what is nfs
nfs refers to the network file system, which is one of the file systems supported by FreeBSD. It allows computers on the network to share resources through the TCP/IP network. NFS is an application based on the UDP/IP protocol. Its implementation mainly uses the remote procedure call RPC mechanism. RPC provides a set of operations for accessing remote files that are independent of the machine, operating system, and low-level transmission protocol.

#The operating environment of this tutorial: linux7.3 system, Dell G3 computer.
1. Introduction to nfs
Network File System, English Network File System (NFS), is a UNIX presentation layer protocol developed by SUN. Enables users to access files elsewhere on the network just like using their own computer.
NFS is an application based on the UDP/IP protocol. Its implementation mainly uses the remote procedure call RPC mechanism. RPC provides a set of operations for accessing remote files that are independent of the machine, operating system, and low-layer transmission protocol. RPC uses XDR support. XDR is a machine-independent data description encoding protocol. It encodes and decodes data transmitted over the Internet in a format independent of any machine architecture, and supports the transmission of data between heterogeneous systems.
1.1 nfs features
- NFS (Network File System) is a network file system. It is one of the file systems supported by FreeBSD. It allows Resources are shared between computers through the TCP/IP network
- In NFS applications, the local NFS client application can transparently read and write files located on the remote NFS server, just like accessing local files
- nfs is suitable for file sharing between Linux and Unix, but cannot realize file sharing between Linux and Windows.
- nfs is a protocol running at the application layer, and it listens to 2049/tcp and 2049
- nfs service on /udp socket can only be authenticated based on IP
1.2 Application scenarios of nfs
nfs has many practical applications Application scenarios, the following are some common scenarios:
- Multiple machines share a CDROM or other device. This is cheaper and more convenient for installing software on multiple machines
- In large networks, it may be convenient to configure a central NFS server to house all users' home directories. These directories can be exported to the network so that users can always get the same home directory no matter which workstation they log in on.
- Different clients can watch movie and TV files on NFS, saving local space
- The work data completed on the client can be backed up and saved to the user's own path on the NFS server
1.3 nfs system composition
nfs system must have at least Two main parts:
- One nfs server
- Several clients
The architecture diagram of the nfs system is as follows:
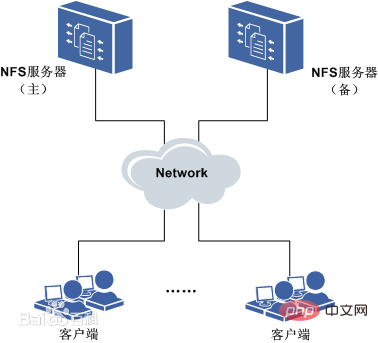
Clients remotely access data stored on the NFS server through the TCP/IP network
Before the NFS server is officially enabled, some NFS parameters need to be configured based on the actual environment and needs
2. nfs working mechanism
nfs is based on rpc to realize network file system sharing. So let’s talk about rpc first.
2.1 RPC
RPC (Remote Procedure Call Protocol), a remote procedure call protocol, is a method of requesting services from a remote computer program through the network without Understand the protocols of underlying network technologies.
The RPC protocol assumes the existence of some transport protocol, such as TCP or UDP, to carry information data between communicating programs. In the OSI network communication model, RPC spans the transport layer and application layer.
RPC adopts client/server mode. The requester is a client, and the service provider is a server.
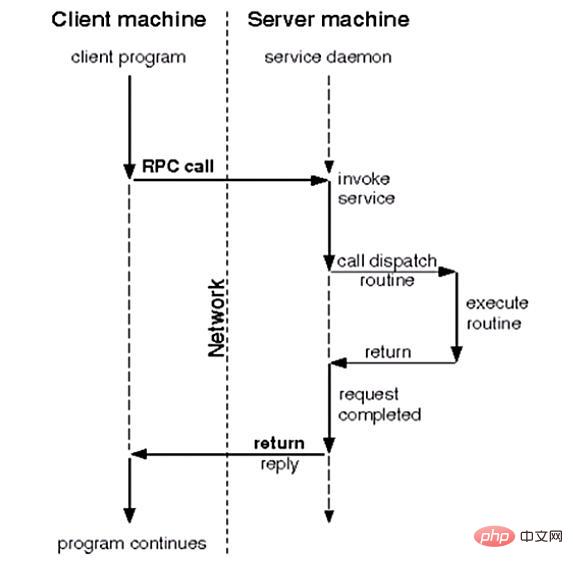
The working mechanism of rpc is shown in the figure above. Let’s describe it below:
- The client program initiates an RPC system call and sends it to another host (server) based on the TCP protocol.
- The server listens on a certain socket. When receiving the client's system After calling the request, execute the received request and the parameters passed through the local system call, and return the result to the local service process
- After receiving the returned execution result, the service process on the server side will It is encapsulated into a response message and then returned to the client through the rpc protocol
- The client calls the process to receive the reply information, obtains the process result, and then calls the execution to continue
2.2 nfs working mechanism
The NFS server runs four processes:
nfsd
-
mountd
idmapd
portmapper
idmapd
Realize centralized mapping of user accounts and map all accounts to NFSNOBODY, but when accessing, they can access as a local user
mountd
Used to verify whether the client is in the list of clients allowed to access this NFS file system. If so, access is allowed (issue a token and hold the token to find nfsd), otherwise Access denied
The service port of mountd is random, and the random port number is provided by the rpc service (portmapper)
nfsd
nfs daemon, listening on 2049/tcp and 2049/udp ports
is not responsible for file storage (the local kernel of the NFS server is responsible for scheduling storage), Used to understand the rpc request initiated by the client, transfer it to the local kernel, and then store it on the specified file system
portmapper
NFS server's rpc service, which listens on 111/TCP and 111/UDP sockets, is used to manage remote procedure calls (RPC)
The following is an example to illustrate the simple work of NFS Process:
Requirements: View the information of the file file. This file is stored on the remote NFS server host (mounted in the local directory /shared/nfs)
- The client initiates a command to view file information (ls file) to the kernel. The kernel learns through the NFS module that this file is not a file in the local file system. It is a file on the remote NFS host
- The kernel of the client host encapsulates the instruction (system call) to view the file information into an rpc request through the RPC protocol and sends it to the NFS server host through TCP port 111 portmapper
- The portmapper (RPC service process) of the NFS server host tells the client that the mountd service of the NFS server is on a certain port. You go to it to verify
Because mountd is on When providing services, a port number must be registered with portmapper, so portmapper knows which port it is working on.
- After the client learns the port number of the server's mountd process, it uses the known server mountd Port number request verification
- After receiving the verification request, mountd verifies whether the client that initiated the request is in the list of clients allowed to access this NFS file system. If so, access is allowed (issue a token, hold the token to Find nfsd), otherwise access is denied
- After passing the verification, the client uses the token issued by mountd to find the nfsd process of the server and requests to view a certain file
- The nfsd process of the server initiates a local system call. Request to the kernel to view the information of the file that the client wants to view
- The kernel of the server executes the system call requested by nfsd and returns the result to the nfsd service
- After the nfsd process receives the result returned by the kernel Encapsulate it into an rpc request message and return it to the client through the tcp/ip protocol
For more related knowledge, please visit the FAQ column!
The above is the detailed content of what is nfs. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 What is linux NFS and how to use it
May 12, 2023 pm 04:13 PM
What is linux NFS and how to use it
May 12, 2023 pm 04:13 PM
nfs is the abbreviation of network file system, that is, network file system. The network file system is one of the file systems supported by freebsd, also known as nfs. nfs allows a system to share directories and files with others on the network. By using NFS, users and programs can access files on remote systems as if they were local files. nfs is based on the rpc protocol. nfs itself only plays a role in sharing, while connection and data transmission with the client are the functions of the rpc protocol. nfs is mainly controlled through two daemons: 1.rpc.nfsd------- It is used to control whether clients can connect to, nfsserver2.rpc.mount
 What is the method for NFS installation and configuration under Linux?
May 19, 2023 pm 07:46 PM
What is the method for NFS installation and configuration under Linux?
May 19, 2023 pm 07:46 PM
1. Server-side software: Install nfs-utils and portmap (rpcbind) nfs-utils: Provide rpc.nfsd and rpc.mountd, two nfsdaemons packages portmap: nfs can actually be regarded as an rpcserverprogram, and to start an rpcserverprogram , we must do a good job corresponding to the port, and such tasks are completed by portmap. In layman's terms, portmap is used for port mapping. daemonspc.nfsd that nfs needs to start: Mainly complex login permission detection, etc. must be por
 How to mount settings through nfs network file system in linux
May 15, 2023 pm 05:25 PM
How to mount settings through nfs network file system in linux
May 15, 2023 pm 05:25 PM
Introduction to nfs nfs is the abbreviation of network file system, that is, network file system. Network file system is one of the file systems supported by freebsd, also known as nfs. nfs allows a system to share directories and files with others on the network. By using NFS, users and programs can access files on remote systems as if they were local files. The most obvious benefits of nfs: 1. Local workstations use less disk space because normal data can be stored on one machine and accessible through the network. 2. Users do not need to have a home directory in every machine on the network. The home directory can be placed on an nfs server and available everywhere on the network.
 Detailed explanation of linux nfs shared storage service.
Feb 19, 2024 pm 06:00 PM
Detailed explanation of linux nfs shared storage service.
Feb 19, 2024 pm 06:00 PM
LinuxNFS (NetworkFileSystem) is a protocol and service for sharing file systems on a network. The client computer can access files and directories on the remote server through the network to implement operations similar to local files. Client-server model: LinuxNFS adopts the client-server model. The server is the provider of the file system, which is responsible for managing files and directories and responding to client requests. Clients are computers using the NFS protocol that connect to the server over the network and request access to files and directories. File sharing: Through LinuxNFS, the file system on the server can be shared with multiple clients. The client can read, write, and
 what is nfs
Nov 29, 2022 am 11:16 AM
what is nfs
Nov 29, 2022 am 11:16 AM
nfs refers to the network file system, which is one of the file systems supported by FreeBSD. It allows computers on the network to share resources through the TCP/IP network. NFS is an application based on the UDP/IP protocol. Its implementation mainly uses the remote procedure call RPC mechanism. RPC provides a set of operations for accessing remote files that are independent of the machine, operating system, and low-level transmission protocol.
 How to build NFS server with nginx
May 23, 2023 pm 12:55 PM
How to build NFS server with nginx
May 23, 2023 pm 12:55 PM
Introduction: What is an nfs server? NFS (Network File System) is a network file system. Its biggest function is to allow different machines and different operating systems to share files with each other through the network. Users can access files elsewhere on the network just like Same as using your own computer. Why do you need the nfs server to get data from the same place to ensure the consistency of website data? No matter which back-end server the load balancer distributes the request to, the content seen by the client is consistent. Whether nfs server is the best solution? No, nfs is a relatively cheap solution 1. Generally, companies will not use it. The performance is not particularly high. It is recommended to use a dedicated storage server. Advantages and Disadvantages of nfs
 How to set up highly available network storage (such as NFS) on Linux
Jul 06, 2023 am 09:33 AM
How to set up highly available network storage (such as NFS) on Linux
Jul 06, 2023 am 09:33 AM
How to set up highly available network storage (such as NFS) on Linux Introduction: Network File System (NFS) is a commonly used distributed file system that allows files to be shared between different computers. In a Linux environment, we can ensure system stability and reliability by setting up highly available network storage. This article will explain how to set up highly available NFS on Linux and provide some code examples. Step 1: Install NFS First, we need to install the NFS package on all nodes. In most Lin
 Completely delete scanned harmful programs with one command
Feb 19, 2024 pm 01:57 PM
Completely delete scanned harmful programs with one command
Feb 19, 2024 pm 01:57 PM
Completely delete scanned harmful programs with one command Author: Tian Yi (formyz) An NFS server is shared by multiple Web projects. These directories include PHP programs, pictures, HTML pages, documents and attachments uploaded by users, etc. Because some web frameworks are old and do not perform strict security checks on uploaded files, although this NFS server is located in a protected internal network, a large number of malicious files are still uploaded by people with ulterior motives. The programmer was strongly requested to update the program (Discuz), and the reply was that the update was too difficult to handle on the program. From the system management level, the temporary measure is just to install the shadu software, scan the shared directory, and then delete these harmful files.






