Do you know iterable objects and iterators in JavaScript?
Iteration is a method of accessing collection elements; objects that can be iterated are called iterable objects; an iterator is an object that can remember the traversal position. The iterator object starts accessing from the first element of the collection until After all elements have been accessed, the iterator can only move forward and not backward.
Lazy evaluation
Lazy evaluation is often translated as "lazy calculation" or "lazy calculation", which refers to calculating the value of an expression only when it is actually needed to be executed.
The opposite of lazy evaluation is early evaluation. Early evaluation, also known as greedy evaluation or strict evaluation, is the evaluation strategy of most traditional programming languages.
The benefits of making full use of the characteristics of lazy evaluation are mainly reflected in the following two aspects:
Avoid unnecessary calculations and improve performance.
Saves space and makes infinite loop data structures possible.
Iterators
Iterators in ES6 make it possible to lazily evaluate and create user-defined sequences of data. Iteration is a mechanism for traversing data. An iterator is a pointer used to traverse the elements of a data structure (called an Iterable), a pointer used to produce a sequence of values.
An iterator is an object that can be iterated. It abstracts the data container so that it behaves like an iterable object.
The iterator does not calculate the value of each item when instantiated and only generates the next value when requested. This is very useful, especially for large data sets or sequences of infinite elements.
Iterable objects
An iterable object is a data structure that wants its elements to be publicly accessible. Many objects in JS are iterable. They may not be easy to detect, but if you examine carefully, you will find the characteristics of iteration:
new Map([iterable])
new WeakMap([iterable])
new Set([iterable])
new WeakSet([iterable])
- ##Promise.all([iterable]) ##Promise.race([iterable])
- Array.from([iterable])
- Also requires an iterable object, otherwise, it will throw a type error, for example:
- for ... of
- ... (expand operator)
- const [a, b, ..] = iterable (destructuring assignment)
- There are many built-in iterable items in JavaScript:
String,Array,TypedArray,Map,Set.
Iteration protocol
Iterators and iterable objects follow the iteration protocol.
A protocol is a set of interfaces and specifies how to use them.
Iterators follow the iterator protocol, and iterables follow the iterable protocol.Iterable protocol
To make an object iterable, it must implement an iterator method through Symbol.iterator, which is a factory for iterators .
Using TypeScript, the iterable protocol looks like this:
interface Iterable {
[Symbol.iterator]() : Iterator;
}Symbol.iterator]() is a parameterless function. Calling it on an iterable object means we can access the iterable object through this, which can be a regular function or a generator function.
Iterator protocolThe iterator protocol defines a standard way to generate a sequence of values.
In order for an object to become an iterator, it must implement the next() method. Iterators can implement the return() method, which we will discuss later in this article.
Using TypeScript, the iterator protocol is as follows:
interface Iterator {
next() : IteratorResult;
return?(value?: any): IteratorResult;
}IteratorResult is defined as follows:
interface IteratorResult {
value?: any;
done: boolean;
}- done informs the consumer whether the iterator has been Used, false means there are still values to be generated, true means the iterator has ended.
- value can be any JS value, it is the value displayed to the consumer.
- When done is true, value can be omitted.
Composition
Iterators and iterable objects can be represented by the following picture:
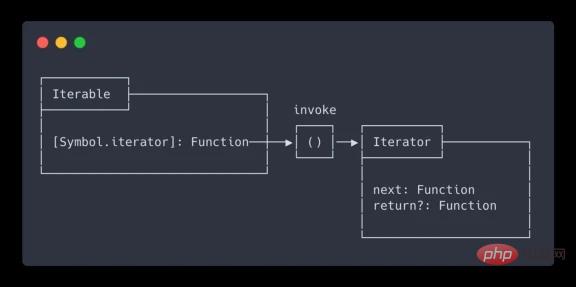 Example
Example
Basic knowledge has been introduced. Next, let’s use some examples to deepen our image.
Range IteratorWe start with a very basic iterator, the createRangeIterator iterator.
We manually call it.next() to get the next IteratorResult. The last call returns {done: true}, which means the iterator is now used and no longer produces any values.
function createRangeIterator(from, to) {
let i = from;
return {
next() {
if (i <= to) {
return { value: i++, done: false };
} else {
return { done: true };
}
}
}
}
const it = createRangeIterator(1, 3);
console.log(it.next());
console.log(it.next());
console.log(it.next());
console.log(it.next());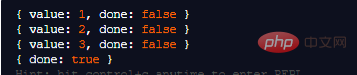
Earlier in this article, I have mentioned that certain statements in JS require a Iterable object. Therefore, our previous example will not work when used with a for...of loop.
But it is very easy to create objects that conform to the iterator and iterable protocols.
function createRangeIterator (from, to) {
let i = from
return {
[Symbol.iterator] () {
return this
},
next() {
if (i <= to) {
return { value: i++, done: false }
} else {
return { done: true }
}
}
}
}
const it = createRangeIterator(1, 3)
for (const i of it) {
console.log(i)
}无限序列迭代器
迭代器可以表示无限制大小的序列,因为它们仅在需要时才计算值。
注意不要在无限迭代器上使用扩展运算符(...),JS 将尝试消费迭代器,由于迭代器是无限的,因此它将永远不会结束。 所以你的应用程序将崩溃,因为内存已被耗尽
同样,for ... of 循环也是一样的情况,所以要确保能退出循环:
function createEvenNumbersIterator () {
let value = 0
return {
[Symbol.iterator] () {
return this
},
next () {
value += 2
return { value, done: false}
}
}
}
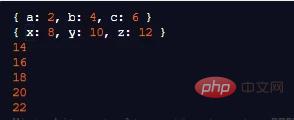
const it = createEvenNumbersIterator()
const [a, b, c] = it
console.log({a, b, c})
const [x, y, z] = it
console.log({ x, y, z })
for (const even of it) {
console.log(even)
if (even > 20) {
break
}
}
关闭迭代器
前面我们提到过,迭代器可以有选择地使用return()方法。 当迭代器直到最后都没有迭代时使用此方法,并让迭代器进行清理。
for ... of循环可以通过以下方式更早地终止迭代:
break
continue
throw
return
function createCloseableIterator () {
let idx = 0
const data = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e']
function cleanup() {
console.log('Performing cleanup')
}
return {
[Symbol.iterator]() { return this },
next () {
if (idx <= data.length - 1) {
return { value: data[idx++], done: false }
} else {
cleanup()
return { done: true }
}
},
return () {
cleanup()
return { done: true }
}
}
}
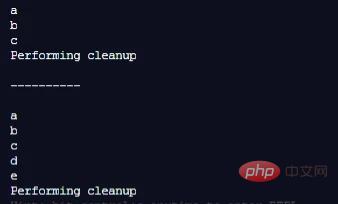
const it = createCloseableIterator()
for (const value of it) {
console.log(value)
if (value === 'c') {
break
}
}
console.log('\n----------\n')
const _it = createCloseableIterator();
for (const value of _it) {
console.log(value);
}
如果知道迭代器已经结束,则手动调用cleanup()函数。
如果突然完成,则return()起作用并为我们进行清理。
【推荐学习:javascript高级教程】
The above is the detailed content of Do you know iterable objects and iterators in JavaScript?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 PHP and Vue: a perfect pairing of front-end development tools
Mar 16, 2024 pm 12:09 PM
PHP and Vue: a perfect pairing of front-end development tools
Mar 16, 2024 pm 12:09 PM
PHP and Vue: a perfect pairing of front-end development tools. In today's era of rapid development of the Internet, front-end development has become increasingly important. As users have higher and higher requirements for the experience of websites and applications, front-end developers need to use more efficient and flexible tools to create responsive and interactive interfaces. As two important technologies in the field of front-end development, PHP and Vue.js can be regarded as perfect tools when paired together. This article will explore the combination of PHP and Vue, as well as detailed code examples to help readers better understand and apply these two
 Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
JavaScript tutorial: How to get HTTP status code, specific code examples are required. Preface: In web development, data interaction with the server is often involved. When communicating with the server, we often need to obtain the returned HTTP status code to determine whether the operation is successful, and perform corresponding processing based on different status codes. This article will teach you how to use JavaScript to obtain HTTP status codes and provide some practical code examples. Using XMLHttpRequest
 Questions frequently asked by front-end interviewers
Mar 19, 2024 pm 02:24 PM
Questions frequently asked by front-end interviewers
Mar 19, 2024 pm 02:24 PM
In front-end development interviews, common questions cover a wide range of topics, including HTML/CSS basics, JavaScript basics, frameworks and libraries, project experience, algorithms and data structures, performance optimization, cross-domain requests, front-end engineering, design patterns, and new technologies and trends. . Interviewer questions are designed to assess the candidate's technical skills, project experience, and understanding of industry trends. Therefore, candidates should be fully prepared in these areas to demonstrate their abilities and expertise.
 Is Django front-end or back-end? check it out!
Jan 19, 2024 am 08:37 AM
Is Django front-end or back-end? check it out!
Jan 19, 2024 am 08:37 AM
Django is a web application framework written in Python that emphasizes rapid development and clean methods. Although Django is a web framework, to answer the question whether Django is a front-end or a back-end, you need to have a deep understanding of the concepts of front-end and back-end. The front end refers to the interface that users directly interact with, and the back end refers to server-side programs. They interact with data through the HTTP protocol. When the front-end and back-end are separated, the front-end and back-end programs can be developed independently to implement business logic and interactive effects respectively, and data exchange.
 Exploring Go language front-end technology: a new vision for front-end development
Mar 28, 2024 pm 01:06 PM
Exploring Go language front-end technology: a new vision for front-end development
Mar 28, 2024 pm 01:06 PM
As a fast and efficient programming language, Go language is widely popular in the field of back-end development. However, few people associate Go language with front-end development. In fact, using Go language for front-end development can not only improve efficiency, but also bring new horizons to developers. This article will explore the possibility of using the Go language for front-end development and provide specific code examples to help readers better understand this area. In traditional front-end development, JavaScript, HTML, and CSS are often used to build user interfaces
 Django: A magical framework that can handle both front-end and back-end development!
Jan 19, 2024 am 08:52 AM
Django: A magical framework that can handle both front-end and back-end development!
Jan 19, 2024 am 08:52 AM
Django: A magical framework that can handle both front-end and back-end development! Django is an efficient and scalable web application framework. It is able to support multiple web development models, including MVC and MTV, and can easily develop high-quality web applications. Django not only supports back-end development, but can also quickly build front-end interfaces and achieve flexible view display through template language. Django combines front-end development and back-end development into a seamless integration, so developers don’t have to specialize in learning
 Combination of Golang and front-end technology: explore how Golang plays a role in the front-end field
Mar 19, 2024 pm 06:15 PM
Combination of Golang and front-end technology: explore how Golang plays a role in the front-end field
Mar 19, 2024 pm 06:15 PM
Combination of Golang and front-end technology: To explore how Golang plays a role in the front-end field, specific code examples are needed. With the rapid development of the Internet and mobile applications, front-end technology has become increasingly important. In this field, Golang, as a powerful back-end programming language, can also play an important role. This article will explore how Golang is combined with front-end technology and demonstrate its potential in the front-end field through specific code examples. The role of Golang in the front-end field is as an efficient, concise and easy-to-learn
 How to get HTTP status code in JavaScript the easy way
Jan 05, 2024 pm 01:37 PM
How to get HTTP status code in JavaScript the easy way
Jan 05, 2024 pm 01:37 PM
Introduction to the method of obtaining HTTP status code in JavaScript: In front-end development, we often need to deal with the interaction with the back-end interface, and HTTP status code is a very important part of it. Understanding and obtaining HTTP status codes helps us better handle the data returned by the interface. This article will introduce how to use JavaScript to obtain HTTP status codes and provide specific code examples. 1. What is HTTP status code? HTTP status code means that when the browser initiates a request to the server, the service






