 Operation and Maintenance
Operation and Maintenance
 Linux Operation and Maintenance
Linux Operation and Maintenance
 What does linux operation and maintenance do?
What does linux operation and maintenance do?
What does linux operation and maintenance do?
Linux operation and maintenance work: 1. Service monitoring; 2. Service fault management; 3. Service capacity management; 4. Service performance optimization; 5. Service global traffic scheduling; 6. Service task scheduling; 7 , Service security guarantee; 8. Automatic service release and deployment; 9. Service cluster management; 10. Database management, etc.

#The operating environment of this tutorial: linux5.9.8 system, Dell G3 computer.
The main work content of Linux operation and maintenance
Linux operation and maintenance is the position with the largest number of people and the highest salary among many jobs. The focus of this article is Introducing the career of Linux operation and maintenance, this article is jointly written by Marco Education, an organization specializing in Linux operation and maintenance learning and career development, and enthusiasts.
Internet Linux operation and maintenance work is service-centered and takes stability, security, and efficiency as the three basic points to ensure that the company's Internet business can provide users with high-quality services 7×24 hours. Operations and maintenance responsibilities cover the product life cycle from design to release, operation and maintenance, changes and upgrades, and offline.
The responsibilities of operation and maintenance are important and extensive throughout the entire life cycle of a product, but the responsibilities of operation and maintenance engineers are not limited to this part of the work. They also need to summarize the problems encountered in the work and extract relevant technical directions, Develop related tools and platforms to support/optimize business development and improve operation and maintenance efficiency. Related technical work mainly includes:
Service monitoring technology: including the development and application of monitoring platforms, Guarantee of accuracy, real-time and comprehensiveness of service monitoring
Service fault management: including service fault plan design, automated execution of the plan, fault summary and feedback to product/system Optimize at the design level to improve product stability
Service capacity management: measuring service capacity, planning service room construction, expansion, migration, etc.
Service performance optimization: improve service performance and response speed from all directions, including network optimization, operating system optimization, application optimization, client optimization, etc., and improve user experience
Service global traffic scheduling: The traffic accessing the service is allocated to each computer room according to the capacity and service status.
Service task scheduling: The scheduling of various scheduled/non-scheduled tasks of the service Trigger and status monitoring
Service security: including service access security, attack prevention, permission control, etc.
Data transmission technology: including p2p R&D and application of various transmission technologies, as well as solutions to problems such as long-distance big data transmission
Service automatic release and deployment: development of deployment platforms/tools, and use of platforms/tools, Achieve safe and efficient service release
Service cluster management: including service server management, large-scale cluster management, etc.
Service cost optimization : Reduce the resources used for service operation as much as possible and reduce service operation costs
Database Management (DBA): Make database services more stable and more efficient by designing, developing and managing high-performance database clusters Efficient and easier to manage.
Platform development: development and management of platforms such as docker, and service access technology
Development optimization and development of distributed storage platforms Access
, etc., any work related to service quality, efficiency, cost, security, etc., and the technologies, components, tools, and platforms involved are all operated and maintained. within the category. Doing a good job in each technical direction and completing the corresponding component, tool, and platform research and development can play a positive role in fulfilling operation and maintenance responsibilities and exert a key influence on the development of the business.
Linux operation and maintenance work classification
Operation and maintenance work has many directions. With the continuous development of business scale, the more mature Internet companies , the operation and maintenance positions will be divided into more details. At present, many large Internet companies only have system operation and maintenance in their early stages. As the requirements for scale and service quality increase, work has gradually been subdivided. Under normal circumstances, the work classification (see Figure 1-1) and responsibilities of the operation and maintenance team are as follows.
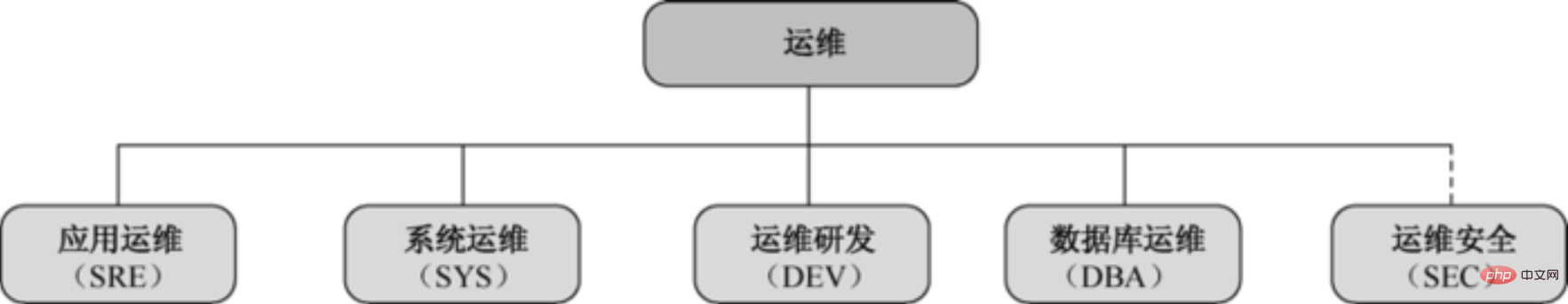
2.1-Application Operation and Maintenance (SRE): Application Operation and Maintenance is responsible for online service changes, service status monitoring, service disaster recovery and data backup, etc., and performs maintenance on services. Routine troubleshooting, emergency fault handling, etc. The job responsibilities are as follows: design review, service management, resource management, routine inspections, plan management, and data backup.
2.2-System Operation and Maintenance (SYS): Responsible for the construction of IDC, network, CDN and basic services (LVS, NTP, DNS); responsible for asset management, server selection, delivery and maintenance. The job responsibilities are as follows: IDC data center construction, network construction, LVS load balancing and SNAT construction, CDN planning and construction, server selection, delivery and maintenance, kernel selection and OS related maintenance work, asset management, and basic service construction.
2.3-Database Operation and Maintenance (DBA): Database operation and maintenance is responsible for data storage solution design, database table design, index design and SQL optimization, and changes, monitoring, backup, high-availability design and other work on the database. Detailed work content As follows: design review, capacity planning, data backup and disaster recovery, database monitoring, database security, database high availability and performance optimization, automated system construction, operation and maintenance research and development, operation and maintenance platform, monitoring system, and automated deployment system.
2.4-Operation and Maintenance Security (SEC): Operation and maintenance security is responsible for the security reinforcement of networks, systems and businesses, etc., conducts regular security scans, penetration tests, develops security tools and systems, and responds to security incidents. Processing, the work content is as follows: safety system establishment, safety training, risk assessment, safety construction, safety compliance, and emergency response.
Linux operation and maintenance daily use software and skills
The operation and maintenance platforms and tools used by operation and maintenance engineers include:
Web server: apache, tomcat, nginx, lighttpd
Monitoring: nagios, ganglia, cacti, zabbix
Automatic Deployment: ansible, sshpt, salt
Configuration management: puppet, cfengine
Load balancing: lvs, haproxy, nginx
Transmission tools: scribe, flume
Backup tools: rsync, wget
Database: mysql, oracle, sqlserver
Distributed platform: hdfs, mapreduce, spark, storm, hive
Distributed database: hbase, cassandra, redis, MongoDB
Containers: lxc, docker
Virtualization: openstack, xen, kvm
Security: kerberos , selinux, acl, iptables
Problem tracing: netstat, top, tcpdump, last
Operation and maintenance is based on technology and is guaranteed by technology Products provide higher quality services. The responsibilities of operation and maintenance work and their position in the business determine that operation and maintenance engineers need to have more extensive knowledge and in-depth technical capabilities:
Solid basic computer knowledge, including computer system architecture , operating system, network technology, etc.;
General application requires understanding of operating system, network, security, storage, CDN, DB, etc., and knowing their related principles;
Programming ability, ranging from the development of small operation and maintenance tools to the development of large-scale operation and maintenance systems/platforms, requires good programming ability;
Data analysis ability: Able to organize and analyze various data of system operation to identify problems and find solutions;
Rich system knowledge, including system tools, typical system architecture, common platform selection, etc. ;
The ability to comprehensively utilize tools and platforms;
Related recommendations: "Linux Video Tutorial"
The above is the detailed content of What does linux operation and maintenance do?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 What computer configuration is required for vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:48 PM
What computer configuration is required for vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:48 PM
VS Code system requirements: Operating system: Windows 10 and above, macOS 10.12 and above, Linux distribution processor: minimum 1.6 GHz, recommended 2.0 GHz and above memory: minimum 512 MB, recommended 4 GB and above storage space: minimum 250 MB, recommended 1 GB and above other requirements: stable network connection, Xorg/Wayland (Linux)
 Linux Architecture: Unveiling the 5 Basic Components
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Linux Architecture: Unveiling the 5 Basic Components
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:04 AM
The five basic components of the Linux system are: 1. Kernel, 2. System library, 3. System utilities, 4. Graphical user interface, 5. Applications. The kernel manages hardware resources, the system library provides precompiled functions, system utilities are used for system management, the GUI provides visual interaction, and applications use these components to implement functions.
 How to run java code in notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:39 PM
How to run java code in notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:39 PM
Although Notepad cannot run Java code directly, it can be achieved by using other tools: using the command line compiler (javac) to generate a bytecode file (filename.class). Use the Java interpreter (java) to interpret bytecode, execute the code, and output the result.
 vscode cannot install extension
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:18 PM
vscode cannot install extension
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:18 PM
The reasons for the installation of VS Code extensions may be: network instability, insufficient permissions, system compatibility issues, VS Code version is too old, antivirus software or firewall interference. By checking network connections, permissions, log files, updating VS Code, disabling security software, and restarting VS Code or computers, you can gradually troubleshoot and resolve issues.
 How to check the warehouse address of git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
How to check the warehouse address of git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
To view the Git repository address, perform the following steps: 1. Open the command line and navigate to the repository directory; 2. Run the "git remote -v" command; 3. View the repository name in the output and its corresponding address.
 Can vscode be used for mac
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:36 PM
Can vscode be used for mac
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:36 PM
VS Code is available on Mac. It has powerful extensions, Git integration, terminal and debugger, and also offers a wealth of setup options. However, for particularly large projects or highly professional development, VS Code may have performance or functional limitations.
 How to use VSCode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 11:21 PM
How to use VSCode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 11:21 PM
Visual Studio Code (VSCode) is a cross-platform, open source and free code editor developed by Microsoft. It is known for its lightweight, scalability and support for a wide range of programming languages. To install VSCode, please visit the official website to download and run the installer. When using VSCode, you can create new projects, edit code, debug code, navigate projects, expand VSCode, and manage settings. VSCode is available for Windows, macOS, and Linux, supports multiple programming languages and provides various extensions through Marketplace. Its advantages include lightweight, scalability, extensive language support, rich features and version
 vscode terminal usage tutorial
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
vscode terminal usage tutorial
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
vscode built-in terminal is a development tool that allows running commands and scripts within the editor to simplify the development process. How to use vscode terminal: Open the terminal with the shortcut key (Ctrl/Cmd). Enter a command or run the script. Use hotkeys (such as Ctrl L to clear the terminal). Change the working directory (such as the cd command). Advanced features include debug mode, automatic code snippet completion, and interactive command history.





