How to use Lambda expressions in Java?
Introduction to Lambda expressions
#The essence of Lambda expression is just a "syntax sugar", which is inferred by the compiler and helps you convert and wrap it into regular code , so you can use less code to achieve the same functionality.
Lambda expressions are an important new feature in Java SE 8.
Lambda and anonymous inner classes
Lamda expression refers to application in SAM (SingleAbstractMethod, an interface containing an abstract method) environment A simplified form of definition.
Advantages of Lambda over anonymous inner classes
Conciseness (see "Functional Interface" below for details)
Lamda over anonymous inner classes Disadvantages of the class
#The interface corresponding to Lamda can only have one method.
The interface corresponding to the anonymous inner class can have multiple methods
Requirements for the interface
1.Lambda stipulates that there can only be one method that needs to be implemented in the interface (ie, abstract method).
In an interface, the following ones can exist at the same time: one abstract method (there can only be one), multiple default methods, and multiple static methods.
// There is another new feature in jdk 8: default. The method modified by default will have a default implementation and is not a method that must be implemented, so it does not affect the use of Lambda expressions.
2.@FunctionalInterface: Used to modify functional interfaces.
@FunctionalInterface can be written or not. This annotation is mainly used for compile-level error checking: when the interface does not conform to the functional interface definition, the compiler will report an error.
Correct example, no error reported:
@FunctionalInterface
public interface HelloWorldService {
void sayHello(String msg);
}Incorrect example, error reported:
The interface contains two abstract methods, which violates the definition of functional interface, prompting that the interface Multiple non-overridden abstract methods were found.
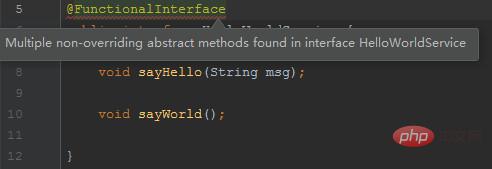
Note: Adding or not adding @FunctionalInterface has no effect on whether the interface is a functional interface. This annotation only reminds the compiler to check whether the interface only contains one abstract method.
Variables and scope
Lambda expressions can only reference outer local variables marked final. That is, local variables defined outside the scope cannot be modified inside the lambda, otherwise a compilation error will be reported
The local variables of the Lambda expression do not need to be declared final, but they must not be modified by subsequent code (i.e. Implicitly with final semantics)
Lambda expressions are not allowed to declare a parameter or local variable with the same name as a local variable.
Format
Important features of lambda expressions
Optional type declaration: No need to declare parameter types, the compiler Parameter values can be identified uniformly.
Optional parameter parentheses: One parameter does not need to be defined with parentheses, but multiple parameters need to be defined with parentheses.
Optional braces: If the body contains a statement, braces are not required. Example: () -> Sysout.out.println("Test");
Optional return keyword: If the body has only one expression return value, the compiler will automatically Return value, curly braces need to be specified to indicate that the expression returns a value.
Simple example of Lambda expression
1. No parameters are required, the return value is 5
() -> 5
2. Receive one parameter (number type) and return 2 times its value
x -> 2 * x
3. Accept 2 parameters (number) and return them The difference
(x, y) -> x – y
4. Receive 2 int type integers and return their sum
(int x, int y) -> ; System.out.print(s)
Syntax formatFormat:
(parameters) - > statement or (parameters) ->{ statements; }
Left side: the parameter list of the Lambda expressionRight side: the functions that need to be performed in the Lambda expression (Lambda body)
##() -> Sysout.out.println("Test") ;
Syntax format 2: There is one parameter and no return value
(X)-> Sysout.out.println(x );
Grammar format three: If there is a parameter bracket, you don’t need to write it
Grammar format 4: There are more than two parameters, a return value, and there are multiple statements in the Lambda body. {}
needs to be used in the syntax body. <div class="code" style="position:relative; padding:0px; margin:0px;"><pre class='brush:php;toolbar:false;'> Comparator<Integer> comparator = (o1, o2) -> {
System.out.println("Test");
return Integer.compare(o1, o2);
};</pre><div class="contentsignin">Copy after login</div></div>
##Comparator comparator = (o1, o2)-> Integer.compare(o1, o2);
语法格式六:表达式的参数列表的数据类型可以省略不写,JVM编译器通过上下文推断出数据类型
(x ,y ) ->Integer.compare(x ,y)
实例
无参数无返回值
package org.example.a;
@FunctionalInterface
interface Interface {
void run();
}
public class Demo{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Interface params = new Interface() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("Anonymous Internal Class: ");
}
};
Interface params1 = () -> System.out.println("Lambda: ");
params.run();
params1.run();
}
}执行结果
Anonymous Internal Class:
Lambda:
有参数无返回值
package org.example.a;
@FunctionalInterface
interface Interface {
void run(String s);
}
public class Demo{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Interface params = new Interface() {
@Override
public void run(String s) {
System.out.println("Anonymous Internal Class: " + s);
}
};
Interface params1 = (s) -> System.out.println("Lambda: " + s);
params.run("hello");
params1.run("hi");
}
}执行结果
Anonymous Internal Class: hello
Lambda: hi
有参数有返回值
package org.example.a;
@FunctionalInterface
interface Interface {
String run(String s);
}
public class Demo{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Interface params = new Interface() {
@Override
public String run(String s) {
System.out.println("Anonymous Internal Class: " + s);
return "abc";
}
};
Interface params1 = (s) -> {
System.out.println("Lambda: " + s);
return "def";
};
System.out.println(params.run("hello"));
System.out.println(params1.run("hi"));
}
}执行结果
Anonymous Internal Class: hello
abc
Lambda: hi
def
lambda作为参数
传递一个函数
package org.example.a;
interface IRun {
String welcome(String string);
}
class Util {
public static long executionTime1(IRun iRun, String string) {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(iRun.welcome(string));
//本处刻意添加这一无意义延时,防止执行太快返回0
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
return endTime - startTime;
}
public long executionTime2(IRun iRun, String string) {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(iRun.welcome(string));
//本处刻意添加这一无意义延时,防止执行太快返回0
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
return endTime - startTime;
}
public static String hello(String string){
String tmp;
tmp = "hello: " + string;
return tmp;
}
public String hi(String string){
String tmp;
tmp = "hi: " + string;
return tmp;
}
}
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
long time1 = Util.executionTime1(Util::hello, "Tony");
long time2 = new Util().executionTime2(new Util()::hi, "Pepper");
System.out.println("time1: " + time1 + "ms");
System.out.println("time2: " + time2 + "ms");
}
}执行结果
hello: Tony
hi: Pepper
time1: 11ms
time2: 11ms
直接传递lambda函数
package org.example.a;
interface IRun {
String welcome(String string);
}
class Util {
public static long executionTime(IRun iRun, String string) {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(iRun.welcome(string));
//本处刻意添加这一无意义延时,防止执行太快返回0
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
return endTime - startTime;
}
}
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
long time = Util.executionTime((string -> {
String tmp;
tmp = "hello: " + string;
return tmp;
})
, "Tony");
System.out.println("time: " + time + "ms");
}
}执行结果
hello: Tony
time: 11ms
遍历集合
package org.example.a;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Demo{
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("aaa");
list.add("bbb");
//以前的循环方式
for (String string : list) {
System.out.println(string);
}
//使用lambda表达式输出list中的每个值
list.forEach(c->{
System.out.println(c);
});
// 在 Java 8 中使用双冒号操作符(double colon operator)。也属于lamda表达式
list.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}执行结果
aaa
bbb
aaa
bbb
aaa
bbb
创建线程
package org.example.a;
public class Demo{
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("Anonymous Internal Class !");
}
}).start();
new Thread(() -> System.out.println("Lambda !")).start();
}
}执行结果
Anonymous Internal Class !
Lambda !
排序
package org.example.a;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Comparator;
public class Demo{
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] players = {"Rafael Nadal", "Novak Djokovic", "Stanislas Wawrinka"};
Arrays.sort(players, new Comparator<String>() {
@Override
public int compare(String o1, String o2) {
return (o1.compareTo(o2));
}
});
// Comparator<String> sortByName = (String s1, String s2) -> (s1.compareTo(s2));
// Arrays.sort(players, sortByName);
// Arrays.sort(players, (String s1, String s2) -> (s1.compareTo(s2)));
for(String string:players){
System.out.println(string);
}
}
}执行结果(换成注释掉的两种任意一种都是一样的)
Novak Djokovic
Rafael Nadal
Stanislas Wawrinka
The above is the detailed content of How to use Lambda expressions in Java?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is
 PHP: A Key Language for Web Development
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP: A Key Language for Web Development
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP is a scripting language widely used on the server side, especially suitable for web development. 1.PHP can embed HTML, process HTTP requests and responses, and supports a variety of databases. 2.PHP is used to generate dynamic web content, process form data, access databases, etc., with strong community support and open source resources. 3. PHP is an interpreted language, and the execution process includes lexical analysis, grammatical analysis, compilation and execution. 4.PHP can be combined with MySQL for advanced applications such as user registration systems. 5. When debugging PHP, you can use functions such as error_reporting() and var_dump(). 6. Optimize PHP code to use caching mechanisms, optimize database queries and use built-in functions. 7
 PHP vs. Python: Understanding the Differences
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP vs. Python: Understanding the Differences
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages, and the choice should be based on project requirements. 1.PHP is suitable for web development, with simple syntax and high execution efficiency. 2. Python is suitable for data science and machine learning, with concise syntax and rich libraries.
 Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Capsules are three-dimensional geometric figures, composed of a cylinder and a hemisphere at both ends. The volume of the capsule can be calculated by adding the volume of the cylinder and the volume of the hemisphere at both ends. This tutorial will discuss how to calculate the volume of a given capsule in Java using different methods. Capsule volume formula The formula for capsule volume is as follows: Capsule volume = Cylindrical volume Volume Two hemisphere volume in, r: The radius of the hemisphere. h: The height of the cylinder (excluding the hemisphere). Example 1 enter Radius = 5 units Height = 10 units Output Volume = 1570.8 cubic units explain Calculate volume using formula: Volume = π × r2 × h (4
 PHP vs. Other Languages: A Comparison
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP vs. Other Languages: A Comparison
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP is suitable for web development, especially in rapid development and processing dynamic content, but is not good at data science and enterprise-level applications. Compared with Python, PHP has more advantages in web development, but is not as good as Python in the field of data science; compared with Java, PHP performs worse in enterprise-level applications, but is more flexible in web development; compared with JavaScript, PHP is more concise in back-end development, but is not as good as JavaScript in front-end development.
 PHP vs. Python: Core Features and Functionality
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:16 AM
PHP vs. Python: Core Features and Functionality
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:16 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages and are suitable for different scenarios. 1.PHP is suitable for web development and provides built-in web servers and rich function libraries. 2. Python is suitable for data science and machine learning, with concise syntax and a powerful standard library. When choosing, it should be decided based on project requirements.
 Create the Future: Java Programming for Absolute Beginners
Oct 13, 2024 pm 01:32 PM
Create the Future: Java Programming for Absolute Beginners
Oct 13, 2024 pm 01:32 PM
Java is a popular programming language that can be learned by both beginners and experienced developers. This tutorial starts with basic concepts and progresses through advanced topics. After installing the Java Development Kit, you can practice programming by creating a simple "Hello, World!" program. After you understand the code, use the command prompt to compile and run the program, and "Hello, World!" will be output on the console. Learning Java starts your programming journey, and as your mastery deepens, you can create more complex applications.






