 Operation and Maintenance
Operation and Maintenance
 Nginx
Nginx
 How to use nginx proxy map as cache to solve cross-domain problems
How to use nginx proxy map as cache to solve cross-domain problems
How to use nginx proxy map as cache to solve cross-domain problems
1. Error generation conditions
// 采用openlayers加载天地图
var layer = new ol.layer.tile({
source: new ol.source.xyz({
// crossorigin: 'anonymous', // 是否请求跨域操作
url: url // 天地图地址
})
});If the crossorigin attribute is not used, cross-domain problems will not occur, and generally this parameter will not be set.
The usage scenario of this parameter is as described on the official website:
the crossorigin attribute for loaded images. note that you must provide a crossorigin value if you are using the webgl renderer or if you want to access pixel data with the canvas renderer. see https://developer.mozilla.org/en-us/docs/web/html/cors_enabled_image for more detail.
Consult mdn documentation (https: //developer.mozilla.org/zh-cn/docs/web/html/cors_settings_attributes), you can find that crossorigin has two values
In the development process, often You need to run the development version locally and the production version on the server. When two versions are accessed in the same browser, cross-domain problems will occur if crossorigin is set, such as the error shown in the figure below,
has been blocked by cors policy: no 'access-control-allow -origin'header is present on the requested resource.
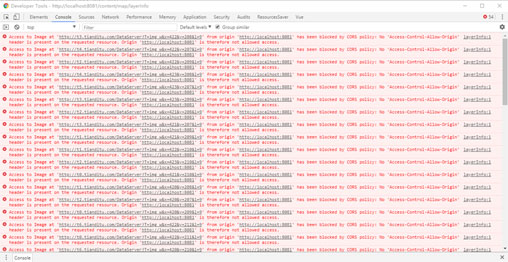
Note: This problem will only occur after crossorigin is set on Tiantu. It will not appear on Google basemap. The reason Yes:
The origin attribute of the request header returned by Tiantu is set to the currently visited IP, while the origin attribute of the Google base map is set to *, which means that systems with different IPs cache Google tiles in the browser You can still access the google basemap afterwards.
2. Error resolution method
2.1 Simple and violent method
The simple and violent solution is to clear the browser Cache images, at the same time, only view one of the systems. If you want to view another system, you must clear the browser image cache in advance
2.2 Delete the crossorigin attribute
Re-examine the map requirements and determine whether the crossorigin attribute is really needed. If not, this problem will not occur at all
2.3 nginx proxy solution
If The previous methods feel inappropriate, so use nginx as a proxy. It can solve cross-domain problems and cache tiles locally to speed up access.
Go directly to the configuration file.
#user nobody;
worker_processes 4;
#error_log logs/error.log;
#error_log logs/error.log notice;
#error_log logs/error.log info;
#pid logs/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
#log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
# '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
# '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#access_log logs/access.log main;
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65;
#gzip on;
client_max_body_size 20m;
# 关键代码块1
proxy_temp_path ../proxy_cache/tianditu_temp;
proxy_cache_path ../proxy_cache/tianditu levels=1:2 keys_zone=cache_one:200m inactive=1d max_size=30g;
upstream tianditu_server {
server t0.tianditu.com weight=1 max_fails=2 fail_timeout=30s;
server t1.tianditu.com weight=1 max_fails=2 fail_timeout=30s;
server t2.tianditu.com weight=1 max_fails=2 fail_timeout=30s;
server t3.tianditu.com weight=1 max_fails=2 fail_timeout=30s;
server t4.tianditu.com weight=1 max_fails=2 fail_timeout=30s;
server t5.tianditu.com weight=1 max_fails=2 fail_timeout=30s;
server t6.tianditu.com weight=1 max_fails=2 fail_timeout=30s;
}
server {
listen 8088;
server_name localhost;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
# 关键代码块2
location /dataserver {
more_set_headers 'access-control-allow-origin: *';
add_header access-control-allow-headers x-requested-with;
add_header access-control-allow-methods get,post,options;
proxy_cache cache_one;
proxy_cache_key $uri$is_args$args;
proxy_pass http://tianditu_server/dataserver;
}
}
}Let’s explain the configuration file:
Key code block 1:
1. Use nginx upstream to configure a set of service addresses for load balancing Use, the effect is better than openlayers sequentially traverse t0 to t6
2, set the proxy cache temporary address and cache address, here you can use the relative path
Key code block 2
After matching the dataserver, you need to
1. Set the cross-domain header. Here a new nginx module-headers-more is used, which needs to be added when compiling nginx. If it is windows To use nginx, you can use the installation package of this website: https://openresty.org, which pre-compiles many nginx practical modules
2. Use proxy_pass to proxy the address to http://tianditu_server/dataserver address on, where tianditu_server is the name of the service group configured with load balancing above.
The above is the detailed content of How to use nginx proxy map as cache to solve cross-domain problems. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to check the name of the docker container
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
How to check the name of the docker container
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
You can query the Docker container name by following the steps: List all containers (docker ps). Filter the container list (using the grep command). Gets the container name (located in the "NAMES" column).
 How to configure nginx in Windows
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:57 PM
How to configure nginx in Windows
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:57 PM
How to configure Nginx in Windows? Install Nginx and create a virtual host configuration. Modify the main configuration file and include the virtual host configuration. Start or reload Nginx. Test the configuration and view the website. Selectively enable SSL and configure SSL certificates. Selectively set the firewall to allow port 80 and 443 traffic.
 How to check whether nginx is started
Apr 14, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
How to check whether nginx is started
Apr 14, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
How to confirm whether Nginx is started: 1. Use the command line: systemctl status nginx (Linux/Unix), netstat -ano | findstr 80 (Windows); 2. Check whether port 80 is open; 3. Check the Nginx startup message in the system log; 4. Use third-party tools, such as Nagios, Zabbix, and Icinga.
 How to start containers by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
How to start containers by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
Docker container startup steps: Pull the container image: Run "docker pull [mirror name]". Create a container: Use "docker create [options] [mirror name] [commands and parameters]". Start the container: Execute "docker start [Container name or ID]". Check container status: Verify that the container is running with "docker ps".
 How to configure cloud server domain name in nginx
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:18 PM
How to configure cloud server domain name in nginx
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:18 PM
How to configure an Nginx domain name on a cloud server: Create an A record pointing to the public IP address of the cloud server. Add virtual host blocks in the Nginx configuration file, specifying the listening port, domain name, and website root directory. Restart Nginx to apply the changes. Access the domain name test configuration. Other notes: Install the SSL certificate to enable HTTPS, ensure that the firewall allows port 80 traffic, and wait for DNS resolution to take effect.
 How to create containers for docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:18 PM
How to create containers for docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:18 PM
Create a container in Docker: 1. Pull the image: docker pull [mirror name] 2. Create a container: docker run [Options] [mirror name] [Command] 3. Start the container: docker start [Container name]
 How to check nginx version
Apr 14, 2025 am 11:57 AM
How to check nginx version
Apr 14, 2025 am 11:57 AM
The methods that can query the Nginx version are: use the nginx -v command; view the version directive in the nginx.conf file; open the Nginx error page and view the page title.
 How to start nginx server
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
How to start nginx server
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
Starting an Nginx server requires different steps according to different operating systems: Linux/Unix system: Install the Nginx package (for example, using apt-get or yum). Use systemctl to start an Nginx service (for example, sudo systemctl start nginx). Windows system: Download and install Windows binary files. Start Nginx using the nginx.exe executable (for example, nginx.exe -c conf\nginx.conf). No matter which operating system you use, you can access the server IP





