 Database
Database
 Redis
Redis
 How to use Go and Lua to solve the inventory and overselling problems in Redis flash sale
How to use Go and Lua to solve the inventory and overselling problems in Redis flash sale
How to use Go and Lua to solve the inventory and overselling problems in Redis flash sale
0. Introduction
Go language connects go-redis to connect to the database. If you don’t understand this part yet, it is recommended that you learn this part of the knowledge first.
In addition, this flash sale mainly solves two problems. The first is the oversold problem, and the other is the inventory problem.
There is no special page designed to simulate concurrency. We directly use gorountine and stay for 10 seconds before calling the request.
To deal with the oversold problem, just introduce go-redis watch with transaction processing [equivalent to optimistic locking].
The inventory problem is a little more troublesome. You need to use Lua to edit the script, but you don't need to download the Lua compilation environment on your own machine. Go provides related support. For this part, don’t panic. The basic structure is as follows:
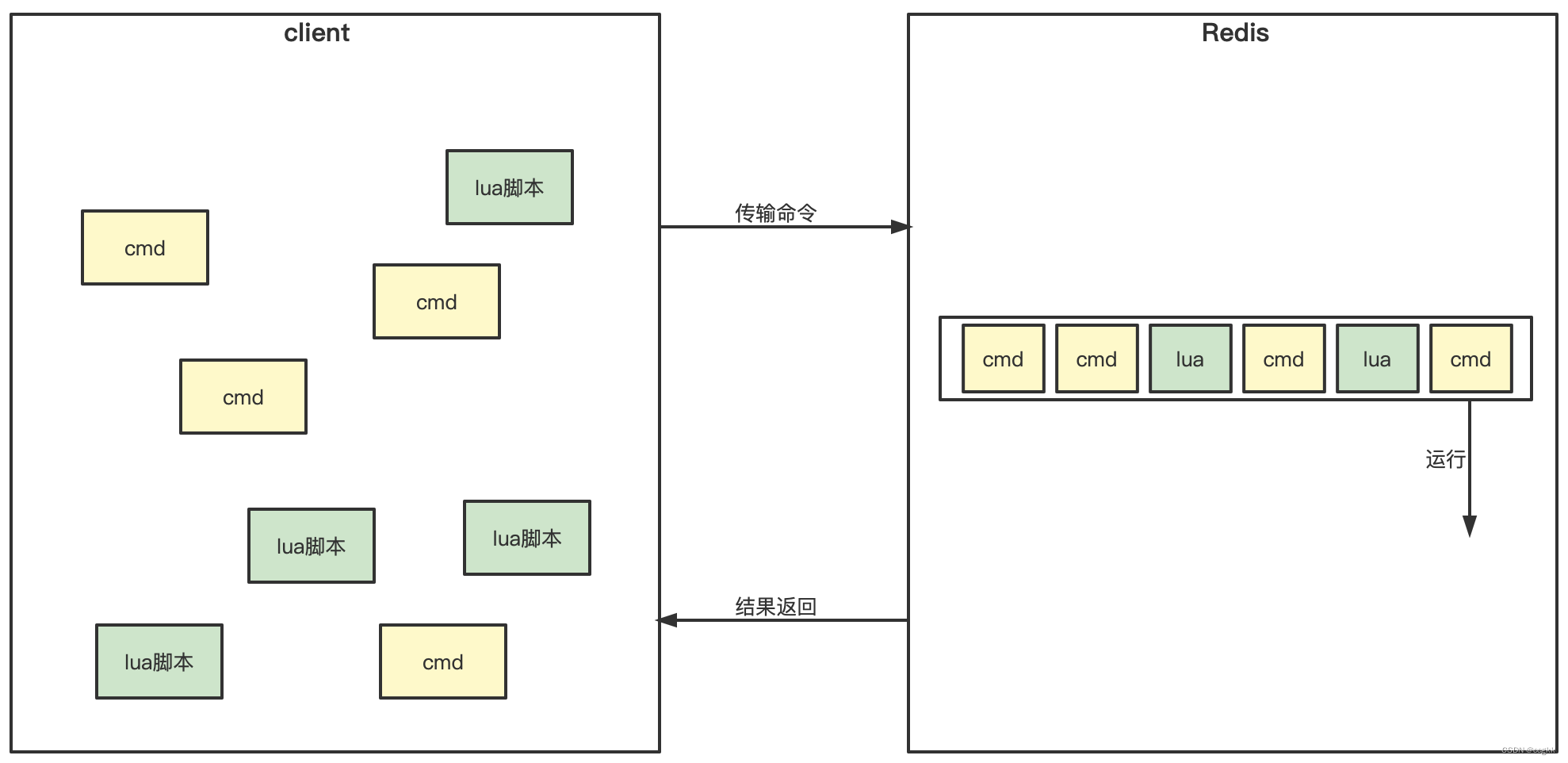
1. Simple version
In concurrent situations, oversold and negative values may occur. Appear in the Redis database. Even if you make judgments on the data before operating.
func MsCode(uuid, prodid string) bool {
// 1、对uuid和prodid进行非空判断
if uuid == "" || prodid == "" {
return false
}
//2、获取连接
rdb := DB
//3、拼接key
kcKey := "kc:" + prodid + ":qt"
userKey := "sk:" + prodid + ":user"
//4、获取库存
str, err := rdb.Get(ctx, kcKey).Result()
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
fmt.Println("秒杀还未开始.......")
return false
}
// 5、判断用户是否重复秒杀操作
flag, err := rdb.SIsMember(ctx, userKey, userKey).Result()
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
if flag {
fmt.Println("你已经参加了秒杀,无法再次参加。。。。")
return false
}
// 6、判断商品数量,如果库存数量小于1,秒杀结束
str, err = rdb.Get(ctx, kcKey).Result()
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
n, err := strconv.Atoi(str)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
if n < 1 {
fmt.Println("秒杀结束,请下次再来吧。。。。")
return false
}
// 7、秒杀过程
// 7.1、库存减1
num, err := rdb.Decr(ctx, kcKey).Result()
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
if num != 0 {
// 7.2、添加用户
rdb.SAdd(ctx, userKey, uuid)
}
return true
}
func main() {
// 并发的版本
for i := 0; i < 20; i++ {
go func() {
uuid := GenerateUUID()
prodid := "1023"
time.Sleep(10 * time.Second)
MsCode(uuid, prodid)
}()
}
time.Sleep(15 * time.Second)
}2. Solve oversold
Use watch to monitor the key. The key parts are as follows. However, this situation will bring about a problem. Even if there is remaining inventory, there will be people who cannot buy it.
err = rdb.Watch(ctx, func(tx *redis.Tx) error {
n, err := tx.Get(ctx, kcKey).Int()
if err != nil && err != redis.Nil {
return err
}
if n <= 0 {
return fmt.Errorf("抢购结束了!请下次早点来。。。。")
}
_, err = tx.TxPipelined(ctx, func(pipeliner redis.Pipeliner) error {
err := pipeliner.Decr(ctx, kcKey).Err()
if err != nil {
return err
}
err = pipeliner.SAdd(ctx, userKey, uuid).Err()
if err != nil {
return err
}
return nil
})
return err
}, kcKey)3. Solve the inventory problem Lua
Lua can better solve this problem by operating redis. In order to avoid inventory problems that pessimistic locking may cause in Redis, you should consider using optimistic locking. Because Redis does not have built-in optimistic locking support, we need to use Lua to write relevant scripts. It mainly has the following advantages:
Write complex or multi-step redis operations as a script and submit it to redis for execution at one time, reducing the number of repeated connections to redis. Improve performance.
luan script is similar to a redis transaction, has a certain degree of atomicity, will not be queued by other commands, and can complete some redis transactional operations.
The Lua script function of redis can only be used in versions above redis2.6.
Use lua scripts to eliminate users and solve the overselling problem.
After redis version 2.6, the contention problem is solved through Lua script. In fact, redis uses its single-threaded feature to solve multi-task concurrency problems using task queues.
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"github.com/go-redis/redis/v8"
"net"
"time"
)
func useLua(userid, prodid string) bool {
//编写脚本 - 检查数值,是否够用,够用再减,否则返回减掉后的结果
var luaScript = redis.NewScript(`
local userid=KEYS[1];
local prodid=KEYS[2];
local qtKey="sk:"..prodid..":qt";
local userKey="sk:"..prodid..":user";
local userExists=redis.call("sismember",userKey,userid);
if tonumber(userExists)==1 then
return 2;
end
local num=redis.call("get",qtKey);
if tonumber(num)<=0 then
return 0;
else
redis.call("decr",qtKey);
redis.call("SAdd",userKey,userid);
end
return 1;
`)
//执行脚本
n, err := luaScript.Run(ctx, DB, []string{userid, prodid}).Result()
if err != nil {
return false
}
switch n {
case int64(0):
fmt.Println("抢购结束")
return false
case int64(1):
fmt.Println(userid, ":抢购成功")
return true
case int64(2):
fmt.Println(userid, ":已经抢购了")
return false
default:
fmt.Println("发生未知错误!")
return false
}
return true
}
func main() {
// 并发的版本
for i := 0; i < 20; i++ {
go func() {
uuid := GenerateUUID()
prodid := "1023"
time.Sleep(10 * time.Second)
useLua(uuid, prodid)
}()
}
time.Sleep(15 * time.Second)
}The above is the detailed content of How to use Go and Lua to solve the inventory and overselling problems in Redis flash sale. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear Redis data: Use the FLUSHALL command to clear all key values. Use the FLUSHDB command to clear the key value of the currently selected database. Use SELECT to switch databases, and then use FLUSHDB to clear multiple databases. Use the DEL command to delete a specific key. Use the redis-cli tool to clear the data.
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
Using the Redis directive requires the following steps: Open the Redis client. Enter the command (verb key value). Provides the required parameters (varies from instruction to instruction). Press Enter to execute the command. Redis returns a response indicating the result of the operation (usually OK or -ERR).
 How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
Using Redis to lock operations requires obtaining the lock through the SETNX command, and then using the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time. The specific steps are: (1) Use the SETNX command to try to set a key-value pair; (2) Use the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time for the lock; (3) Use the DEL command to delete the lock when the lock is no longer needed.
 How to configure Lua script execution time in centos redis
Apr 14, 2025 pm 02:12 PM
How to configure Lua script execution time in centos redis
Apr 14, 2025 pm 02:12 PM
On CentOS systems, you can limit the execution time of Lua scripts by modifying Redis configuration files or using Redis commands to prevent malicious scripts from consuming too much resources. Method 1: Modify the Redis configuration file and locate the Redis configuration file: The Redis configuration file is usually located in /etc/redis/redis.conf. Edit configuration file: Open the configuration file using a text editor (such as vi or nano): sudovi/etc/redis/redis.conf Set the Lua script execution time limit: Add or modify the following lines in the configuration file to set the maximum execution time of the Lua script (unit: milliseconds)
 How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
Use the Redis command line tool (redis-cli) to manage and operate Redis through the following steps: Connect to the server, specify the address and port. Send commands to the server using the command name and parameters. Use the HELP command to view help information for a specific command. Use the QUIT command to exit the command line tool.
 How to set the redis expiration policy
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:03 PM
How to set the redis expiration policy
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:03 PM
There are two types of Redis data expiration strategies: periodic deletion: periodic scan to delete the expired key, which can be set through expired-time-cap-remove-count and expired-time-cap-remove-delay parameters. Lazy Deletion: Check for deletion expired keys only when keys are read or written. They can be set through lazyfree-lazy-eviction, lazyfree-lazy-expire, lazyfree-lazy-user-del parameters.





