 Operation and Maintenance
Operation and Maintenance
 Linux Operation and Maintenance
Linux Operation and Maintenance
 Check how many partitions there are in linux
Check how many partitions there are in linux
Check how many partitions there are in linux
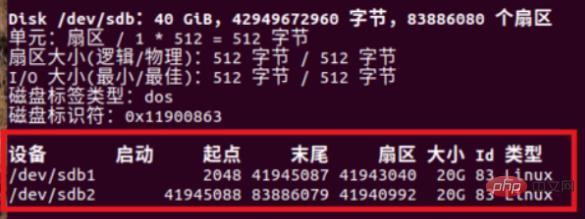
How to check how many partitions there are in Linux: 1. Open the Linux terminal window; 2. Enter the "Fdisk-L" command and press Enter; 3. View the partition list in the terminal window and view the disk The partition information is sufficient.

#The operating environment of this tutorial: linux5.9.8 system, Dell G3 computer.
How many partitions does Linux have?
How to check the partition situation in LINUX:
1. First, open the terminal and enter Fdisk -L and press Enter.
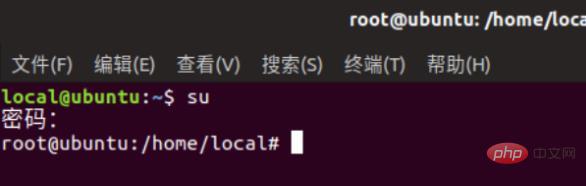
2. This is the partition list.
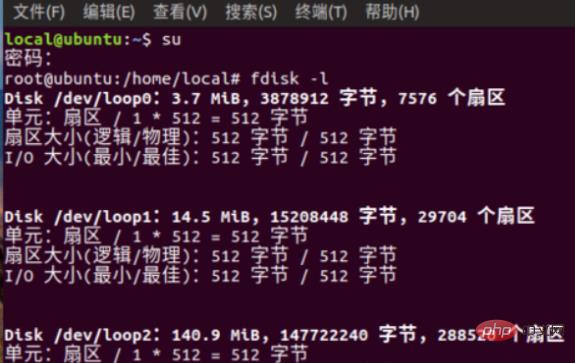
#3. Find two 40G partition words in the picture. These two are the partitions of our hard disk.
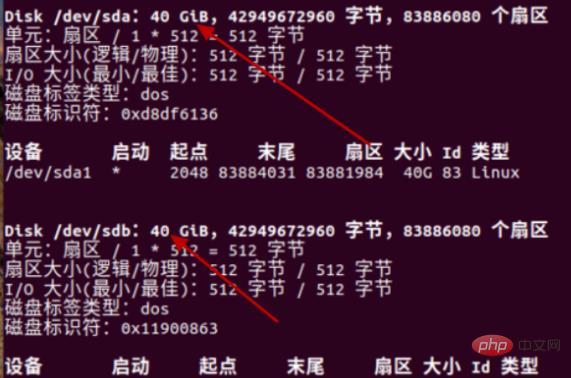
4. The information in the red box is that the disk partition information size is 40G, so sDA and SDB have different meanings.
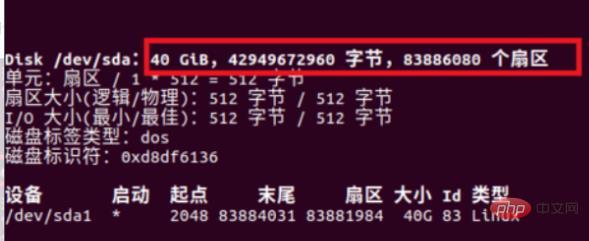
#5. All the equipment in the red box below are listed to complete the rendering.
Related introduction:
df command
df output disk file system usage:
[root@centos ~]# df 文件系统 1K-块 已用 可用 已用% 挂载点 /dev/sda3 11208704 7214792 3993912 65% / devtmpfs 496920 0 496920 0% /dev tmpfs 507752 0 507752 0% /dev/shm tmpfs 507752 6852 500900 2% /run tmpfs 507752 0 507752 0% /sys/fs/cgroup /dev/sda1 201380 103660 97720 52% /boot tmpfs 101552 0 101552 0% /run/user/0
Mainly focus on used percentage and mount points. The one with the words tmpfs is a temporary file system. The data is not saved after the system is powered off. /dev/sda is our disk.
There are several common parameters, -h is displayed in appropriate units, and the default "used" column is KB. -m displays the disk usage in MB. -i displays inode usage. When the disk is formatted, inode and block are generated. I want to draw a grid on a piece of paper. The grid where the content can be stored is block, and inode is the directory index pointing to the block. Linux may encounter an situation where the inode is used up and there is still a block left, but at this time the system cannot write files to the disk.
Computer storage media units mainly include Byte, KB, MB, GB, and TB. The above are arranged in ascending order, and the conversion base is 1024. There is also a smaller unit called bit, which represents 0 or 1, which can be said to convey an amount of information. 8bit=1Byte, this conversion base is not 1024. We commonly use Mbps (b is bit, ps is per second) in terms of network transmission speed. We can get inspiration from this unit:
can be understood as the computer transmitting a string of information represented by 01 through the network cable.
The 100M broadband I bought, the maximum download and write speed to the disk is 100Mbit/s=1.25 MB/s
In addition, when installing Linux, the disk is also divided into swap space, which cannot be viewed with the df command. Check the swap space and use free.
du command
du -sh file can check the disk usage of a file or directory. -s displays the total usage. If -s is not added when viewing the directory, the status of each file in the directory will be displayed. -h displays size in appropriate units.
The file size can also be seen in ls -l. But unlike the du command, ls displays the actual file size, while du displays the occupied disk size. In fact, it is quite easy to understand. As mentioned earlier, disk formatting is like drawing a grid on a white paper, so each block will have a certain size to store content. One block cannot contain the contents of multiple files, otherwise it will cause confusion. In other words, even if the file occupies half the block size, this block is no longer used by other files. du measures the file size from the block size, while ls measures it from the amount of bit information stored in the file. Of course du can also view the file content size, you need to use the parameter -sb.
Disk Partition
fdisk -l Check the status of the disk currently mounted on the system. fdisk is also a partitioning tool, and fdisk /dev/sdb is an sdb disk partition. When a new disk is put into use, it is generally partitioned and then formatted, or it can be formatted directly.
Enter the fdisk format partition command into the terminal, enter m to get help, and detailed guidance will be listed. The commonly used ones are: n to create a new partition, w to save the settings, and d to delete the partition. We are experimenting with adding disks to the virtual machine. You may need to restart the virtual machine to recognize the newly created disk. Most real servers support hot-swappable disks.
Use fdisk partition to set up to 4 primary partitions (primary). If there is a need for more partitions, set up 3 primary partitions (primary) and 1 extended partition (extended). Multiple logical partitions can be set up in the extended partition. In short, primary extended
One feature: the logical partition number starts from 5, and the partition numbers are consecutive. The partition numbers of the primary partition may not be consecutive.
After setting the disk partition, be sure to save and exit, otherwise the partition will be lost.
Related recommendations: "Linux Video Tutorial"
The above is the detailed content of Check how many partitions there are in linux. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 What computer configuration is required for vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:48 PM
What computer configuration is required for vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:48 PM
VS Code system requirements: Operating system: Windows 10 and above, macOS 10.12 and above, Linux distribution processor: minimum 1.6 GHz, recommended 2.0 GHz and above memory: minimum 512 MB, recommended 4 GB and above storage space: minimum 250 MB, recommended 1 GB and above other requirements: stable network connection, Xorg/Wayland (Linux)
 Linux Architecture: Unveiling the 5 Basic Components
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Linux Architecture: Unveiling the 5 Basic Components
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:04 AM
The five basic components of the Linux system are: 1. Kernel, 2. System library, 3. System utilities, 4. Graphical user interface, 5. Applications. The kernel manages hardware resources, the system library provides precompiled functions, system utilities are used for system management, the GUI provides visual interaction, and applications use these components to implement functions.
 How to run java code in notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:39 PM
How to run java code in notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:39 PM
Although Notepad cannot run Java code directly, it can be achieved by using other tools: using the command line compiler (javac) to generate a bytecode file (filename.class). Use the Java interpreter (java) to interpret bytecode, execute the code, and output the result.
 vscode cannot install extension
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:18 PM
vscode cannot install extension
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:18 PM
The reasons for the installation of VS Code extensions may be: network instability, insufficient permissions, system compatibility issues, VS Code version is too old, antivirus software or firewall interference. By checking network connections, permissions, log files, updating VS Code, disabling security software, and restarting VS Code or computers, you can gradually troubleshoot and resolve issues.
 How to check the warehouse address of git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
How to check the warehouse address of git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
To view the Git repository address, perform the following steps: 1. Open the command line and navigate to the repository directory; 2. Run the "git remote -v" command; 3. View the repository name in the output and its corresponding address.
 Can vscode be used for mac
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:36 PM
Can vscode be used for mac
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:36 PM
VS Code is available on Mac. It has powerful extensions, Git integration, terminal and debugger, and also offers a wealth of setup options. However, for particularly large projects or highly professional development, VS Code may have performance or functional limitations.
 vscode terminal usage tutorial
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
vscode terminal usage tutorial
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
vscode built-in terminal is a development tool that allows running commands and scripts within the editor to simplify the development process. How to use vscode terminal: Open the terminal with the shortcut key (Ctrl/Cmd). Enter a command or run the script. Use hotkeys (such as Ctrl L to clear the terminal). Change the working directory (such as the cd command). Advanced features include debug mode, automatic code snippet completion, and interactive command history.
 How to use VSCode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 11:21 PM
How to use VSCode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 11:21 PM
Visual Studio Code (VSCode) is a cross-platform, open source and free code editor developed by Microsoft. It is known for its lightweight, scalability and support for a wide range of programming languages. To install VSCode, please visit the official website to download and run the installer. When using VSCode, you can create new projects, edit code, debug code, navigate projects, expand VSCode, and manage settings. VSCode is available for Windows, macOS, and Linux, supports multiple programming languages and provides various extensions through Marketplace. Its advantages include lightweight, scalability, extensive language support, rich features and version





