Six magical built-in functions in Python

Life is short, novices learn Python!
I am a rookie brother. Today, we will share 6 magical built-in functions at once. In many computer books, they are also usually introduced as higher-order functions. And in my daily work, I often use them to make code faster and easier to understand.
Lambda function
The Lambda function is used to create anonymous functions, that is, functions without names. It is just an expression, and the function body is much simpler than def. Anonymous functions are used when we need to create a function that performs a single operation and can be written in one line.
lambda [arg1 [,arg2,.....argn]]:expression
The body of lambda is an expression, not a code block. Only limited logic can be encapsulated in lambda expressions. For example:
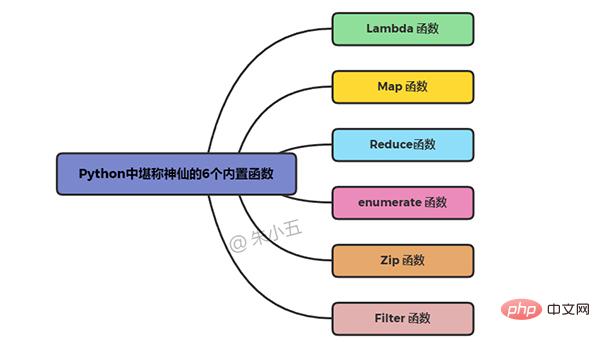
lambda x: x+2
If we also want to call the function defined by def at any time, we can assign the lambda function to such a function object.
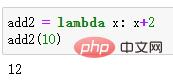
add2 = lambda x: x+2 add2(10)
Output result:
Using the Lambda function, the code can be simplified a lot. Here is another example.
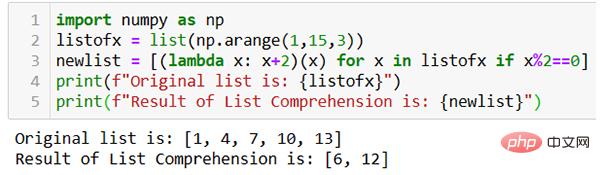
As shown in the figure above, the result list newlist is generated with one line of code using the lambda function.
Map function
The map() function maps a function to all elements of an input list.
map(function,iterable)
For example, we first create a function to return an uppercase input word, and then apply this function to all elements in the list colors.
def makeupper(word): return word.upper() colors=['red','yellow','green','black'] colors_uppercase=list(map(makeupper,colors)) colors_uppercase
Output result:

In addition, we can also use anonymous function lambda to cooperate with the map function, which can be more streamlined.
colors=['red','yellow','green','black'] colors_uppercase=list(map(lambda x: x.upper(),colors)) colors_uppercase
If we don’t use the Map function, we need to use a for loop.
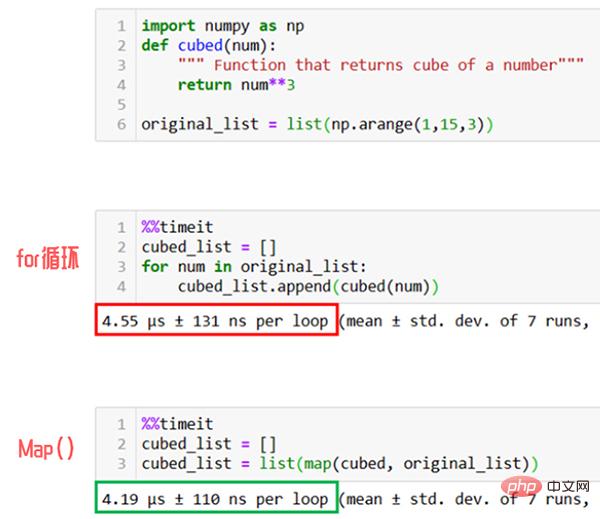
#As shown in the figure above, in actual use, the Map function will be 1.5 times faster than the for loop method of sequentially listing elements.
Reduce function
Reduce() is a very useful function when you need to perform some calculations on a list and return the result. For example, when you need to calculate the product of all elements of a list of integers, you can use the reduce function. [1]
The biggest difference between it and the function is that the mapping function (function) in reduce() receives two parameters, while map receives one parameter.
reduce(function, iterable[, initializer])
Next we use an example to demonstrate the code execution process of reduce().
from functools import reduce def add(x, y) : # 两数相加 return x + y numbers = [1,2,3,4,5] sum1 = reduce(add, numbers) # 计算列表和
The result sum1 = 15 is obtained, and the code execution process is shown in the animation below.
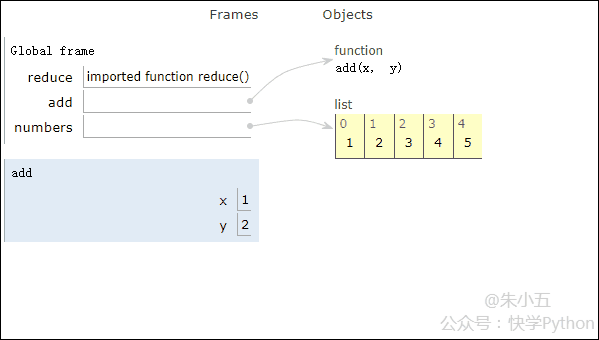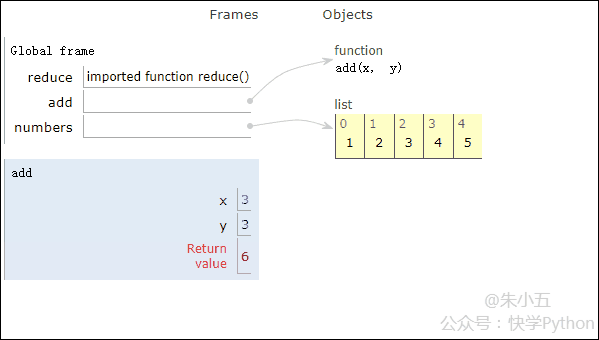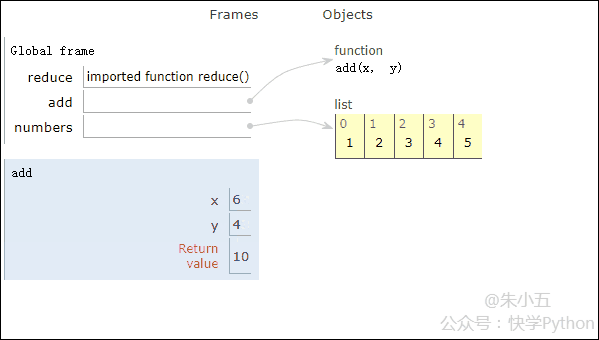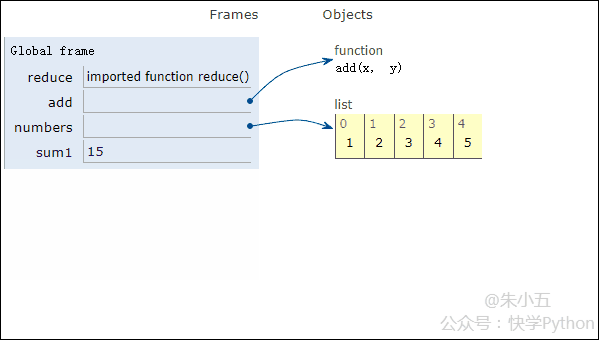
▲Code execution process animation
Combined with the above figure, we will see that reduce applies an addition function add() to a list[1 ,2,3,4,5], the mapping function receives two parameters, and reduce() continues to accumulate the result with the next element of the list.
In addition, we can also use anonymous function lambda to cooperate with the reduce function, which can be more streamlined.
from functools import reduce numbers = [1,2,3,4,5] sum2 = reduce(lambda x, y: x+y, numbers)
The output sum2= 15 is obtained, which is consistent with the previous result.
Note: reduce() has been moved to the functools module since Python 3.x [2]. If we want to use it, we need to import it from functools import reduce.
enumerate function
The enumerate() function is used to combine a traversable data object (such as a list, tuple or string) into an index sequence, while listing the data and data subscripts. It is generally used in for loops. Its syntax is as follows:
enumerate(iterable, start=0)
Its two parameters, one is a sequence, iterator or other object that supports iteration; the other is the starting position of the subscript, which starts from 0 by default, and can also be used since Defines the starting number of the counter.
colors = ['red', 'yellow', 'green', 'black'] result = enumerate(colors)
If we have a color list that stores colors, we will get an enumerate object after running it. It can be used directly in a for loop or converted to a list. The specific usage is as follows.
for count, element in result:
print(f"迭代编号:{count},对应元素:{element}")

Zip 函数
zip()函数用于将可迭代的对象作为参数,将对象中对应的元素打包成一个个元组,然后返回由这些元组组成的列表[3]。
我们还是用两个列表作为例子演示:
colors = ['red', 'yellow', 'green', 'black'] fruits = ['apple', 'pineapple', 'grapes', 'cherry'] for item in zip(colors,fruits): print(item)
输出结果:
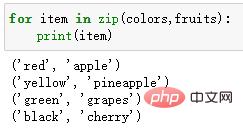
当我们使用zip()函数时,如果各个迭代器的元素个数不一致,则返回列表长度与最短的对象相同。
prices =[100,50,120] for item in zip(colors,fruits,prices): print(item)

Filter 函数
filter()函数用于过滤序列,过滤掉不符合条件的元素,返回由符合条件元素组成的新列表,其语法如下所示[4]。
filter(function, iterable)
比如举个例子,我们可以先创建一个函数来检查单词是否为大写,然后使用filter()函数过滤出列表中的所有奇数:
def is_odd(n): return n % 2 == 1 old_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10] new_list = filter(is_odd, old_list) print(newlist)
输出结果:

今天分享的这6个内置函数,在使用 Python 进行数据分析或者其他复杂的自动化任务时非常方便。
The above is the detailed content of Six magical built-in functions in Python. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP is mainly procedural programming, but also supports object-oriented programming (OOP); Python supports a variety of paradigms, including OOP, functional and procedural programming. PHP is suitable for web development, and Python is suitable for a variety of applications such as data analysis and machine learning.
 Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
PHP is suitable for web development and rapid prototyping, and Python is suitable for data science and machine learning. 1.PHP is used for dynamic web development, with simple syntax and suitable for rapid development. 2. Python has concise syntax, is suitable for multiple fields, and has a strong library ecosystem.
 PHP and Python: A Deep Dive into Their History
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP and Python: A Deep Dive into Their History
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP originated in 1994 and was developed by RasmusLerdorf. It was originally used to track website visitors and gradually evolved into a server-side scripting language and was widely used in web development. Python was developed by Guidovan Rossum in the late 1980s and was first released in 1991. It emphasizes code readability and simplicity, and is suitable for scientific computing, data analysis and other fields.
 Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python is more suitable for beginners, with a smooth learning curve and concise syntax; JavaScript is suitable for front-end development, with a steep learning curve and flexible syntax. 1. Python syntax is intuitive and suitable for data science and back-end development. 2. JavaScript is flexible and widely used in front-end and server-side programming.
 How to run sublime code python
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:48 AM
How to run sublime code python
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:48 AM
To run Python code in Sublime Text, you need to install the Python plug-in first, then create a .py file and write the code, and finally press Ctrl B to run the code, and the output will be displayed in the console.
 Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
VS Code can run on Windows 8, but the experience may not be great. First make sure the system has been updated to the latest patch, then download the VS Code installation package that matches the system architecture and install it as prompted. After installation, be aware that some extensions may be incompatible with Windows 8 and need to look for alternative extensions or use newer Windows systems in a virtual machine. Install the necessary extensions to check whether they work properly. Although VS Code is feasible on Windows 8, it is recommended to upgrade to a newer Windows system for a better development experience and security.
 Where to write code in vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
Where to write code in vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
Writing code in Visual Studio Code (VSCode) is simple and easy to use. Just install VSCode, create a project, select a language, create a file, write code, save and run it. The advantages of VSCode include cross-platform, free and open source, powerful features, rich extensions, and lightweight and fast.
 Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
VS Code can be used to write Python and provides many features that make it an ideal tool for developing Python applications. It allows users to: install Python extensions to get functions such as code completion, syntax highlighting, and debugging. Use the debugger to track code step by step, find and fix errors. Integrate Git for version control. Use code formatting tools to maintain code consistency. Use the Linting tool to spot potential problems ahead of time.






