What are the expansion methods of go language?
Go language expansion methods include: 1. Slice expansion. When using append to add elements to Slice, if the Slice space is insufficient, Slice expansion will be triggered; 2. Map expansion. There are two conditions that trigger Map expansion: 1. When the load factor is greater than 6.5, that is, the average number of key-value pairs stored in each bucket reaches 6.5; 2. When the number of overflows is greater than 2^15, that is, when the number of overflows exceeds 32768.

The operating environment of this tutorial: Windows 7 system, GO version 1.18, Dell G3 computer.
Slice expansion
Trigger
When using append to append elements to Slice, if the Slice space is insufficient, Slice will be triggered Expansion
Principle
Expansion is actually to reallocate a larger memory, copy the original Slice data into the new Slice, then return to the new Slice, and then append the data to it after expansion .
Mechanism
Before V1.8:
The selection of expansion capacity follows the following rules:
- If the original Slice capacity is less than 1024 , the new Slice capacity will be expanded to 2 times the original;
- If the original Slice capacity is greater than or equal to 1024, the new Slice capacity will be expanded to 1.25 times the original;
// 1.17及以前的版本中
// old指切片的旧容量, cap指期望的新容量
func growslice(old, cap int) int {
newcap := old
doublecap := newcap + newcap
// 如果期望容量大于旧容量的2倍,则直接使用期望容量作为最终容量
if cap > doublecap {
newcap = cap
} else {
// 如果旧容量小于1024,则直接翻倍
if old < 1024 {
newcap = doublecap
} else {
// 每次增长大约1.25倍
for 0 < newcap && newcap < cap {
newcap += newcap / 4
}
if newcap <= 0 {
newcap = cap
}
}
}
// 这里忽略了对齐操作
return newcap
}V1 After .8:
The selection of new expansion capacity follows the following rules: (has a smoother expansion coefficient)
- If the original Slice capacity is less than 256, the new Slice capacity will be expanded to 2 times the original;
- If the original Slice capacity is greater than or equal to 256, the new Slice capacity will be expanded to the original New capacity = (original capacity 3*256)/4
// 只关心扩容规则的简化版growslice
func growslice(old, cap int) int {
newcap := old
doublecap := newcap + newcap
if cap > doublecap {
newcap = cap
} else {
const threshold = 256 // 不同点1
if old < threshold {
newcap = doublecap
} else {
for 0 < newcap && newcap < cap {
newcap += (newcap + 3*threshold) / 4 // 不同点2
}
if newcap <= 0 {
newcap = cap
}
}
}
return newcap
}Map expansion
There are two conditions for triggering expansion:
Load factor> 6.5, that is, the average number of key-value pairs stored in each bucket reaches 6.5. IncrementExpansion
- ##When the number of overflows > 2^15, that is, when the number of overflows exceeds 32768.
Equal amountExpansion/rearrangement
Note: Creating an overflow bucket does not belong to the expansion mechanism
- #When the load factor is too large, a new bucket space is opened, and the number of buckets is twice the previous number The new space is referenced by buckets. The old space was referenced by oldbuckets
- Then the data in oldbuckets will be gradually moved to the newly opened buckets space
Increment Expansion
will trigger a relocation every time the map is accessed, and each time 2 key-value pairs will be relocated. After all key-value pairs in oldbuckets have been relocated, delete oldbuckets.
The following figure shows a map containing a fully loaded bucket (for the convenience of description, the value area of the bucket is omitted in the figure):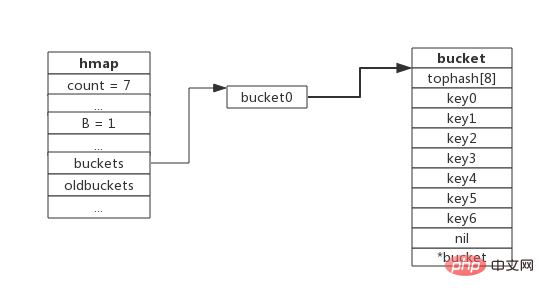
capacity expansion operation will be triggered. After capacity expansion, the new insertion key will be written into the new bucket. Note that because the load factor is triggered, the overflow bucket is not created.
When the 8th key-value pair is inserted,capacity expansion will be triggered. The schematic diagram after expansion is as follows:
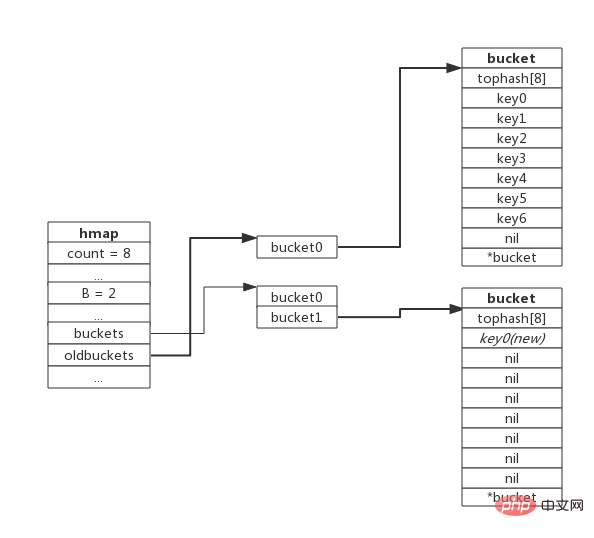
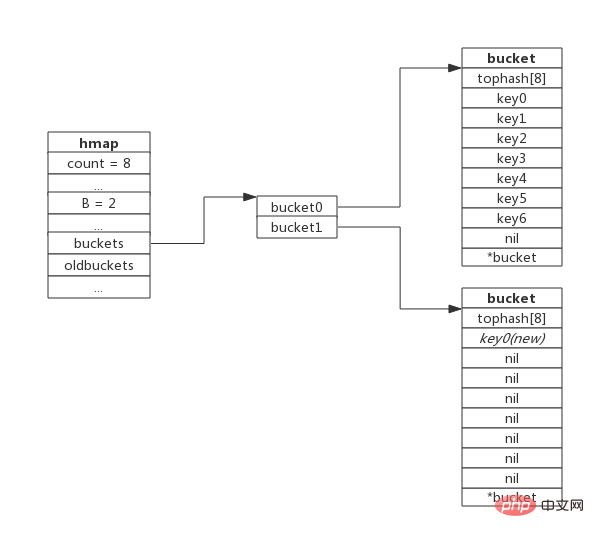
Equal amountExpansion/rearrangement
The so-called equal amountExpansion is not actually an expansion of capacity, the number of buckets No change, redo the relocation action similar to IncrementExpansion, and rearrange the loose key-value pairs to make the bucket usage higher and ensure faster access. In extreme scenarios, such as constant additions and deletions, and key-value pairs are concentrated in a small number of buckets, this will cause the number of overflow buckets to increase, but the load factor is not high, making it impossible to perform incremental migration. , as shown in the figure below:
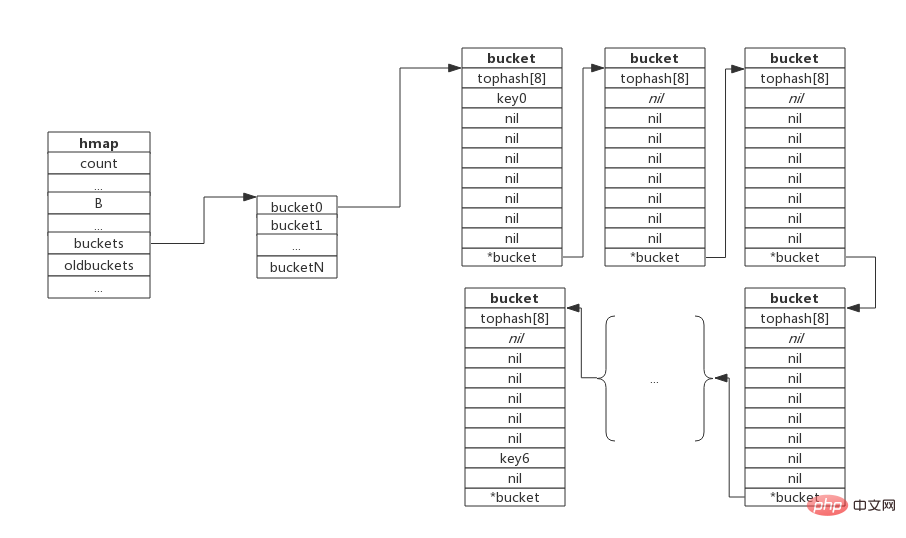
expansion is performed, that is, the number of buckets remains unchanged, and the number of overflow buckets will be reduced after reorganization, which saves space and improves access efficiency.
【Related recommendations:Go video tutorial, Programming teaching】
The above is the detailed content of What are the expansion methods of go language?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 What libraries are used for floating point number operations in Go?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 02:06 PM
What libraries are used for floating point number operations in Go?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 02:06 PM
The library used for floating-point number operation in Go language introduces how to ensure the accuracy is...
 What is the problem with Queue thread in Go's crawler Colly?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 02:09 PM
What is the problem with Queue thread in Go's crawler Colly?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 02:09 PM
Queue threading problem in Go crawler Colly explores the problem of using the Colly crawler library in Go language, developers often encounter problems with threads and request queues. �...
 In Go, why does printing strings with Println and string() functions have different effects?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 02:03 PM
In Go, why does printing strings with Println and string() functions have different effects?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 02:03 PM
The difference between string printing in Go language: The difference in the effect of using Println and string() functions is in Go...
 How to solve the user_id type conversion problem when using Redis Stream to implement message queues in Go language?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 04:54 PM
How to solve the user_id type conversion problem when using Redis Stream to implement message queues in Go language?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 04:54 PM
The problem of using RedisStream to implement message queues in Go language is using Go language and Redis...
 What should I do if the custom structure labels in GoLand are not displayed?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 05:09 PM
What should I do if the custom structure labels in GoLand are not displayed?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 05:09 PM
What should I do if the custom structure labels in GoLand are not displayed? When using GoLand for Go language development, many developers will encounter custom structure tags...
 Which libraries in Go are developed by large companies or provided by well-known open source projects?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 04:12 PM
Which libraries in Go are developed by large companies or provided by well-known open source projects?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 04:12 PM
Which libraries in Go are developed by large companies or well-known open source projects? When programming in Go, developers often encounter some common needs, ...
 Golang's Purpose: Building Efficient and Scalable Systems
Apr 09, 2025 pm 05:17 PM
Golang's Purpose: Building Efficient and Scalable Systems
Apr 09, 2025 pm 05:17 PM
Go language performs well in building efficient and scalable systems. Its advantages include: 1. High performance: compiled into machine code, fast running speed; 2. Concurrent programming: simplify multitasking through goroutines and channels; 3. Simplicity: concise syntax, reducing learning and maintenance costs; 4. Cross-platform: supports cross-platform compilation, easy deployment.
 How to ensure concurrency is safe and efficient when writing multi-process logs?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 03:51 PM
How to ensure concurrency is safe and efficient when writing multi-process logs?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 03:51 PM
Efficiently handle concurrency security issues in multi-process log writing. Multiple processes write the same log file at the same time. How to ensure concurrency is safe and efficient? This is a...






