Let's talk about the elimination strategy of Redis cache
Redis What are the elimination strategies for cache? This article will talk with you about the Redis cache elimination strategy and introduce the cache strategy setting suggestions. I hope it will be helpful to you!

Redis (Remote Dictionary Server), the remote dictionary service, is an open source log type written in ANSI C language, supports the network, and can be based on memory or persistence. , Key-Value database, and provide APIs in multiple languages. [Related recommendations: Redis Video Tutorial]
It has the following characteristics:
- It runs based on memory and has high performance features
- Supports distributed, theoretically unlimited expansion of the
- key-value storage structure, efficient query
- provides multiple development language APIs, and is easy to integrate with existing business systems.
Usually used in business systems for distributed cache, centralized session storage, distributed locks and other application scenarios.
Whether it is local cache or distributed cache, in order to ensure higher performance, memory is used to save data. Due to cost and memory limitations, when the stored data exceeds the cache capacity, the cached data needs to be cached. Cull. Common elimination strategies include FIFO to eliminate the oldest data, LRU to eliminate the least recently used data, and LFU to eliminate the least recently used data.
Redis cache elimination policy trigger
In the production environment, we do not allow redis to have swap behavior. Therefore, the maximum memory usage is generally limited. Redis provides the configuration parameter maxmemory to specify the maximum memory usage.
The following configurations are legal:
maxmemory 1000KB maxmemory 100MB maxmemory 1GB maxmemory 0 # 表示不做限制,一般不会用
redis.conf configuration file is as follows
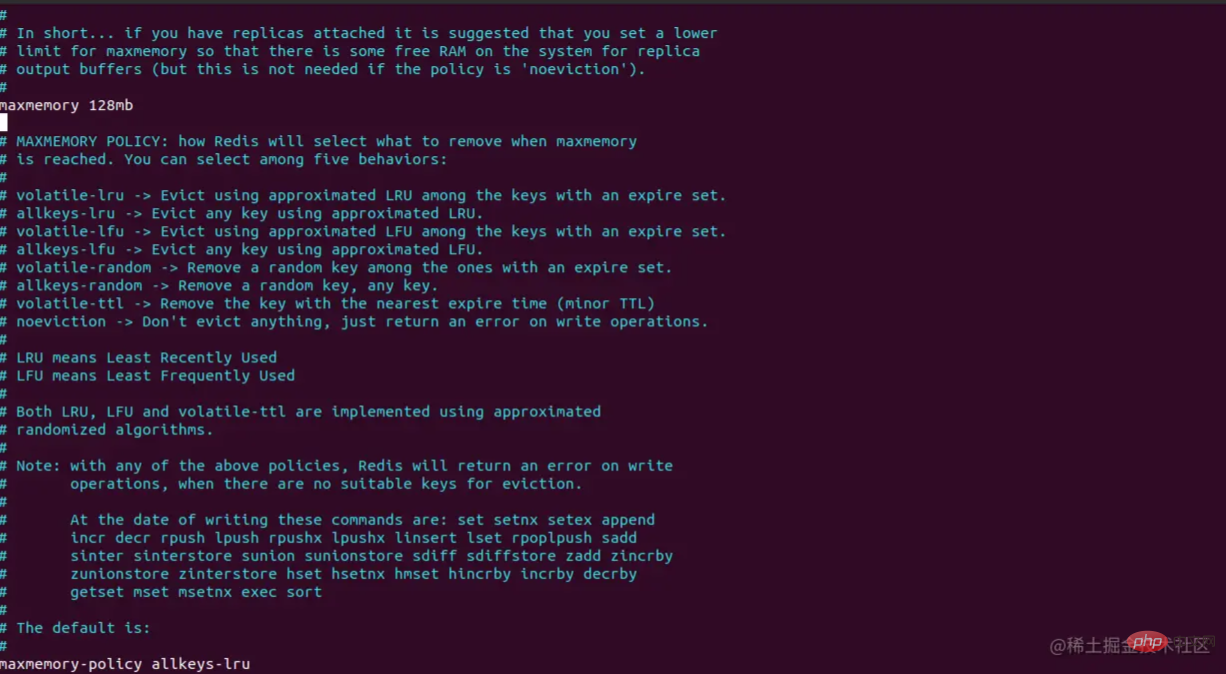
##8 8 Redis cache strategies
- volatile-lru deletes the least commonly used data among the data with a set timeout;
- allkeys-lru queries all keys Delete the least frequently used data in the data, which is the most widely used strategy; volatile-random randomly deletes the data that has set a timeout; allkeys- random queries all keys and then deletes them randomly; volatile-ttl queries all data with a set timeout, sorts them immediately, and deletes data that is about to expire; noeviction ( Default) If set to this attribute, no deletion operation will be performed, and an error will be returned if the memory overflows;
- volatile-lfu evicts the least frequently used key from all keys configured with an expiration time. ; allkeys-lfu evicts the least frequently used keys from all keys;
Redis-based LRU and LFU algorithms
LRU algorithm
The Redis LRU algorithm is not an exact implementation. This means that Redis cannot select thebesteviction candidate, i.e. the one with the most visits in the past. Instead, it attempts to run an approximation of the LRU algorithm by sampling a small number of keys and then evicting the best (with the earliest access time) of the sampled keys. However, starting with Redis 3.0, the algorithm has been improved and can also select some good candidates for eviction. This improves the performance of the algorithm, allowing it to more closely resemble the behavior of the real LRU algorithm.
The important thing about the Redis LRU algorithm is that you
cantune the accuracy of the algorithm by changing the number of samples to check for each eviction. This parameter is controlled by the following configuration directive: maxmemory-samples 5
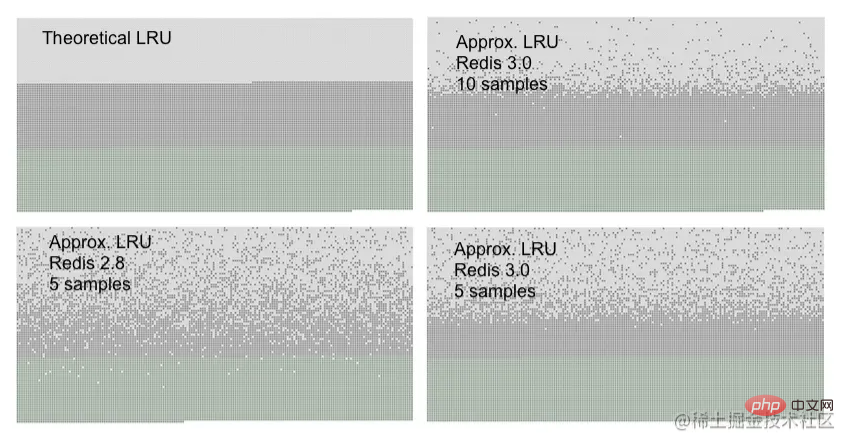 #The test that generates the above chart populates a Redis server with a given number of keys. Keys are accessed from first to last, so the first key is the best candidate for eviction using the LRU algorithm. An additional 50% of the keys were later added to force eviction of half of the old keys.
#The test that generates the above chart populates a Redis server with a given number of keys. Keys are accessed from first to last, so the first key is the best candidate for eviction using the LRU algorithm. An additional 50% of the keys were later added to force eviction of half of the old keys.
You can see three kinds of points in the picture, forming three different bands.
The light gray band is the evicted object.- The gray band is an object that has not been evicted.
- In a theoretical LRU implementation, we would expect that of the old keys, the first half will expire. The Redis LRU algorithm will only expire old keys with
. LRU is simply a model that predicts the likelihood that a given key will be accessed in the future. Additionally, if your data access pattern closely resembles a power law, most accesses will be in key sets that the LRU approximation algorithm can handle well.
Disadvantages: A large amount of cold data may be accessed within a certain period of time to generate a large amount of hot dataLFU 算法 从 Redis 4.0 开始,可以使用新的最不常用驱逐模式。这种模式在某些情况下可能会更好(提供更好的命中率/未命中率),因为使用 LFU Redis 会尝试跟踪项目的访问频率,因此很少使用的项目会被驱逐,而经常使用的项目有更高的机会留在记忆中。 如果您认为在 LRU,最近访问过但实际上几乎从未被请求过的项目不会过期,因此风险是驱逐将来有更高机会被请求的密钥。LFU 没有这个问题,一般应该更好地适应不同的访问模式。 配置LFU模式,可以使用以下策略: LFU 类似于 LRU:它使用一个概率计数器,称为莫里斯计数器,以便仅使用每个对象的几位来估计对象访问频率,并结合衰减周期,以便计数器随着时间的推移而减少:在某些时候,我们不再希望将密钥视为经常访问的密钥,即使它们过去是这样,以便算法可以适应访问模式的转变。 这些信息的采样与 LRU 发生的情况类似(如本文档的前一部分所述),以便选择驱逐的候选人。 然而,与 LRU 不同的是,LFU 具有某些可调参数:例如,如果不再访问频繁项,它的排名应该以多快的速度降低?还可以调整 Morris 计数器范围,以便更好地使算法适应特定用例。 默认情况下,Redis 4.0 配置为: 这些应该是合理的值并经过实验测试,但用户可能希望使用这些配置设置以选择最佳值。 有关如何调整这些参数的说明可以redis.conf在源代码分发的示例文件中找到,但简单地说,它们是: 衰减时间是显而易见的,它是计数器应该衰减的分钟数,当采样并发现它比该值更旧时。一个特殊值0意味着:每次扫描时总是衰减计数器,很少有用。 计数器对数因子会改变需要多少次命中才能使频率计数器饱和,这恰好在 0-255 的范围内。系数越高,需要越多的访问以达到最大值。根据下表,系数越低,低访问计数器的分辨率越好: 淘汰最近一段时间被访问次数最少的数据,以次数作为参考。 缺点: 1. 最近加入的数据常常容易被剔除,因为其起始方法次数比较少, 2. 如果频率时间度量为 1 个小时,则平均一天每个小时内访问频率 1000 的热点数据可能会被 2个小时的一段时间访问的频率为 1001 的数据剔除掉。可能会出现一些临界值的数据。 建议:了解Redis 的淘汰策略之后,在平时使用尽量主动设置/更新 key 的 expire 时间主动剔除不活跃的旧数据, 有助于提升查询性能 更多编程相关知识,请访问:编程入门!! The above is the detailed content of Let's talk about the elimination strategy of Redis cache. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!lfu-log-factor 10
lfu-decay-time 1
+--------+------------+------------+------------+------------+------------+
| factor | 100 hits | 1000 hits | 100K hits | 1M hits | 10M hits |
+--------+------------+------------+------------+------------+------------+
| 0 | 104 | 255 | 255 | 255 | 255 |
+--------+------------+------------+------------+------------+------------+
| 1 | 18 | 49 | 255 | 255 | 255 |
+--------+------------+------------+------------+------------+------------+
| 10 | 10 | 18 | 142 | 255 | 255 |
+--------+------------+------------+------------+------------+------------+
| 100 | 8 | 11 | 49 | 143 | 255 |
+--------+------------+------------+------------+------------+------------+
缓存策略设置建议

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear Redis data: Use the FLUSHALL command to clear all key values. Use the FLUSHDB command to clear the key value of the currently selected database. Use SELECT to switch databases, and then use FLUSHDB to clear multiple databases. Use the DEL command to delete a specific key. Use the redis-cli tool to clear the data.
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
Using the Redis directive requires the following steps: Open the Redis client. Enter the command (verb key value). Provides the required parameters (varies from instruction to instruction). Press Enter to execute the command. Redis returns a response indicating the result of the operation (usually OK or -ERR).
 How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
Using Redis to lock operations requires obtaining the lock through the SETNX command, and then using the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time. The specific steps are: (1) Use the SETNX command to try to set a key-value pair; (2) Use the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time for the lock; (3) Use the DEL command to delete the lock when the lock is no longer needed.
 How to configure Lua script execution time in centos redis
Apr 14, 2025 pm 02:12 PM
How to configure Lua script execution time in centos redis
Apr 14, 2025 pm 02:12 PM
On CentOS systems, you can limit the execution time of Lua scripts by modifying Redis configuration files or using Redis commands to prevent malicious scripts from consuming too much resources. Method 1: Modify the Redis configuration file and locate the Redis configuration file: The Redis configuration file is usually located in /etc/redis/redis.conf. Edit configuration file: Open the configuration file using a text editor (such as vi or nano): sudovi/etc/redis/redis.conf Set the Lua script execution time limit: Add or modify the following lines in the configuration file to set the maximum execution time of the Lua script (unit: milliseconds)
 How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
Use the Redis command line tool (redis-cli) to manage and operate Redis through the following steps: Connect to the server, specify the address and port. Send commands to the server using the command name and parameters. Use the HELP command to view help information for a specific command. Use the QUIT command to exit the command line tool.
 How to set the redis expiration policy
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:03 PM
How to set the redis expiration policy
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:03 PM
There are two types of Redis data expiration strategies: periodic deletion: periodic scan to delete the expired key, which can be set through expired-time-cap-remove-count and expired-time-cap-remove-delay parameters. Lazy Deletion: Check for deletion expired keys only when keys are read or written. They can be set through lazyfree-lazy-eviction, lazyfree-lazy-expire, lazyfree-lazy-user-del parameters.






