What is fastdfs and docker
fastdfs is an open source distributed file system. Its functions include file storage, file synchronization, file access, etc., solving the problems of large-capacity storage and load balancing; docker is an open source application container engine that can be packaged Application and dependency packages into a portable image.

The operating environment of this tutorial: linux7.3 system, docker-1.13.1 version, Dell G3 computer.
What is fastdfs and docker
FastDFS is an open source distributed file system written in c language. FastDFS is tailor-made for the Internet, fully considering redundant backup, load balancing, linear expansion and other mechanisms, and focusing on high availability, high performance and other indicators. Using FastDFS, it is easy to build a high-performance file server cluster to provide file upload and download. Waiting for service.
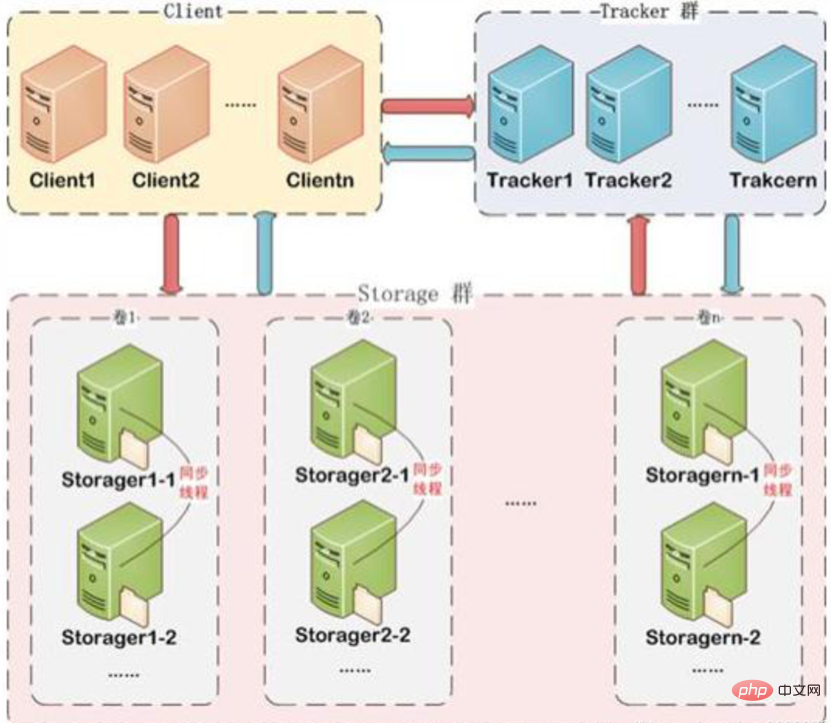
FastDFS architecture includes Tracker server and Storage server. The client requests the Tracker server to upload and download files, and the Storage server finally completes the file upload and download through Tracker server scheduling.
The role of the Tracker server is load balancing and scheduling. Through the Tracker server, the Storage server can be found according to some policies when uploading files to provide file upload services. The tracker can be called a tracking server or a scheduling server.
Storage server is used for file storage. Files uploaded by the client are eventually stored on the Storage server. Storageserver does not implement its own file system but uses the file system of the operating system to manage files. Storage can be called a storage server.
Two roles on the server side:
Tracker: manages the cluster, and the tracker can also implement the cluster. Each tracker node has equal status. Collect the status of the Storage cluster.
Storage: To actually save files, Storage is divided into multiple groups, and the files saved between each group are different. Each group can have multiple members. The content stored inside the group members is the same. The status of the group members is the same. There is no concept of master and slave.
2. File upload process
Upload file process
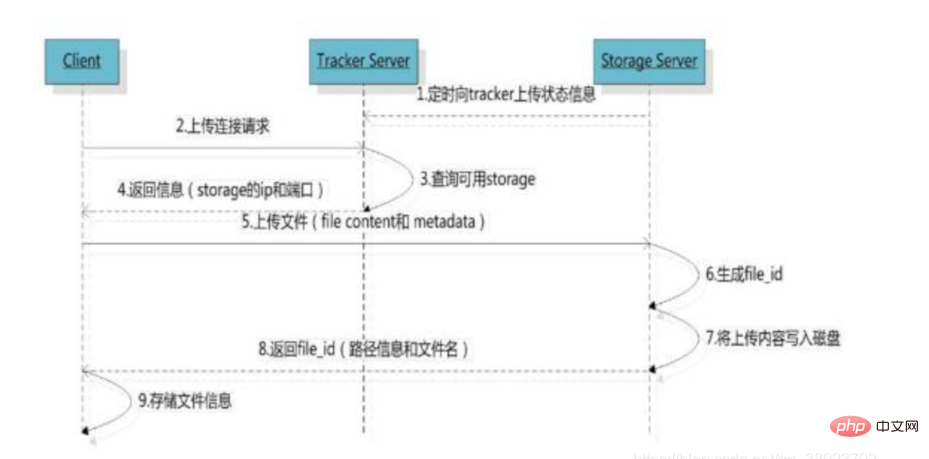
After the client uploads the file, the storage server returns the file ID to the client. This file ID is used to access index information for the file later. File index information includes: group name, virtual disk path, two-level data directory, and file name.
File name
group1/M00/00/00/wKi9hVz-GUKABj4gAAOTipWhnKM434.jpg
Group name: the name of the storage group where the file is uploaded, after the file is uploaded successfully If the storage server returns it, the client needs to save it by itself.
Virtual disk path: the virtual path configured by storage, corresponding to the disk option store_path*. If store_path0 is configured, it is M00, if store_path1 is configured, it is M01, and so on.
Data two-level directory: The two-level directory created by the storage server under each virtual disk path is used to store data files.
File name: different from when the file is uploaded. It is generated by the storage server based on specific information. The file name includes: source storage server IP address, file creation timestamp, file size, random number, file extension and other information.
3. Simple FastDFS construction
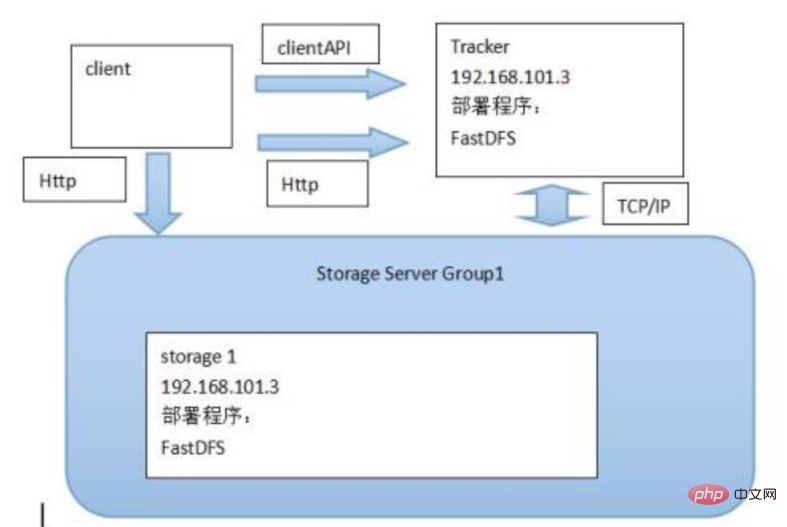
Simple FastDFS
4. Install FastDFS using Docker
4.1 . Obtain the image
You can use the existing FastDFS Docker image to run FastDFS.
You can obtain the image by downloading
docker image pull delron/fastdfs
You can also directly use the existing image backup file
docker load -i 文件路径/fastdfs_docker.tar
After loading the image, you can start the tracker and storage running FastDFS .
4.2. Run tracker
Execute the following command to start the tracker service
docker run -dti --network=host --name tracker -v /var/fdfs/tracker:/var/fdfs delron/fastdfs tracker
We map the fastDFS tracker running directory to the local /var/fdfs /tracker directory.
Execute the following command to check whether the tracker is running
docker container ls
If you want to stop the tracker service, you can execute the following command
docker container stop tracker
After stopping, re-run the tracker, you can execute the following command
docker container start tracker
4.3. Run storage
Execute the following command to start the storage service
docker run -dti --network=host --name storage -e TRACKER_SERVER=10.211.55.5:22122 -v /var/fdfs/storage:/var/fdfs delron/fastdfs storage
TRACKER_SERVER=The ip address of this machine: 22122, the ip address of this machine is not required Using 127.0.0.1
we map the fastDFS storage running directory to the local /var/fdfs/storage directory
Execute the following command to check whether the storage is running
docker container ls
If you want to stop the storage service, you can execute the following command
docker container stop storage
After stopping, re-run storage, you can execute the following command
docker container start storage
Note: If it cannot be re-run, you can delete /var/fdfs/storage fdfs_storaged.pid file in the /data directory, and then run storage again.
Recommended learning: "docker video tutorial"
The above is the detailed content of What is fastdfs and docker. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to exit the container by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:15 PM
How to exit the container by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:15 PM
Four ways to exit Docker container: Use Ctrl D in the container terminal Enter exit command in the container terminal Use docker stop <container_name> Command Use docker kill <container_name> command in the host terminal (force exit)
 How to copy files in docker to outside
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:12 PM
How to copy files in docker to outside
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:12 PM
Methods for copying files to external hosts in Docker: Use the docker cp command: Execute docker cp [Options] <Container Path> <Host Path>. Using data volumes: Create a directory on the host, and use the -v parameter to mount the directory into the container when creating the container to achieve bidirectional file synchronization.
 How to check the name of the docker container
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
How to check the name of the docker container
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
You can query the Docker container name by following the steps: List all containers (docker ps). Filter the container list (using the grep command). Gets the container name (located in the "NAMES" column).
 How to start mysql by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
How to start mysql by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
The process of starting MySQL in Docker consists of the following steps: Pull the MySQL image to create and start the container, set the root user password, and map the port verification connection Create the database and the user grants all permissions to the database
 How to restart docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:06 PM
How to restart docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:06 PM
How to restart the Docker container: get the container ID (docker ps); stop the container (docker stop <container_id>); start the container (docker start <container_id>); verify that the restart is successful (docker ps). Other methods: Docker Compose (docker-compose restart) or Docker API (see Docker documentation).
 How to update the image of docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:03 PM
How to update the image of docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:03 PM
The steps to update a Docker image are as follows: Pull the latest image tag New image Delete the old image for a specific tag (optional) Restart the container (if needed)
 How to create containers for docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:18 PM
How to create containers for docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:18 PM
Create a container in Docker: 1. Pull the image: docker pull [mirror name] 2. Create a container: docker run [Options] [mirror name] [Command] 3. Start the container: docker start [Container name]
 How to view the docker process
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:48 AM
How to view the docker process
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:48 AM
Docker process viewing method: 1. Docker CLI command: docker ps; 2. Systemd CLI command: systemctl status docker; 3. Docker Compose CLI command: docker-compose ps; 4. Process Explorer (Windows); 5. /proc directory (Linux).






