 Operation and Maintenance
Operation and Maintenance
 Linux Operation and Maintenance
Linux Operation and Maintenance
 What is the linux root directory for?
What is the linux root directory for?
What is the linux root directory for?
The Linux root directory "/" is the organizer of the Linux file system and the highest-level leader; the entrance to the Linux file system is the root directory "/", and all directories, files, and devices are also located there. Under the root directory "/". Linux directories all start from the root. The entire directory structure is an inverted tree structure. "/" is the root of the tree, and the subfolders are the trunk and leaves.

#The operating environment of this tutorial: centos7 system, Dell G3 computer. '
The root directory of the Linux system (/)
The file system of Linux and UNIX is a hierarchical structure with "/" as the root The tree file structure, "/" is therefore called the root directory.
All files and directories are placed under the root directory "/". There are subdirectories such as /bin, /home, /usr and so on under the root directory /.
This is the basic directory structure of centos7:
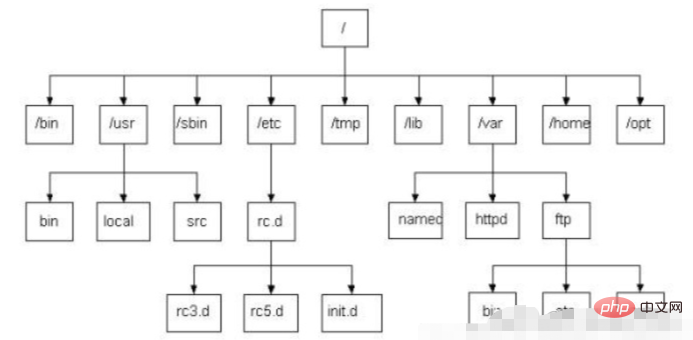
The difference between the Linux directory and the Windows directory. In Windows, a hard disk is divided into several drive letters. Usually They are C, D, and E drives, but there is no concept of drive letters in Linux. Here, "start from the root", the root is /, and there are usually these folders in the root directory, such as /etc, /var, and /usr.
The directories of unix/linux all start from the root. The entire directory structure is an inverted tree structure, / is the root of the tree, and the subfolders are the trunk and leaves.

Explanation:
We call / the root of Linux. That is, the file system of the Linux operating system. The entrance to the Linux file system is /, and all directories, files, and devices are under /. / is the organizer of the Linux file system and the highest-level leader.
Directory structure introduction
/boot
This directory is used to store the files and kernel required for system startup , boot menu and required configuration files, etc. Normally this folder is not operated on.
/dev
is used to store system mounting devices and exists as a file.
The drive letters in Windows do not exist here, there are just various files representing different devices. For example, cdrom represents the optical drive device, and sda and sdb represent the hard disk devices. After partitioning, logical hard disks such as sda1 and sda2 will be formed, and the same is true for sdb.
Special mounting devices include /dev/null and dev/zero. /null is a device in the system that can receive unlimited data. It is like a black hole that is never full. You can move the data to be deleted into /null; /zero has a lot of random characters, which will continue to be generated when the system runs, but it will not Output to the system. If you want to generate a file of a specified size, you need to use it. When mounting a swap partition for the system, you need to use the /dev/zero device.
Usually when partitioning the hard disk, setting the raid will be performed in this folder, and is generally not performed at other times.
/etc Important
The configuration files used to prevent system configuration files and install software will be placed here by default. When you need to modify system settings, you must go to this folder to perform operations.
Commonly used files and folders under/etc:
- Modify and view the Linux host name-/etc/hostname file. The modification here is a permanent modification. After the modification, restart the system to take effect.
- Modify the mapping of ip and host name in this machine——/etc/hosts file, which is equivalent to local DNS resolution
- Modify user environment variables, default parameters in shell, system functions, add aliases— —/etc/profile,/etc/bashrc
Note that the file needs to be executable - Set the system character set——/etc/locale.conf
- Common system configuration directory /etc/sysconf, such as network card configuration:
/etc/sysconf/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth33 - View system information——/etc/os-release, /etc/system- release
- rc.local——runs in parallel with system startup (boot), runs before system service (systemd) runs, and is often used to mount disks or start higher priority services
- /etc/service——System service default port
/lib, /lib64
system library.
/bin,/sbin
Place executable command binary files.
/mnt
The default mounting directory is not the only directory that can be mounted. Devices can be mounted in general directories in Linux. Open the mounted directory and operate Data in the device is manipulated just like data in a normal folder.
Use the mount command when mounting, and the umount command to uninstall the device. Repeated mounting will overwrite the previous mounting.
/proc
This folder is used to place the virtual file system, system kernel, processes, external devices and network status.
The configuration information read by the system will be re-read every time it is restarted. The files therein cannot be modified at will, such as CPU information and memory information. Some modifications will become invalid after restarting the system.
/root
The super administrator’s home directory, while the ordinary administrator’s directories are unified under /home.
Super administrators can operate any data in Linux, while ordinary administrators can only modify and delete files in their own home directory, and only part of others can be viewed.
/tmp
Stores temporary files. This folder is shared by all people.
/opt
Some third-party software will be installed here, but it is usually not used very much.
/usr
Directory that stores user data. If, user installs software data, user installs commands, user installs libraries, etc.
- /usr/share——Place help and description folders, you can also place shared files
- /usr/local——The default location for software installed by users
/var
The folder where variable files are stored. System cache, temporary data, and frequently changing data will be placed here.
- /log system log, server log, etc.
- /spool stores scheduled task information
Summary
The most commonly used directories in daily life are /etc, /var, and /usr. Other directories are rarely touched. If you are using a cloud server, you do not need to manually mount the hard disk or anything. (except for mounting NFS), there is no need to manually partition the hard disk, the installation system will partition it by default.
When we want to modify system parameters, just enter /etc and find the corresponding modifications. After modifying most configuration files, we need to restart the service (service) or execute a special refresh command (source, bash). Usually the installed software configuration file or the folder where the configuration file is placed will have a software name command and be placed under /etc, but some will add a d after the name to indicate that the software has multiple configuration files.
Recommended learning: Linux video tutorial
The above is the detailed content of What is the linux root directory for?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 What computer configuration is required for vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:48 PM
What computer configuration is required for vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:48 PM
VS Code system requirements: Operating system: Windows 10 and above, macOS 10.12 and above, Linux distribution processor: minimum 1.6 GHz, recommended 2.0 GHz and above memory: minimum 512 MB, recommended 4 GB and above storage space: minimum 250 MB, recommended 1 GB and above other requirements: stable network connection, Xorg/Wayland (Linux)
 Linux Architecture: Unveiling the 5 Basic Components
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Linux Architecture: Unveiling the 5 Basic Components
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:04 AM
The five basic components of the Linux system are: 1. Kernel, 2. System library, 3. System utilities, 4. Graphical user interface, 5. Applications. The kernel manages hardware resources, the system library provides precompiled functions, system utilities are used for system management, the GUI provides visual interaction, and applications use these components to implement functions.
 How to run java code in notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:39 PM
How to run java code in notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:39 PM
Although Notepad cannot run Java code directly, it can be achieved by using other tools: using the command line compiler (javac) to generate a bytecode file (filename.class). Use the Java interpreter (java) to interpret bytecode, execute the code, and output the result.
 vscode cannot install extension
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:18 PM
vscode cannot install extension
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:18 PM
The reasons for the installation of VS Code extensions may be: network instability, insufficient permissions, system compatibility issues, VS Code version is too old, antivirus software or firewall interference. By checking network connections, permissions, log files, updating VS Code, disabling security software, and restarting VS Code or computers, you can gradually troubleshoot and resolve issues.
 Can vscode be used for mac
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:36 PM
Can vscode be used for mac
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:36 PM
VS Code is available on Mac. It has powerful extensions, Git integration, terminal and debugger, and also offers a wealth of setup options. However, for particularly large projects or highly professional development, VS Code may have performance or functional limitations.
 How to check the warehouse address of git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
How to check the warehouse address of git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
To view the Git repository address, perform the following steps: 1. Open the command line and navigate to the repository directory; 2. Run the "git remote -v" command; 3. View the repository name in the output and its corresponding address.
 vscode terminal usage tutorial
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
vscode terminal usage tutorial
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
vscode built-in terminal is a development tool that allows running commands and scripts within the editor to simplify the development process. How to use vscode terminal: Open the terminal with the shortcut key (Ctrl/Cmd). Enter a command or run the script. Use hotkeys (such as Ctrl L to clear the terminal). Change the working directory (such as the cd command). Advanced features include debug mode, automatic code snippet completion, and interactive command history.
 How to use VSCode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 11:21 PM
How to use VSCode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 11:21 PM
Visual Studio Code (VSCode) is a cross-platform, open source and free code editor developed by Microsoft. It is known for its lightweight, scalability and support for a wide range of programming languages. To install VSCode, please visit the official website to download and run the installer. When using VSCode, you can create new projects, edit code, debug code, navigate projects, expand VSCode, and manage settings. VSCode is available for Windows, macOS, and Linux, supports multiple programming languages and provides various extensions through Marketplace. Its advantages include lightweight, scalability, extensive language support, rich features and version





