Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 Take you step by step to understand asynchronous programming in JavaScript
Take you step by step to understand asynchronous programming in JavaScript
Take you step by step to understand asynchronous programming in JavaScript
This article will introduce you to asynchronous programming in JavaScript. It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to everyone.

Asynchronous means non-synchronous....
This section may be a bit boring, but it is a very important concept in JavaScript and is very useful. It is necessary to learn.
Purpose
- Improve development efficiency and write easy-to-maintain code
Introduction question
- Why does the page get stuck when requesting? ?
$.ajax({
url: "www.xx.com/api",
async: false, // true
success: function(result) {
console.log(result);
},
});- Why is the data updated but the DOM not updated? ?
// 异步批量更新DOM(vue-nextTick)
// <p id="app">{{num}}</p>
new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
num: 0,
},
mounted() {
let dom = document.getElementById("app");
while (this.num !== 100) {
this.num++;
}
console.log("Vue num=" + this.num, "DOM num=" + dom.innerHTML);
// Vue num=100,DOM num=0
// nextTick or setTimeout
},
});The reasons for asynchronous generation
Cause: single thread (one point in time, only do one thing), the browser's JS engine is single threaded caused.
Single thread means that there is only one thread responsible for interpreting and executing IavaScript code in the JS engine. You might as well call it the main thread.
The so-called single thread means that only one task can be completed at a time. If there are multiple tasks, they must be queued. The previous task is completed before the next task is executed.
First take a look at the thread diagram of the browser kernel:
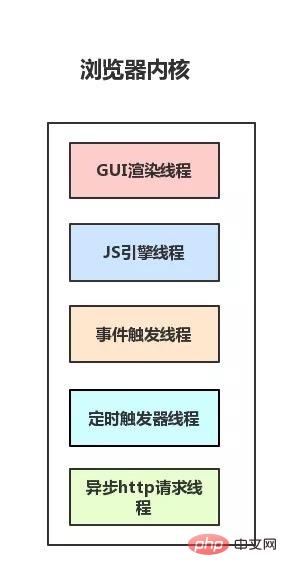
Among them, The rendering thread and the JS thread are mutually exclusive .
Suppose there are two functions, one modifying and one deleting, operating a DOM node at the same time. If there are multiple threads, if the two threads are executed at the same time, there will definitely be a deadlock and there will be problems.
Why JS should be designed as single-threaded, because of the special environment of the browser.
Advantages and disadvantages of single thread:
The advantage of this mode is that it is relatively simple to implement and the execution environment is relatively simple; The disadvantage is that as long as one task takes a long time, the subsequent Tasks must be queued and waited, which will delay the execution of the entire program. Common browser unresponsiveness (suspended death) is often caused by a certain piece of Javascript code running for a long time (such as an infinite loop), causing the entire page to get stuck in this place and other tasks cannot be performed.
Common blockage (infinite loop):
while (true) {}JS was originally designed to be a script language that runs in the browser, so we didn’t want to make it so complicated, so we just designed It has become a single thread, that is, can only do one thing at a time.
In order to solve single-thread blockingthis shortcoming: asynchronous is generated.
Take the example of eating instant noodles:
- Synchronous: Buy instant noodles => Boil water (staring) => Cook noodles => Eat instant noodles
- Asynchronous : Buy instant noodles => Boil water (the water boils and the kettle sounds - callback) => Watch TV => Cook noodles (the noodles are ready and the kettle rings - callback) => Watch TV => Call me when it's done => Eat instant noodles
Watching TV is an asynchronous operation, and the sound of the kettle is a callback function.
Asynchronous Programming
Most of the code in JS is executed synchronously. Only a few functions are executed asynchronously. Asynchronously executed code requires asynchronous programming. .
Asynchronous code
setTimeout(() => {
console.log("log2");
}, 0);
console.log("log1");
// ?? log1 log2Characteristics of asynchronous code: It is not executed immediately, but needs to wait and be executed at a certain point in the future.
| Synchronous code | Asynchronous code |
|---|---|
##<script>Code | Network request (Ajax)|
| Timer (setTimeout, setInterval) | |
| Promise(then) | |
Callback function
The most common way to write asynchronous code is to use a callback function.- HTTP network request (the request is successful and the xx operation is performed after identification) DOM event binding mechanism (the xx operation is performed after the user triggers the event) Timer (setTimeout, setInterval) (Execute xx operation after reaching the set time)
// 注意到click方法中是一个函数而不是一个变量
// 它就是回调函数
$("#btn_1").click(function() {
alert("Btn 1 Clicked");
});
// 或者
function click() {
// 它就是回调函数
alert("Btn 1 Clicked");
}
$("#btn_1").click(click);
Three ways of asynchronous programming
- callback
function getOneNews() {
$.ajax({
url: topicsUrl,
success: function(res) {
let id = res.data[0].id;
$.ajax({
url: topicOneUrl + id,
success: function(ress) {
console.log(ress);
render(ress.data);
},
});
},
});
}- promise
function getOneNews() {
axios
.get(topicsUrl)
.then(function(response) {
let id = response.data.data[0].id;
return axios.get(topicOneUrl + id);
})
.then((res) => {
render(res.data.data);
})
.catch(function(error) {
console.log(error);
});
}- async/await
async function getOneNews() {
let listData = await axios.get(topicsUrl);
let id = listData.data.data[0].id;
let data = await axios.get(topicOneUrl + id);
render(data.data.data);
}Online preview
Preview address: http://jsrun.net/s43Kp/embedded/all/ lightQuestion? ?
If multiple asynchronous codes exist at the same time, what should be the order of execution? Which one is executed first and which one is executed later?Macro tasks and micro tasks
Division of asynchronous code, asynchronous code is divided into macro tasks and micro tasks.| Macro tasks (not in a hurry) | Micro tasks (in a hurry) |
|---|---|
Overall code | |