Let's talk about the three caching issues of Redis
This article brings you relevant knowledge about Redis. It mainly introduces three types of cache problems, namely cache penetration, cache breakdown and cache avalanche. I hope it will be helpful to everyone. help.

Recommended learning: Redis learning tutorial
1. Application of Redis cache
In our actual business scenarios, Redis is generally used in conjunction with other databases to reduce the pressure on the back-end database , such as with the relational database MySQL With the use of.
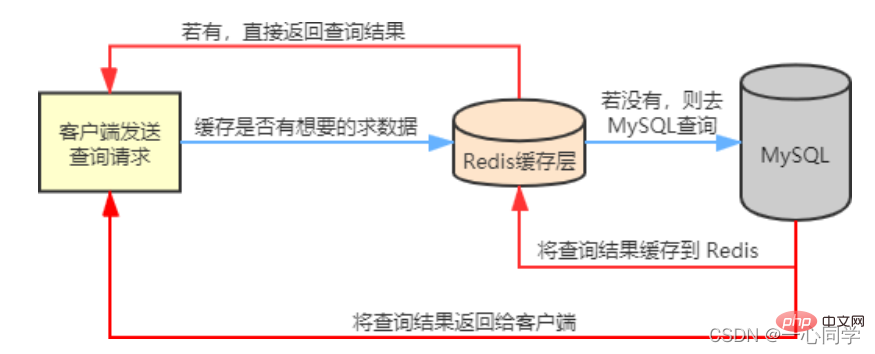
Redis will cache frequently queried data in MySQL, such as Hot data, so that when users come to access, they don't need to query in MySQL, but directly obtain the cached data in Redis, thereby reducing the reading pressure on the back-end database.
If the data queried by the user is not available in Redis, the user's query request will be transferred to the MySQL database. When MySQL returns the data to the client, it will also cache the data in in Redis, so that when users read again, they can get data directly from Redis. The flow chart is as follows:
二, Cache penetration2.1 IntroductionOf course, we are not always able to use Redis as a cache database. Smooth sailing, we will encounter common three cache problems:
- ##Cache penetration
- Cache breakdown
- Cache avalanche
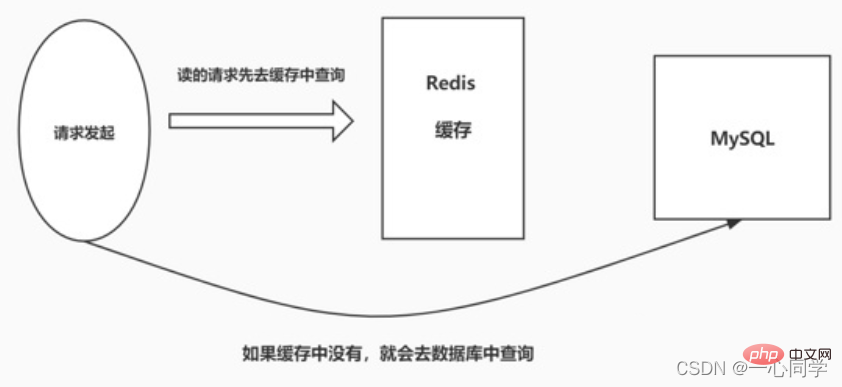
Cache penetration means thatwhen the user queries a certain data, it does not exist in Redis This data means that the cache does not hit. At this time, the query request will be transferred to the persistence layer database MySQL. It is found that the data does not exist in MySQL. MySQL can only return an empty object, which means that the query failed. If there are many such requests, or users use such requests to conduct malicious attacks, it will put a lot of pressure on the MySQL database and even collapse. This phenomenon is called cache penetration.
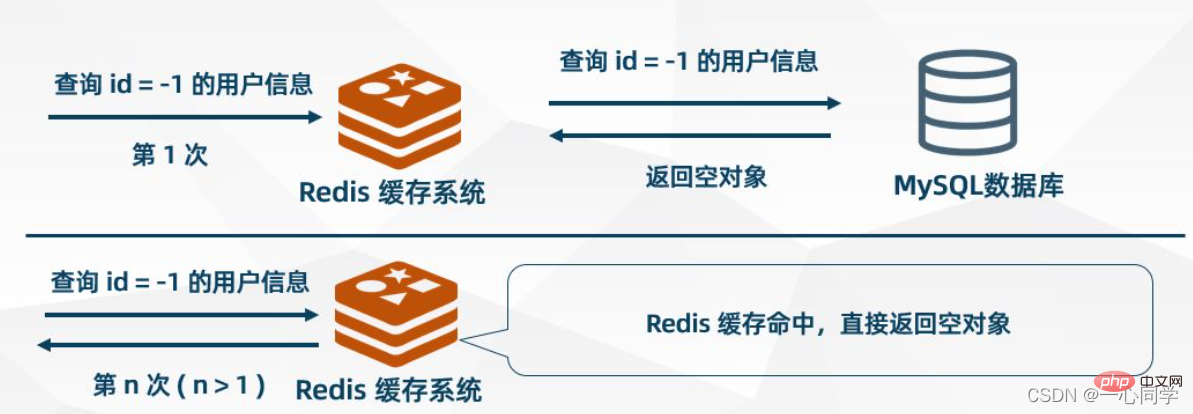
Cache empty objects
When MySQL returns an empty object, Redis caches the object and sets an expiration time for it. When the user initiates the same request again, an empty object will be obtained from the cache. The user's request is blocked at the cache layer, thereby protecting the back-end database, but There are also some problems with this approach. Although the request cannot enter MSQL, this strategy will occupy Redis cache space.
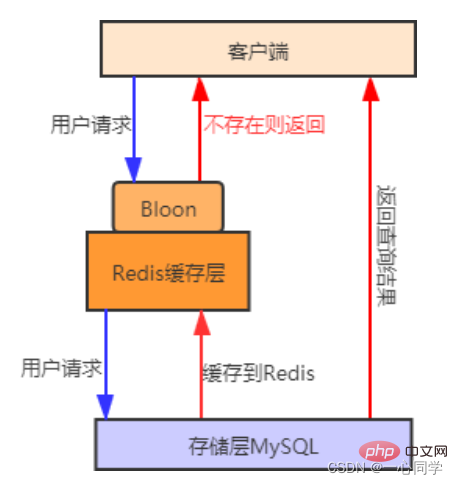
Bloom filter
First put the ones that the user may access All keys of hotspot data are stored in the Bloom filter (also called cache preheating) . When a user requests it, it will first go through the Bloom filter, Bloom filter It will be judged whether the requested key exists. If it does not exist, the request will be rejected directly. Otherwise, the query will continue to be executed. First go to the cache to query. If the cache does not exist, then go to the database to query. Compared with the first method, using the Bloom filter method is more efficient and practical. The process diagram is as follows:
##Cache preheating: refers to cache preheating in advance when the system starts Relevant data is loaded into the Redis cache system. This avoids loading data when the user requests it.
2.3 Comparison of solutions
Both solutions can solve the problem of cache penetration, but their usage scenarios are different:
Cache empty objects: Suitable for scenarios where the number of keys for empty data is limited and the probability of repeated key requests is high.
Bloom filter: Suitable for scenarios where the keys of empty data are different and the probability of repeated key requests is low.
3. Cache breakdown
3.1 Introduction
Cache breakdown refers toThe data queried by the user does not exist in the cache, but does exist in the backend database. The reason for this phenomenon is that is usually caused by the expiration of the key in the cache. For example, a hot data key receives a large number of concurrent accesses all the time. If the key suddenly fails at a certain moment, a large number of concurrent requests will enter the back-end database, causing its pressure to increase instantly. This phenomenon is called cache breakdown.
3.2 Solution
Change the expiration time
Set hotspot data never Expired.
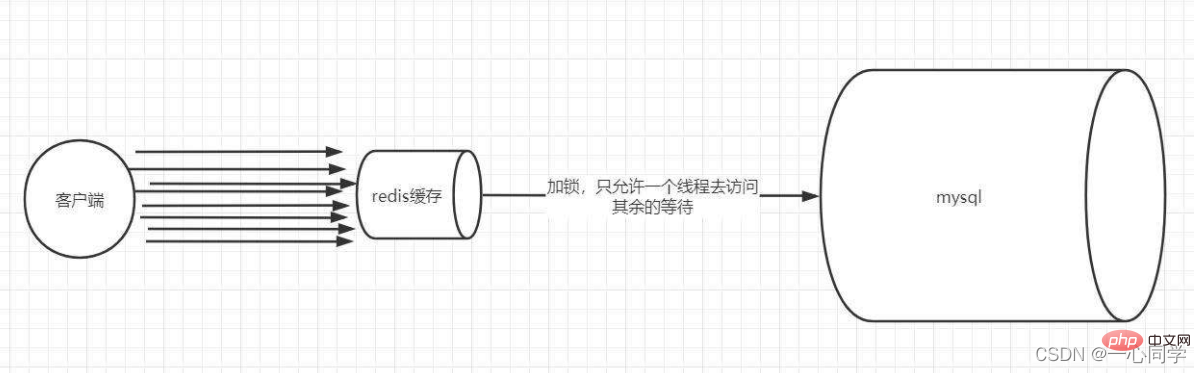
Distributed Lock
Adopt the Distributed Lock method to redesign the cache The usage method is as follows:
- Lock: When we query data by key, we first query the cache. If If not, locking is performed through distributed locks. The first process to acquire the lock enters the back-end database to query and buffers the query results to Redis.
- Unlocking: When other processes find that the lock is occupied by a process, they enter the waiting state. After unlocking, other processes access the cached key in turn. .
3.3 Comparison of solutions
Never expires: This solution has no Setting the real expiration time actually eliminates the series of hazards caused by hot keys, but there will be data inconsistencies and the code complexity will increase.
Mutex lock: This solution is relatively simple, but there are certain hidden dangers. If there is a problem with the cache building process or it takes a long time, there may be a deadlock. There are risks of locks and thread pool blocking, but this method can better reduce the back-end storage load and achieve better consistency.
4. Cache avalanche
4.1 Introduction
##Cache avalanche refers to large batches in the cache keys expire at the same time, and the amount of data access is very large at this time, causing a sudden increase in pressure on the back-end database, and even crashing. This phenomenon is called cache avalanche. It is different from cache breakdown. Cache breakdown occurs when a certain hot key suddenly expires when the amount of concurrency is particularly large, while cache avalanche occurs when a large number of keys expire at the same time, so they are not of the same order of magnitude at all.
4.2 Solution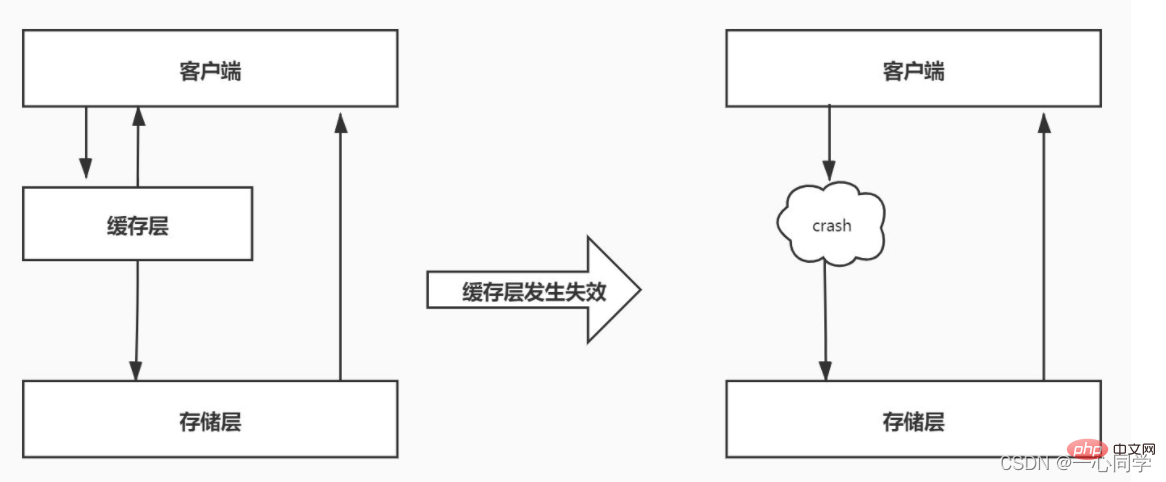
Handling expiration
Cache avalanche and cache breakdown are similar, so you can also use the
hotspot data never expiresmethod to reduce the simultaneous expiration of a large number of keys. Furthermore, set a random expiration time for the key to avoid centralized expiration of keys.
redis high availability
One Redis may hang due to an avalanche, so you can add a few more Redis,
Build a cluster, if one fails, the others can continue to work. Recommended learning:
Redis learning tutorial
The above is the detailed content of Let's talk about the three caching issues of Redis. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear Redis data: Use the FLUSHALL command to clear all key values. Use the FLUSHDB command to clear the key value of the currently selected database. Use SELECT to switch databases, and then use FLUSHDB to clear multiple databases. Use the DEL command to delete a specific key. Use the redis-cli tool to clear the data.
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
Using Redis to lock operations requires obtaining the lock through the SETNX command, and then using the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time. The specific steps are: (1) Use the SETNX command to try to set a key-value pair; (2) Use the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time for the lock; (3) Use the DEL command to delete the lock when the lock is no longer needed.
 How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
Using the Redis directive requires the following steps: Open the Redis client. Enter the command (verb key value). Provides the required parameters (varies from instruction to instruction). Press Enter to execute the command. Redis returns a response indicating the result of the operation (usually OK or -ERR).
 How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
How to read the source code of redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
The best way to understand Redis source code is to go step by step: get familiar with the basics of Redis. Select a specific module or function as the starting point. Start with the entry point of the module or function and view the code line by line. View the code through the function call chain. Be familiar with the underlying data structures used by Redis. Identify the algorithm used by Redis.
 How to configure Lua script execution time in centos redis
Apr 14, 2025 pm 02:12 PM
How to configure Lua script execution time in centos redis
Apr 14, 2025 pm 02:12 PM
On CentOS systems, you can limit the execution time of Lua scripts by modifying Redis configuration files or using Redis commands to prevent malicious scripts from consuming too much resources. Method 1: Modify the Redis configuration file and locate the Redis configuration file: The Redis configuration file is usually located in /etc/redis/redis.conf. Edit configuration file: Open the configuration file using a text editor (such as vi or nano): sudovi/etc/redis/redis.conf Set the Lua script execution time limit: Add or modify the following lines in the configuration file to set the maximum execution time of the Lua script (unit: milliseconds)
 How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
Use the Redis command line tool (redis-cli) to manage and operate Redis through the following steps: Connect to the server, specify the address and port. Send commands to the server using the command name and parameters. Use the HELP command to view help information for a specific command. Use the QUIT command to exit the command line tool.






