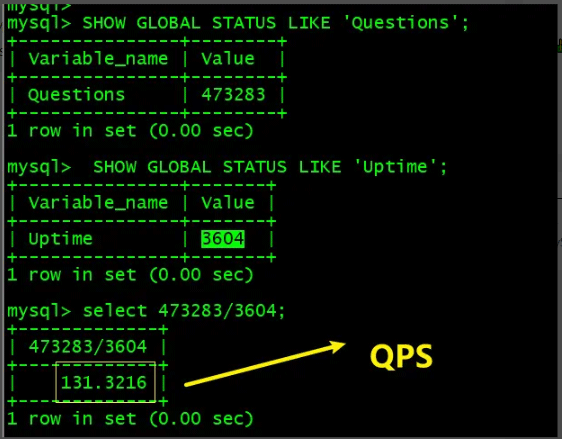
2.2 QPS
Applicable to both InnoDB and MyISAM engines Query rate per second (QPS) is a measure of how much traffic a specific query server handles within a specified period of time, corresponding to fetches/sec, that is, the number of response requests per second, which is the maximum throughput capability
2.3 IOPS
IOPS (Input/Output Per Second) is the input and output volume (or number of reads and writes) per second, which is the main indicator of disk performance. one. IOPS refers to the number of I/O requests that the system can handle per unit time. It is generally measured in the number of I/O requests processed per second. I/O requests are usually read or write data operation requests. For applications with frequent random reads and writes, such as OLTP (Online Transaction Processing), IOPS is a key measurement indicator. Another important indicator is data throughput (Throughput), which refers to the amount of data that can be successfully transmitted per unit time. For applications with a large number of sequential reads and writes, such as VOD (Video On Demand), more attention is paid to throughput indicators. IOPS can be broken down into the following indicators: Total IOPS, disk IOPS under mixed read-write and sequential random I/O loads,
This is most consistent with the actual I/O situation, and most applications focus on this indicator.
Random Read IOPS, IOPS under 100% random read load.
Random Write IOPS, IOPS under 100% random write load.
Sequential Read IOPS, IOPS under 100% sequential read load.
Sequential Write IOPS, IOPS under 100% sequential write load.
The IOPS testing benchmark tools mainly include Iometer, IoZone, FIO, etc., which can be used comprehensively to test the IOPS of the disk under different situations. For application systems, it is necessary to first determine the load characteristics of the data, then select reasonable IOPS indicators for measurement and comparative analysis, and select appropriate storage media and software systems accordingly.
理论上可以计算出磁盘的最大IOPS,即IOPS = 1000 ms/ (Tseek + Troatation),忽略数据传输时间。假设磁盘平均物理寻道时间为3ms, 磁盘转速为7200,10K,15K rpm,则磁盘IOPS理论最大值分别为, IOPS = 1000 / (3 + 60000/7200/2) = 140 IOPS = 1000 / (3 + 60000/10000/2) = 167 IOPS = 1000 / (3 + 60000/15000/2) = 200
3. mysqlslap
3.1 Stress Test
mysqlslap is a tool that comes with MySQL for load performance testing and stress testing. It can simulate multiple clients putting pressure on the database and generate reports to understand the performance of the database.
The running process of mysqlslap is mainly divided into three steps:
① Create libraries and tables, and import data for testing. This process is done by a single thread.
② Start stress testing. This step can be done using multiple threads.
③ Clean test data. This process is done by a single thread.
[root@jeames ~]# mysqlslap --help
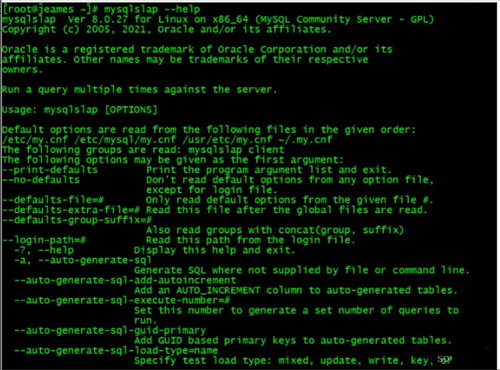
3.2 Case
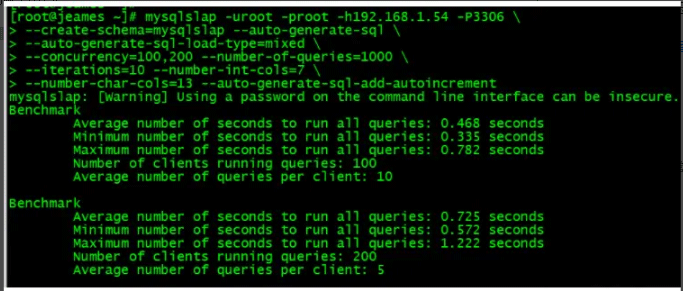
mysqlslap -uroot -proot -h292.168.1.54 -P3306 \ --create-schema=mysqlslap --auto-generate-sql \ --auto-generate-sql-load-type=mixed \ --concurrency=100,200 --number-of-queries=1000 \ --iterations=10 --number-int-cols=7 \ --number-char-cols=13 --auto-generate-sql-add-autoincrement Benchmark #运行所有语句的平均时间,单位秒 Average number of seconds to run all queries: 0.018 seconds #运行所有语句的最小秒数 Minimum number of seconds to run all queries: 0.018 seconds #运行所有语句的最大秒数 Maximum number of seconds to run all queries: 0.018 seconds #客户端数量 Number of clients running queries: 1 #每个客户端运行查询的平均数 Average number of queries per client: 0 该语句表示测试并发为 100 和 200 的情况,进行 1000 次访问(该值一般这样预估出来:并发客户数×每客户查询次数)。这样的测试方法迭代 10 次,最终显示最大、 最小、平均值 其中:--debug-info,代表要额外输出 CPU 以及内存的相关信息。如果报错 Option 'debug-info' used, but is disabled 请取消 debug-info 参数 -number-int-cols=7 表示生成的表中必须有 7 个 int 类型的列 -number-char-cols=13 表示生成的表中必须有 13 个 char 类型的列 -concurrency 代表并发数量,多个可以用逗号隔开,concurrency=10,50,100, 并发连接线程数分别是 10、50、100 个并发。 --engines 代表要测试的引擎,可以有多个,用分隔符隔开。 --iterations 代表要运行这些测试多少次。 --auto-generate-sql 代表用系统自己生成的 SQL 脚本来测试。 --auto-generate-sql-load-type 代表要测试的是读还是写还是两者混合的(read,write,update,mixed) --number-of-queries 代表总共要运行多少次查询。每个客户运行的查询数量可以用查询总数/并发数来计算。 --debug-info 代表要额外输出 CPU 以及内存的相关信息。 --number-int-cols :创建测试表的 int 型字段数量 --auto-generate-sql-add-autoincrement : 代表对生成的表自动添加 auto_increment 列,从 5.1.18 版本开始 --number-char-cols 创建测试表的 char 型字段数量。 --create-schema 测试的 schema,MySQL 中 schema 也就是 database。 --query 使用自定义脚本执行测试,例如可以调用自定义的一个存储过程或者 sql 语句来执行测试。 --only-print 查看语句做了什么。
The above is the detailed content of MySQL performance indicator TPS+QPS+IOPS stress test example analysis. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 MySQL: An Introduction to the World's Most Popular Database
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL: An Introduction to the World's Most Popular Database
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL is an open source relational database management system, mainly used to store and retrieve data quickly and reliably. Its working principle includes client requests, query resolution, execution of queries and return results. Examples of usage include creating tables, inserting and querying data, and advanced features such as JOIN operations. Common errors involve SQL syntax, data types, and permissions, and optimization suggestions include the use of indexes, optimized queries, and partitioning of tables.
 MySQL's Place: Databases and Programming
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL's Place: Databases and Programming
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL's position in databases and programming is very important. It is an open source relational database management system that is widely used in various application scenarios. 1) MySQL provides efficient data storage, organization and retrieval functions, supporting Web, mobile and enterprise-level systems. 2) It uses a client-server architecture, supports multiple storage engines and index optimization. 3) Basic usages include creating tables and inserting data, and advanced usages involve multi-table JOINs and complex queries. 4) Frequently asked questions such as SQL syntax errors and performance issues can be debugged through the EXPLAIN command and slow query log. 5) Performance optimization methods include rational use of indexes, optimized query and use of caches. Best practices include using transactions and PreparedStatemen
 How to connect to the database of apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
How to connect to the database of apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
Apache connects to a database requires the following steps: Install the database driver. Configure the web.xml file to create a connection pool. Create a JDBC data source and specify the connection settings. Use the JDBC API to access the database from Java code, including getting connections, creating statements, binding parameters, executing queries or updates, and processing results.
 Why Use MySQL? Benefits and Advantages
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:17 AM
Why Use MySQL? Benefits and Advantages
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:17 AM
MySQL is chosen for its performance, reliability, ease of use, and community support. 1.MySQL provides efficient data storage and retrieval functions, supporting multiple data types and advanced query operations. 2. Adopt client-server architecture and multiple storage engines to support transaction and query optimization. 3. Easy to use, supports a variety of operating systems and programming languages. 4. Have strong community support and provide rich resources and solutions.
 How to start mysql by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
How to start mysql by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
The process of starting MySQL in Docker consists of the following steps: Pull the MySQL image to create and start the container, set the root user password, and map the port verification connection Create the database and the user grants all permissions to the database
 MySQL's Role: Databases in Web Applications
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:23 AM
MySQL's Role: Databases in Web Applications
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:23 AM
The main role of MySQL in web applications is to store and manage data. 1.MySQL efficiently processes user information, product catalogs, transaction records and other data. 2. Through SQL query, developers can extract information from the database to generate dynamic content. 3.MySQL works based on the client-server model to ensure acceptable query speed.
 Laravel Introduction Example
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:45 PM
Laravel Introduction Example
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:45 PM
Laravel is a PHP framework for easy building of web applications. It provides a range of powerful features including: Installation: Install the Laravel CLI globally with Composer and create applications in the project directory. Routing: Define the relationship between the URL and the handler in routes/web.php. View: Create a view in resources/views to render the application's interface. Database Integration: Provides out-of-the-box integration with databases such as MySQL and uses migration to create and modify tables. Model and Controller: The model represents the database entity and the controller processes HTTP requests.
 How to install mysql in centos7
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:30 PM
How to install mysql in centos7
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:30 PM
The key to installing MySQL elegantly is to add the official MySQL repository. The specific steps are as follows: Download the MySQL official GPG key to prevent phishing attacks. Add MySQL repository file: rpm -Uvh https://dev.mysql.com/get/mysql80-community-release-el7-3.noarch.rpm Update yum repository cache: yum update installation MySQL: yum install mysql-server startup MySQL service: systemctl start mysqld set up booting






