 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
 How to solve the Python error NameError:name 'X' is not defined
How to solve the Python error NameError:name 'X' is not defined
How to solve the Python error NameError:name 'X' is not defined
Python "NameError: name is not defined" occurs when we try to access an undefined variable or function, or before it is defined.
To fix this error, we need to make sure we didn't misspell the variable name and access it after declaring it.
Make sure you don’t misspell a variable or function
Below is the sample code that produces the above error.
employee = {
'name': 'Jiyik',
'age': 30,
}
# ⛔️ NameError: name 'Employee' is not defined. Did you mean: 'employee'?
print(Employee) # ????️ 拼写错误的变量名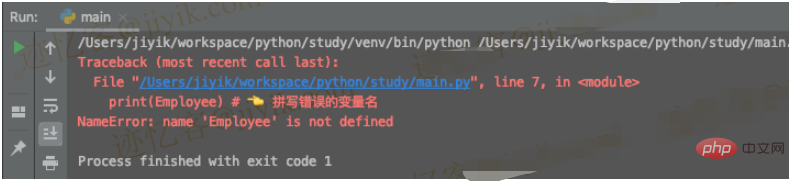
#The problem is that we misspelled the variable name. Note that variable, function, and class names are case-sensitive.
To resolve the error in this case, we must spell the variable name correctly.
employee = {
'name': 'Jiyik',
'age': 30,
}
print(employee)‘
## Access non-existing variables.
- Access a variable, function, or class before declaring it.
- The name of a variable, function, or class is misspelled (names are case-sensitive).
- Do not enclose strings in quotes, such as print(hello).
- Do not enclose dictionary keys in quotes.
- Use built-in modules without importing them first.
- Access scope variables from outside. For example, declare a variable in a function and try to access it from outside.
- Accessing non-existing variables or functions
- #Make sure we are not accessing variables that do not exist or have not been defined yet.
- Accessing non-existing variables or functions
-
Make sure we are not accessing variables that do not exist or have not been defined yet.
# ⛔️ NameError: name 'do_math' is not defined print(do_math(15, 15)) def do_math(a, b): return a + b
Copy after loginThe code example results in a "NameError: function is not defined" error because we are trying to call the function before it is declared.
To resolve this error, move the line that calls the function or accesses the variable after declaring it.
# ✅ 1) 声明函数或变量 def do_math(a, b): return a + b # ✅ 2) 之后访问它 print(do_math(15, 15)) # ????️ 30
Please note that we must also instantiate the class or call the class method after the class declaration.
The same is true when using variables.
# ⛔️ NameError: name 'variable' is not defined. print(variable) variable = 'jiyik.com'
Make sure to move the line accessing the variable below the line declaring it.
variable = 'jiyik.com' print(variable) # ????️ jiyik.com
Forgetting to enclose a string in single or double quotes
Another cause of the error is forgetting to enclose a string in single or double quotes.
def greet(name): return 'Hello ' + name # ⛔️ NameError: name 'Fql' is not defined. Did you mean: 'slice'? greet(Fql) # ????️ 忘记用引号括起字符串
greet function expected to be called with a string, but we forgot to put the string in quotes, so an error with name 'X' being undefined occurred.
This also occurs when passing a string to theprint()
function without surrounding the string in quotes.To resolve this error, enclose the string in quotes.NameError: name is not defineddef greet(name): return 'Hello ' + name greet('Fql')Copy after loginUsing a built-in module without importing itIf we use a built-in module without importing it, it will also cause "
".
# ⛔️ NameError: name 'math' is not defined print(math.floor(15.5))
"NameError: name ‘math’ is not defined" means that we are trying to access a function or property on the math module, but we have not imported the module before accessing the property.
To resolve this error, make sure to import all the modules we are using. Theimport mathimport math print(math.floor(15.5)) # ????️ 15Copy after login
line is required because it loads the
mathmodule into our code.
A module is just a collection of functions and classes. We must load the module before we can access its members. Forgetting to enclose the keys of the dictionary in quotes
This error can also be caused if we have a dictionary and forget to enclose its keys in quotes.
employee = {
'name': 'Jiyik',
# ⛔️ NameError: name 'age' is not defined
age: 30 # ????️ 字典键未包含在引号中
}Unless you have numeric keys in the dictionary, make sure to enclose them in single or double quotes.
employee = {
'name': 'Jiyik',
'age': 30
}Trying to access scope variable from outside
This error also occurs if we try to access scope variable from outside.
def get_message(): message = 'jiyik.com' # ????️ 函数中声明的变量 return message get_message() # ⛔️ NameError: name 'message' is not defined print(message)
The variable is declared in the
get_messagefunction, so it cannot be accessed from the outer scope.
If a variable must be accessed from outside, the best solution is to declare the variable in the external scope. # ????️ 在外部范围内声明变量
message = 'hello world'
def get_message():
return message
get_message()
print(message) # ????️ "hello world"
<div class="code" style="position:relative; padding:0px; margin:0px;"><pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">def get_message():
message = 'jiyik.com'
return message
result = get_message()
print(result) # ????️ "hello world"</pre><div class="contentsignin">Copy after login</div></div>Another option is to mark the variable as global.
def get_message(): # ????️ 将 message 标记为全局 global message # ????️ change its value message = 'hello world' return message get_message() print(message) # ????️ "hello world"
globalmessagekeyword should be avoided as it will make our code harder to read and reasoning.
Trying to access a variable declared in a nested functionIf we try to access a variable declared in a nested function from an outer function, we can mark the variable as non-local variable.The inner function declares a variable nameddef outer(): def inner(): message = 'jiyik.com' print(message) inner() # ⛔️ NameError: name 'message' is not defined print(message) outer()Copy after login
but we try to access the variable from the outer function and get the "name message is not defined" error.
To solve this problem, we can mark the message variables as non-local variables.
def outer(): # ????️ 初始化 message 变量 message = '' def inner(): # ????️ 将 message 标记为 nonlocal nonlocal message message = 'jiyik.com' print(message) inner() print(message) # ????️ "jiyik.com" outer()
nonlocal keyword allows us to use local variables of the enclosing function.
请注意,我们必须在外部函数中初始化消息变量,但我们能够在内部函数中更改它的值。
如果我们不使用 nonlocal 语句,对 print() 函数的调用将返回一个空字符串。
def outer(): # ????️ 初始化 message 变量 message = '' def inner(): # ????️ 在内部范围内声明 message message = 'hello world' print(message) inner() print(message) # ????️ "" outer()
在类定义之前访问它
当我们在定义类之前访问类时,也会发生该错误。
# ⛔️ NameError: name 'Employee' is not defined
emp1 = Employee('jiyik', 100)
class Employee():
def __init__(self, name, salary):
self.name = name
self.salary = salary
def get_name(self):
return self.name要解决该错误,请将实例化行移至类声明下方。
class Employee():
def __init__(self, name, salary):
self.name = name
self.salary = salary
def get_name(self):
return self.name
emp1 = Employee('jiyik', 100)
print(emp1.name) # ????️ jiyik如果我们正在使用来自第三方库的类,则必须先导入该类才能使用它。
请注意在 try/except 块中使用 import 语句
在 try/except 块中使用 import 语句时也可能发生该错误。
try: # ????️ 此处的代码可能会引发错误 import math result = math.floor(15.5) except ImportError: math.floor(18.5) print(math.floor(20.5))
该代码示例有效,但是,如果 import 语句之前的某些代码引发错误,则该模块将不会被导入。
这是一个问题,因为我们正在 except 块中和 try/except 语句之外访问模块。
相反,将导入语句移至文件顶部。
# ✅ 将 import 语句移动到文件顶部 import math try: result = math.floor(15.5) except ImportError: math.floor(18.5) print(math.floor(20.5))
The above is the detailed content of How to solve the Python error NameError:name 'X' is not defined. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP is mainly procedural programming, but also supports object-oriented programming (OOP); Python supports a variety of paradigms, including OOP, functional and procedural programming. PHP is suitable for web development, and Python is suitable for a variety of applications such as data analysis and machine learning.
 Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
PHP is suitable for web development and rapid prototyping, and Python is suitable for data science and machine learning. 1.PHP is used for dynamic web development, with simple syntax and suitable for rapid development. 2. Python has concise syntax, is suitable for multiple fields, and has a strong library ecosystem.
 PHP and Python: A Deep Dive into Their History
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP and Python: A Deep Dive into Their History
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP originated in 1994 and was developed by RasmusLerdorf. It was originally used to track website visitors and gradually evolved into a server-side scripting language and was widely used in web development. Python was developed by Guidovan Rossum in the late 1980s and was first released in 1991. It emphasizes code readability and simplicity, and is suitable for scientific computing, data analysis and other fields.
 Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python is more suitable for beginners, with a smooth learning curve and concise syntax; JavaScript is suitable for front-end development, with a steep learning curve and flexible syntax. 1. Python syntax is intuitive and suitable for data science and back-end development. 2. JavaScript is flexible and widely used in front-end and server-side programming.
 How to run sublime code python
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:48 AM
How to run sublime code python
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:48 AM
To run Python code in Sublime Text, you need to install the Python plug-in first, then create a .py file and write the code, and finally press Ctrl B to run the code, and the output will be displayed in the console.
 Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
VS Code can run on Windows 8, but the experience may not be great. First make sure the system has been updated to the latest patch, then download the VS Code installation package that matches the system architecture and install it as prompted. After installation, be aware that some extensions may be incompatible with Windows 8 and need to look for alternative extensions or use newer Windows systems in a virtual machine. Install the necessary extensions to check whether they work properly. Although VS Code is feasible on Windows 8, it is recommended to upgrade to a newer Windows system for a better development experience and security.
 Where to write code in vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
Where to write code in vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
Writing code in Visual Studio Code (VSCode) is simple and easy to use. Just install VSCode, create a project, select a language, create a file, write code, save and run it. The advantages of VSCode include cross-platform, free and open source, powerful features, rich extensions, and lightweight and fast.
 How to run python with notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:33 PM
How to run python with notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:33 PM
Running Python code in Notepad requires the Python executable and NppExec plug-in to be installed. After installing Python and adding PATH to it, configure the command "python" and the parameter "{CURRENT_DIRECTORY}{FILE_NAME}" in the NppExec plug-in to run Python code in Notepad through the shortcut key "F6".





