How to pass value to vue component
Value passing method: 1. Use props to pass from parent to child; 2. Pass from child to parent, you need to customize the event, use "this.$emit('event name')" to trigger it in the child component, and Use "@event name" in the parent to listen; 3. Between brothers, use the public parent element as a bridge, combine parent and child props to pass parameters, and child and parent custom events; 4. Use routes to pass values; 5. Use $ref to pass values; 6 , use dependency injection to pass to descendants and great-grandchildren; 7. Use $attrs; 8. Use $listeners intermediate events; 9. Use $parent to pass, etc.

The operating environment of this tutorial: windows7 system, vue3 version, DELL G3 computer.
This article will talk about the 10 ways to transfer values in Vue components. There are five or six commonly used methods. Let’s start with a summary picture:
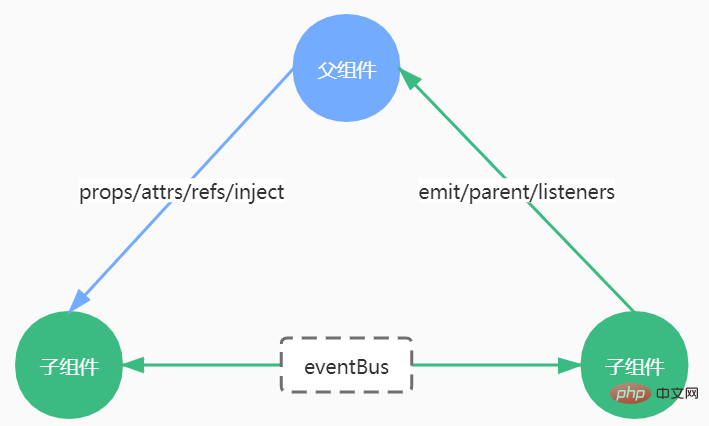
1. Pass the parent component to the child component
Define a props in the child component, that is, props:['msg'], msg can be Objects can also be basic data types
If you want to define a default value, i.e. props:{msg: {type: String, default: 'hello world'}},
If the default value is an object type :props: { msg: { type: Object, default: () => { return { name: 'dan_seek' } } }}
It should be noted that this kind of value transfer is one-way. The value of the parent component cannot be changed (except for reference types, of course); and if the value of props is modified directly, a warning will be reported.
The recommended way to write is to redefine a variable in data() (see Children.vue) and assign props to it. Of course, calculated properties will also work.
Children.vue
<template>
<section>
父组件传过来的消息是:{{myMsg}}
</section>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Children",
components: {},
props:['msg'],
data() {
return {
myMsg:this.msg
}
},
methods: {}
}
</script>Parent.vue
<template>
<div class="parent">
<Children :msg="message"></Children>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Children from '../components/Children'
export default {
name: 'Parent',
components: {
Children
},
data() {
return {
message:'hello world'
}
},
}
</script>2. Pass the child component to the parent component
You need to use custom events here, use this.$emit('myEvent') in the child component to trigger, and then use @myEvent in the parent component to listen
Children.vue
<template>
<div class="parent">
这里是计数:{{parentNum}}
<Children-Com @addNum="getNum"></Children-Com>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import ChildrenCom from '../components/Children'
export default {
name: 'Parent',
components: {
ChildrenCom
},
data() {
return {
parentNum: 0
}
},
methods:{
// childNum是由子组件传入的
getNum(childNum){
this.parentNum = childNum
}
}
}
</script>Parent.vue
<template>
<div class="parent">
这里是计数:{{parentNum}}
<Children-Com @addNum="getNum"></Children-Com>
</div></template><script>
import ChildrenCom from '../components/Children'
export default {
name: 'Parent',
components: {
ChildrenCom },
data() {
return {
parentNum: 0
}
},
methods:{
// childNum是由子组件传入的
getNum(childNum){
this.parentNum = childNum }
}
}</script>##3. Passing values between sibling components
Using custom eventsemit's triggering and monitoring capabilities define a public event bus eventBus, through which we can pass values to any component through it as an intermediate bridge. And through the use of eventBus, you can deepen your understanding of emit.
EventBus.jsimport Vue from 'vue' export default new Vue()
<template>
<section>
<div @click="pushMsg">push message</div>
<br>
</section>
</template>
<script>
import eventBus from './EventBus'
export default {
name: "Children1",
components: {},
data() {
return {
childNum:0
}
},
methods: {
pushMsg(){
// 通过事件总线发送消息
eventBus.$emit('pushMsg',this.childNum++)
}
}
}
</script><template>
<section>
children1传过来的消息:{{msg}}
</section>
</template>
<script>
import eventBus from './EventBus'
export default {
name: "Children2",
components: {},
data() {
return {
msg: ''
}
},
mounted() {
// 通过事件总线监听消息
eventBus.$on('pushMsg', (children1Msg) => {
this.msg = children1Msg
})
}
}
</script><template>
<div class="parent">
<Children1></Children1>
<Children2></Children2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Children1 from '../components/Children1'
import Children2 from '../components/Children2'
export default {
name: 'Parent',
components: {
Children1,
Children2
},
data() {
return {
}
},
methods:{
}
}
</script>4. Passing values between routes
i. Use question marks to pass values
When page A jumps to page B, use this.$router.push('/B?name =danseek')Page B can use this.$route.query.name to get the value passed from page APlease note the difference between router and routeii. Use colons to pass values
Configure the following route:{
path: '/b/:name',
name: 'b',
component: () => import( '../views/B.vue')
},iii. Use the parent-child component to pass the value
Since router-view itself is also a component, we also You can use the parent-child component value transfer method to pass values, and then add props to the corresponding sub-page. Because the route is not refreshed after the type is updated, you cannot directly obtain the latest type value directly in the mounted hook of the sub-page, but use watch.<router-view :type="type"></router-view>
// 子页面
......
props: ['type']
......
watch: {
type(){
// console.log("在这个方法可以时刻获取最新的数据:type=",this.type)
},
},5. Use $ref to pass value
Use the ability of $ref to define an ID for the child component. The parent component can directly access the child component through this ID. Methods and propertiesFirst define a child component Children.vue<template>
<section>
传过来的消息:{{msg}}
</section>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Children",
components: {},
data() {
return {
msg: '',
desc:'The use of ref'
}
},
methods:{
// 父组件可以调用这个方法传入msg
updateMsg(msg){
this.msg = msg
}
},
}
</script><template>
<div class="parent">
<!-- 给子组件设置一个ID ref="children" -->
<Children ref="children"></Children>
<div @click="pushMsg">push message</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Children from '../components/Children'
export default {
name: 'parent',
components: {
Children,
},
methods:{
pushMsg(){
// 通过这个ID可以访问子组件的方法
this.$refs.children.updateMsg('Have you received the clothes?')
// 也可以访问子组件的属性
console.log('children props:',this.$refs.children.desc)
}
},
}
</script>6. Use dependency injection to pass it on to descendants and great-grandchildren
Assume that the parent component has a method getName() and needs to provide it to all descendantsprovide: function () {
return {
getName: this.getName()
}
}Then in any descendant component, we can use
inject to inject the parent component into the current instance Data/method: <div class="code" style="position:relative; padding:0px; margin:0px;"><pre class='brush:php;toolbar:false;'>inject: [&#39;getName&#39;]</pre><div class="contentsignin">Copy after login</div></div>Parent.vue
<template>
<div class="parent">
<Children></Children>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Children from '../components/Children'
export default {
name: 'Parent',
components: {
Children,
},
data() {
return {
name:'dan_seek'
}
},
provide: function () {
return {
getName: this.name
}
},
}
</script>Children.vue
父组件传入的值:{{getName}}
<script>
export default {
name: "Children",
components: {},
data() {
return {
}
},
inject: [&#39;getName&#39;],
}
</script>##7, ancestral grandson $attrsNormally, it is necessary to use the father's props as an intermediate transition, but in this way, the father component will have some attributes that have nothing to do with the parent component's business, and the coupling degree is high. It can be simplified with the help of $attrs, and ancestors and grandchildren No modification is required
GrandParent.vue<template>
<section>
<parent name="grandParent" sex="男" age="88" hobby="code" @sayKnow="sayKnow"></parent>
</section>
</template>
<script>
import Parent from './Parent'
export default {
name: "GrandParent",
components: {
Parent
},
data() {
return {}
},
methods: {
sayKnow(val){
console.log(val)
}
},
mounted() {
}
}
</script><template>
<section>
<p>父组件收到</p>
<p>祖父的名字:{{name}}</p>
<children v-bind="$attrs" v-on="$listeners"></children>
</section>
</template>
<script>
import Children from './Children'
export default {
name: "Parent",
components: {
Children
},
// 父组件接收了name,所以name值是不会传到子组件的
props:['name'],
data() {
return {}
},
methods: {},
mounted() {
}
}
</script><template>
<section>
<p>子组件收到</p>
<p>祖父的名字:{{name}}</p>
<p>祖父的性别:{{sex}}</p>
<p>祖父的年龄:{{age}}</p>
<p>祖父的爱好:{{hobby}}</p>
<button @click="sayKnow">我知道啦</button>
</section>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Children",
components: {},
// 由于父组件已经接收了name属性,所以name不会传到子组件了
props:['sex','age','hobby','name'],
data() {
return {}
},
methods: {
sayKnow(){
this.$emit('sayKnow','我知道啦')
}
},
mounted() {
}
}
</script>父组件收到
祖父的名字:grandParent
子组件收到
祖父的名字:
祖父的性别:男
祖父的年龄:88
祖父的爱好:code
Copy after login
父组件收到 祖父的名字:grandParent 子组件收到 祖父的名字: 祖父的性别:男 祖父的年龄:88 祖父的爱好:code
8. Sun Chuanzu With the help of $listeners intermediate events, Sun can conveniently notify ancestors. For code examples, see 7
9, $parentYou can get the parent component instance through parent, and then you can access the properties and methods of the parent component through this instance. It also has a brother root, You can get the root component instance.
语法:
// 获父组件的数据 this.$parent.foo // 写入父组件的数据 this.$parent.foo = 2 // 访问父组件的计算属性 this.$parent.bar // 调用父组件的方法 this.$parent.baz()
于是,在子组件传给父组件例子中,可以使用this.$parent.getNum(100)传值给父组件。
10、sessionStorage传值
sessionStorage 是浏览器的全局对象,存在它里面的数据会在页面关闭时清除 。运用这个特性,我们可以在所有页面共享一份数据。
语法:
// 保存数据到 sessionStorage sessionStorage.setItem('key', 'value'); // 从 sessionStorage 获取数据 let data = sessionStorage.getItem('key'); // 从 sessionStorage 删除保存的数据 sessionStorage.removeItem('key'); // 从 sessionStorage 删除所有保存的数据 sessionStorage.clear();
注意:里面存的是键值对,只能是字符串类型,如果要存对象的话,需要使用 let objStr = JSON.stringify(obj) 转成字符串然后再存储(使用的时候 let obj = JSON.parse(objStr) 解析为对象)。
这样存对象是不是很麻烦呢,推荐一个库 good-storage ,它封装了sessionStorage ,可以直接用它的API存对象
// localStorage storage.set(key,val) storage.get(key, def) // sessionStorage storage.session.set(key, val) storage.session.get(key, val)
更多请移步:https://github.com/ustbhuangyi/storage#readme
The above is the detailed content of How to pass value to vue component. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
Using Bootstrap in Vue.js is divided into five steps: Install Bootstrap. Import Bootstrap in main.js. Use the Bootstrap component directly in the template. Optional: Custom style. Optional: Use plug-ins.
 How to add functions to buttons for vue
Apr 08, 2025 am 08:51 AM
How to add functions to buttons for vue
Apr 08, 2025 am 08:51 AM
You can add a function to the Vue button by binding the button in the HTML template to a method. Define the method and write function logic in the Vue instance.
 How to use watch in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
How to use watch in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
The watch option in Vue.js allows developers to listen for changes in specific data. When the data changes, watch triggers a callback function to perform update views or other tasks. Its configuration options include immediate, which specifies whether to execute a callback immediately, and deep, which specifies whether to recursively listen to changes to objects or arrays.
 What does vue multi-page development mean?
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
What does vue multi-page development mean?
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Vue multi-page development is a way to build applications using the Vue.js framework, where the application is divided into separate pages: Code Maintenance: Splitting the application into multiple pages can make the code easier to manage and maintain. Modularity: Each page can be used as a separate module for easy reuse and replacement. Simple routing: Navigation between pages can be managed through simple routing configuration. SEO Optimization: Each page has its own URL, which helps SEO.
 How to reference js file with vue.js
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
How to reference js file with vue.js
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
There are three ways to refer to JS files in Vue.js: directly specify the path using the <script> tag;; dynamic import using the mounted() lifecycle hook; and importing through the Vuex state management library.
 How to return to previous page by vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:30 PM
How to return to previous page by vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:30 PM
Vue.js has four methods to return to the previous page: $router.go(-1)$router.back() uses <router-link to="/" component window.history.back(), and the method selection depends on the scene.
 How to use vue traversal
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:48 PM
How to use vue traversal
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:48 PM
There are three common methods for Vue.js to traverse arrays and objects: the v-for directive is used to traverse each element and render templates; the v-bind directive can be used with v-for to dynamically set attribute values for each element; and the .map method can convert array elements into new arrays.
 How to jump to the div of vue
Apr 08, 2025 am 09:18 AM
How to jump to the div of vue
Apr 08, 2025 am 09:18 AM
There are two ways to jump div elements in Vue: use Vue Router and add router-link component. Add the @click event listener and call this.$router.push() method to jump.






