How Nginx implements polling algorithm
Simple polling algorithm
This algorithm is relatively simple. For example, you have three servers
| First Server | 192.168.1.1 |
| Second server | 192.168.1.2 |
| Third server Server | 192.168.1.3 |
After the first request comes, it will access the first server by default, the second request will access the second server, and the third server The first request comes to access the third station, the fourth request comes to access the first station, and so on. The following is a simple algorithm implemented by my code:
public class simplepolling {
/**
* key是ip
*/
public static list <string> ipservice = new linkedlist <>();
static {
ipservice.add("192.168.1.1");
ipservice.add("192.168.1.2");
ipservice.add("192.168.1.3");
}
public static int pos = 0;
public static string getip(){
if(pos >= ipservice.size()){
//防止索引越界
pos = 0;
}
string ip = ipservice.get(pos);
pos ++;
return ip;
}
public static void main(string[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
system.out.println(getip());
}
}
} The result of simulated execution 4 times is
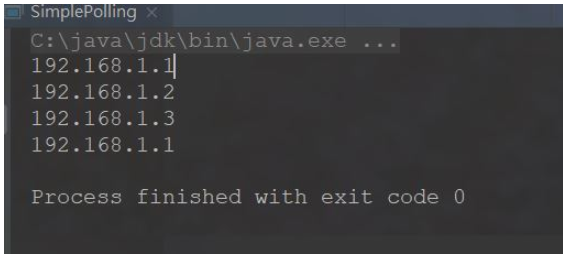
If I have a server performance comparison at this time OK (such as 192.168.1.1), I want this server to handle more requests. At this time, the weight probability is involved. This algorithm cannot be implemented. Please see the polling upgrade algorithm I describe later.
Weighted polling algorithm
At this time, I need to set the weights of the three servers in front of me. For example, the first one is set to 5, the second one is set to 1, and the first one is set to 1. Three settings 1
| First server | 192.168.1.1 | 5 |
| Second server | 192.168.1.2 | 1 |
| 192.168.1.3 | 1 |
public class weightpolling {
/**
* key是ip,value是权重
*/
public static map<string, integer> ipservice = new linkedhashmap<>();
static {
ipservice.put("192.168.1.1", 5);
ipservice.put("192.168.1.2", 1);
ipservice.put("192.168.1.3", 1);
}
public static int requestid = 0;
public static int getandincrement() {
return requestid++;
}
public static string getip(){
//获取总的权重
int totalweight =0;
for (integer value : ipservice.values()) {
totalweight+= value;
}
//获取当前轮询的值
int andincrement = getandincrement();
int pos = andincrement% totalweight;
for (string ip : ipservice.keyset()) {
if(pos < ipservice.get(ip)){
return ip;
}
pos -= ipservice.get(ip);
}
return null;
}
public static void main(string[] args) {
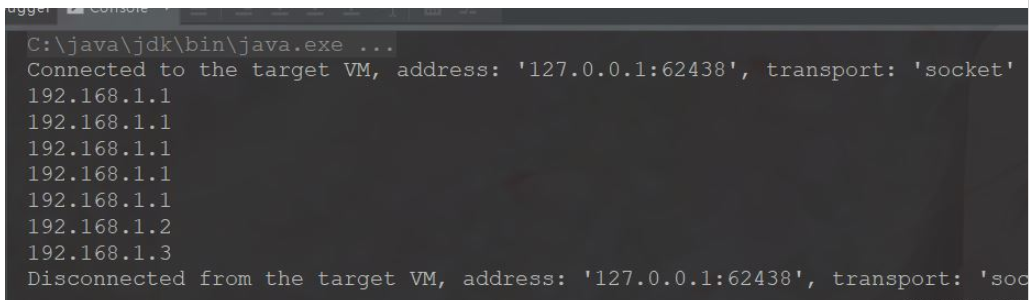
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
system.out.println(getip());
}
}
}
Smooth Weighted Polling Algorithm
This algorithm may be more complicated, and it was a bit confusing when I first looked at it. I don’t quite understand. I’ve read relevant information later and combined it with my own understanding to explain it with pictures and text. The server configuration and weights I gave as an example here are still the same as above| Current weight = own weight current weight after selection | Total weight | Current maximum weight | Returned ip | Current after selection Weight = current maximum weight - total weight | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| {5,1,1} | 7 | 5 | 192.168.1.1 | {-2,1,1} | ##2 |
| 7 | 3 | 192.168.1.1 | {-4,2,2} | 3 | |
| 7 | 3 | 192.168.1.2 | {1,-4 ,3} | 4 | |
| 7 | 6 | 192.168.1.1 | {-1,-3,4} | 5 | |
| 7 | 5 | 192.168.1.3 | {4,-2,-2} | 6 | |
| 7 | 9 | 192.168.1.1 | {2,-1,-1} | 7 | |
| 7 | 7 | 192.168.1.1 | {0,0,0} |
public class polling {
/**
* key是ip,value是权重
*/
public static map <string,integer> ipservice = new linkedhashmap <>();
static {
ipservice.put("192.168.1.1",5);
ipservice.put("192.168.1.2",1);
ipservice.put("192.168.1.3",1);
}
private static map<string,weight> weightmap = new linkedhashmap <>();
public static string getip(){
//计算总的权重
int totalweight = 0;
for (integer value : ipservice.values()) {
totalweight+=value;
}
//首先判断weightmap是否为空
if(weightmap.isempty()){
ipservice.foreach((ip,weight)->{
weight weights = new weight(ip, weight,0);
weightmap.put(ip,weights);
});
}
//给map中得对象设置当前权重
weightmap.foreach((ip,weight)->{
weight.setcurrentweight(weight.getweight() + weight.getcurrentweight());
});
//判断最大权重是否大于当前权重,如果为空或者小于当前权重,则把当前权重赋值给最大权重
weight maxweight = null;
for (weight weight : weightmap.values()) {
if(maxweight ==null || weight.getcurrentweight() > maxweight.getcurrentweight()){
maxweight = weight;
}
}
//最后把当前最大权重减去总的权重
maxweight.setcurrentweight(maxweight.getcurrentweight() - totalweight);
//返回
return maxweight.getip();
}
public static void main(string[] args) {
//模拟轮询7次取ip
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
system.out.println(getip());
}
}
}
class weight{
/**
* ip
*/
private string ip;
/**
* 设置得权重
*/
private int weight;
/**
* 当前权重
*/
private int currentweight;
public weight(string ip, int weight,int currentweight) {
this.ip = ip;
this.weight = weight;
this.currentweight = currentweight;
}
public string getip() {
return ip;
}
public void setip(string ip) {
this.ip = ip;
}
public int getweight() {
return weight;
}
public void setweight(int weight) {
this.weight = weight;
}
public int getcurrentweight() {
return currentweight;
}
public void setcurrentweight(int currentweight) {
this.currentweight = currentweight;
}
}You can see The execution results here are consistent with those described in the table. 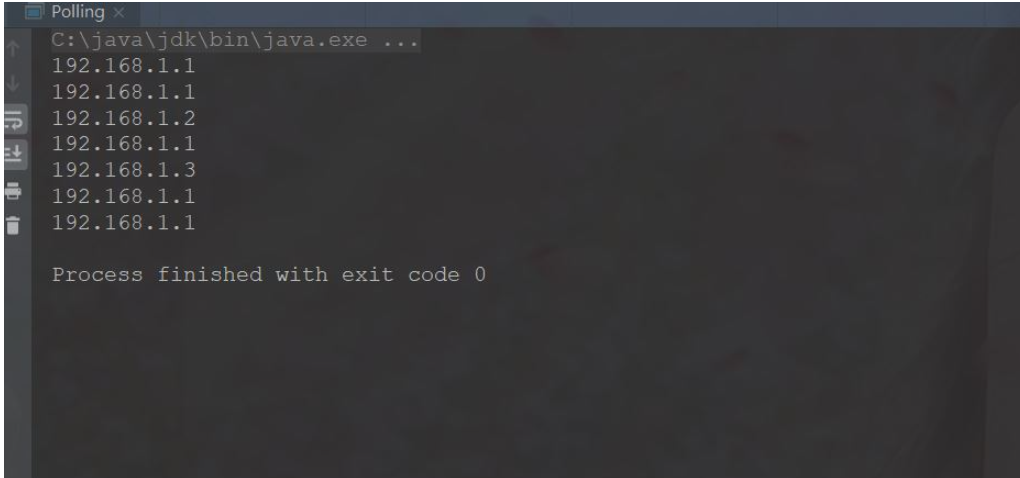
The above is the detailed content of How Nginx implements polling algorithm. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to check the name of the docker container
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
How to check the name of the docker container
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
You can query the Docker container name by following the steps: List all containers (docker ps). Filter the container list (using the grep command). Gets the container name (located in the "NAMES" column).
 How to configure nginx in Windows
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:57 PM
How to configure nginx in Windows
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:57 PM
How to configure Nginx in Windows? Install Nginx and create a virtual host configuration. Modify the main configuration file and include the virtual host configuration. Start or reload Nginx. Test the configuration and view the website. Selectively enable SSL and configure SSL certificates. Selectively set the firewall to allow port 80 and 443 traffic.
 How to configure cloud server domain name in nginx
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:18 PM
How to configure cloud server domain name in nginx
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:18 PM
How to configure an Nginx domain name on a cloud server: Create an A record pointing to the public IP address of the cloud server. Add virtual host blocks in the Nginx configuration file, specifying the listening port, domain name, and website root directory. Restart Nginx to apply the changes. Access the domain name test configuration. Other notes: Install the SSL certificate to enable HTTPS, ensure that the firewall allows port 80 traffic, and wait for DNS resolution to take effect.
 How to check nginx version
Apr 14, 2025 am 11:57 AM
How to check nginx version
Apr 14, 2025 am 11:57 AM
The methods that can query the Nginx version are: use the nginx -v command; view the version directive in the nginx.conf file; open the Nginx error page and view the page title.
 How to check whether nginx is started
Apr 14, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
How to check whether nginx is started
Apr 14, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
How to confirm whether Nginx is started: 1. Use the command line: systemctl status nginx (Linux/Unix), netstat -ano | findstr 80 (Windows); 2. Check whether port 80 is open; 3. Check the Nginx startup message in the system log; 4. Use third-party tools, such as Nagios, Zabbix, and Icinga.
 How to start containers by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
How to start containers by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
Docker container startup steps: Pull the container image: Run "docker pull [mirror name]". Create a container: Use "docker create [options] [mirror name] [commands and parameters]". Start the container: Execute "docker start [Container name or ID]". Check container status: Verify that the container is running with "docker ps".
 How to start nginx server
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
How to start nginx server
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
Starting an Nginx server requires different steps according to different operating systems: Linux/Unix system: Install the Nginx package (for example, using apt-get or yum). Use systemctl to start an Nginx service (for example, sudo systemctl start nginx). Windows system: Download and install Windows binary files. Start Nginx using the nginx.exe executable (for example, nginx.exe -c conf\nginx.conf). No matter which operating system you use, you can access the server IP
 How to create containers for docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:18 PM
How to create containers for docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:18 PM
Create a container in Docker: 1. Pull the image: docker pull [mirror name] 2. Create a container: docker run [Options] [mirror name] [Command] 3. Start the container: docker start [Container name]






