How to use docker to install the web service provided by nginx
1. Pull the image
The docker pull command is used to pull the application image, and the docker pull nginx command is used to pull the latest version of the nginx image. The following is the response result of the image pulling process:
# docker pull nginx Using default tag: latest latest: Pulling from library/nginx c229119241af: Pull complete 2215908dc0a2: Pull complete 08c3cb2073f1: Pull complete 18f38162c0ce: Pull complete 10e2168f148a: Pull complete c4ffe9532b5f: Pull complete Digest: sha256:2275af0f20d71b293916f1958f8497f987b8d8fd8113df54635f2a5915002bf1 Status: Downloaded newer image for nginx:latest docker.io/library/nginx:latest
From the above we can see that the nginx image is pulled from the URL docker.io.
Use the docker images command to view which image files have been downloaded in the current operating system.
# docker images REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE nginx latest 12766a6745ee 33 hours ago 142MB hello-world latest feb5d9fea6a5 6 months ago 13.3kB
REPOSITORY image warehouse and image name. If the image warehouse is not displayed, the default is
docker.ioTAG The version or milestone label of the image, latest represents the latest version
IMAGE ID The unique identifier of the image
CREATED The time when this image was created
SIZE represents the size of the image file
2. Run the image to start the container
Through docker run The command starts a container with the container name nginx-zimug.
# docker run -d --name nginx-zimug -p 80:80 nginx 81bb1211144bc0991a789f860458548643c60b5459466c14d0604be9a4ccbfd7
-dindicates that the container is running in the background--nameCreate a name for the container Name-pPort mapping, the format isHost port:Container port, the above meaning is to map port 80 in the container To port 80 of the host machine, provide external access services. The last field is the image name
When the browser accesses port 80 of the host through the HTTP protocol, the port number can be omitted. The access results obtained are as follows, indicating that our nginx service has been started successfully.

You can view the running container through docker ps, as shown below:
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 81bb1211144b nginx "/docker-entrypoint.…" 11 minutes ago Up 11 minutes 0.0.0.0:80->80/tcp, :::80->80/tcp nginx-zimug
3. File mapping
First of all, it is clear that the contents of files in the container can be modified, but once the container is restarted, all modifications to data files and configuration files written to the container will be lost. Therefore, in order to save the running status and execution results of the container, we need to map some important data files, log files, and configuration files in the container to the host.
Take nginx as an example. nginx has three important file directories:
| Path in the container | Automatically in the host Define the mapping path | |
|---|---|---|
| The directory where website pages are stored | /usr/share/nginx/html | /root/nginx /html |
| nginx configuration file directory | /etc/nginx/nginx.conf | /root/nginx/conf/nginx.conf |
| Log directory | /var/log/nginx | /root/nginx/logs |
Create a new file directory in the host machine
mkdir -p /root/nginx/logs /root/nginx/html /root/nginx/conf;
Copy the files in the container to the host machine
Copy the nginx configuration file to the host machine
docker cp nginx-zimug:/etc/nginx/nginx.conf /root/nginx/conf;
Put a simulated html file into the html directory
Save the following file as index.html and put it into the host's /root/nginx/htmlDirectory, because there is a mapping relationship, it is actually placed in the /usr/share/nginx/html directory of the container.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>使用docker搭建nginx web服务</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2 id="访问成功">访问成功</h2>
<p>厉害了!</p>
</body>
</html>4. Start the container service again
-vThe parameter expresses the mapping relationship between the host file and the file in the container, and the format is -v host Directory: Container file system directory . Start a new container. The name of the container is nginx-prod
docker run -d -p 80:80 \ --name nginx-prod \ -v /root/nginx/html:/usr/share/nginx/html \ -v /root/nginx/conf/nginx.conf:/etc/nginx/nginx.conf \ -v /root/nginx/logs:/var/log/nginx nginx
Before starting the new container, delete the old nginx-zimug container. If the old container is not deleted, the port of the new container will conflict with the port of the old container. Use the following command to delete the container:
docker stop nginx-zimug; docker rm nginx-zimug;
Execute the above docker run command to start a new container. After startup, access port 80 of the host through the browser. The response result is as follows, which proves that nginx is providing web services normally.
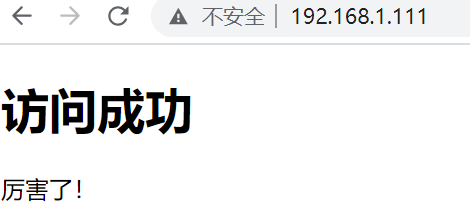
At the same time, you can modify the nginx configuration on the host machine and view the runtime log file. Changing the configuration file will affect the nginx service running in the container because there is a mapping relationship between the host and the configuration file in the container.
The above is the detailed content of How to use docker to install the web service provided by nginx. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to exit the container by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:15 PM
How to exit the container by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:15 PM
Four ways to exit Docker container: Use Ctrl D in the container terminal Enter exit command in the container terminal Use docker stop <container_name> Command Use docker kill <container_name> command in the host terminal (force exit)
 How to check the name of the docker container
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
How to check the name of the docker container
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
You can query the Docker container name by following the steps: List all containers (docker ps). Filter the container list (using the grep command). Gets the container name (located in the "NAMES" column).
 How to copy files in docker to outside
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:12 PM
How to copy files in docker to outside
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:12 PM
Methods for copying files to external hosts in Docker: Use the docker cp command: Execute docker cp [Options] <Container Path> <Host Path>. Using data volumes: Create a directory on the host, and use the -v parameter to mount the directory into the container when creating the container to achieve bidirectional file synchronization.
 How to restart docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:06 PM
How to restart docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:06 PM
How to restart the Docker container: get the container ID (docker ps); stop the container (docker stop <container_id>); start the container (docker start <container_id>); verify that the restart is successful (docker ps). Other methods: Docker Compose (docker-compose restart) or Docker API (see Docker documentation).
 How to start mysql by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
How to start mysql by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
The process of starting MySQL in Docker consists of the following steps: Pull the MySQL image to create and start the container, set the root user password, and map the port verification connection Create the database and the user grants all permissions to the database
 How to update the image of docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:03 PM
How to update the image of docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:03 PM
The steps to update a Docker image are as follows: Pull the latest image tag New image Delete the old image for a specific tag (optional) Restart the container (if needed)
 How to start containers by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
How to start containers by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
Docker container startup steps: Pull the container image: Run "docker pull [mirror name]". Create a container: Use "docker create [options] [mirror name] [commands and parameters]". Start the container: Execute "docker start [Container name or ID]". Check container status: Verify that the container is running with "docker ps".
 How to create containers for docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:18 PM
How to create containers for docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:18 PM
Create a container in Docker: 1. Pull the image: docker pull [mirror name] 2. Create a container: docker run [Options] [mirror name] [Command] 3. Start the container: docker start [Container name]






