Learn Git to configure SSH (common to github, gitee, and gitlab)
Preface
Git warehouses generally have two reading and writing methods: https and ssh. https is very simple and can be accessed directly through account and password, while ssh uses It is more cumbersome, and you need to configure the public key and private key first, because ssh uses RSA-based encryption for verification.
Recommendation (free): Git
SSH configuration
github and gitee both provide Git based on the SSH protocol Service, before using the SSH protocol to access the warehouse, you need to configure the SSH public key of the account/warehouse.
1. Generate key
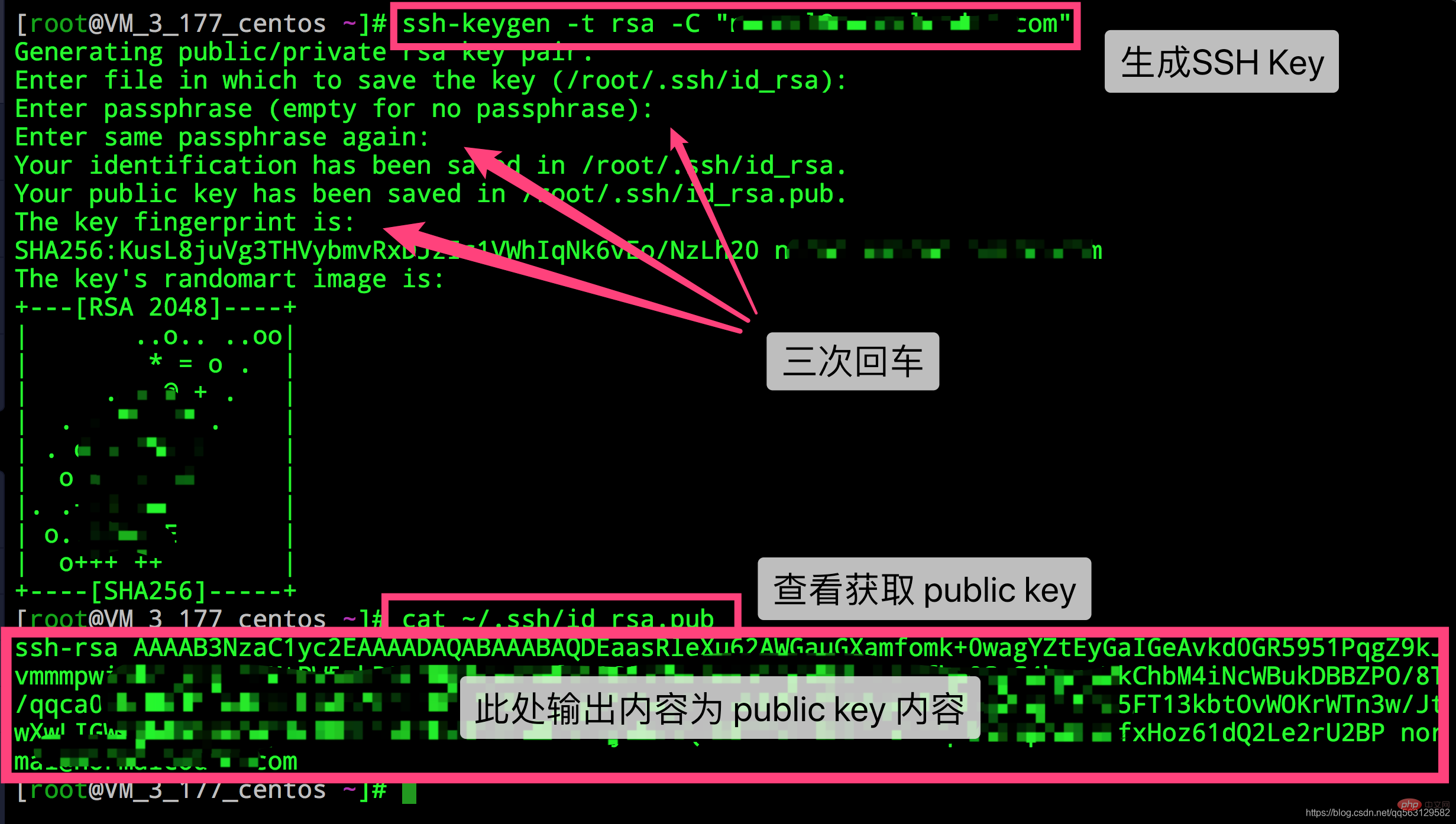
You can generate ssh key by following the command:
ssh-Learn Git to configure SSH (common to github, gitee, and gitlab) -t rsa -C "xxxxx@xxxxx.com" # Generating public/private rsa key pair...
Follow the prompts and press Enter three times to generate ssh key. Obtain your public key by viewing the contents of the ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub file
cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub # ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAADAQABAAABAQC6eNtGpNGwstc....
2. Deploy the public key
Copy the generated ssh key, add the generated public key to the warehouse through the warehouse homepage"Management"->"Deployment Public Key Management"->"Add Deployment Public Key". 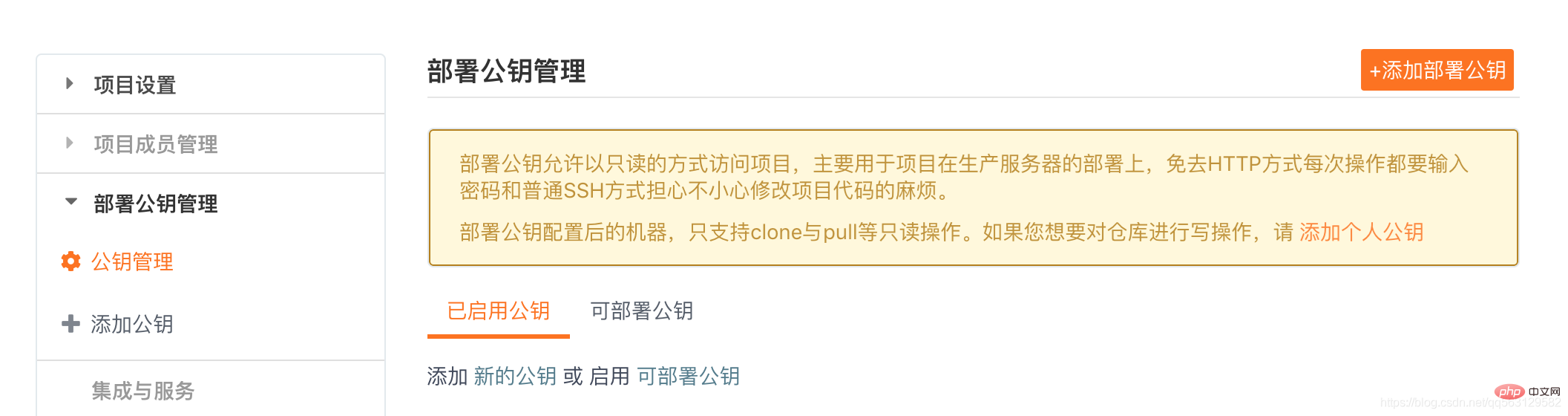
3. Add ssh trust locally
After adding, enter
ssh -T git@gitee.com
in the Terminal. For first time use, you need to confirm and add the host to this Machine SSH trusted list. If the content Hi XXX! You’ve successfully authenticated, but Gitee.com does not provide shell access. is returned, the addition is successful.
SSH Add Tips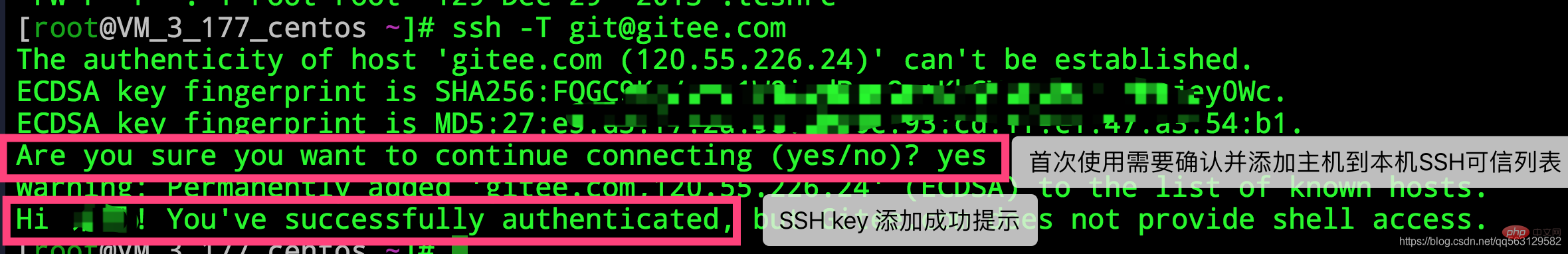
After the addition is successful, you can use the SSH protocol to operate the warehouse.
4. Warehouse public key and deployable public key
In order to facilitate users to use a set of public keys under multiple project warehouses and avoid the tediousness of repeated deployment and management, Code Cloud has launched The "Deployable Public Key" function supports the use of the deployed public key of another warehouse space under the current account name/participation in one warehouse space to achieve public key sharing.
SourceTree settings
Users who use git generally use SourceTree more. After configuring ssh, they need to be imported into sourceTree before they can be used.
1. Create or import ssh key
Click[Tools] -> [Create or import SSH key]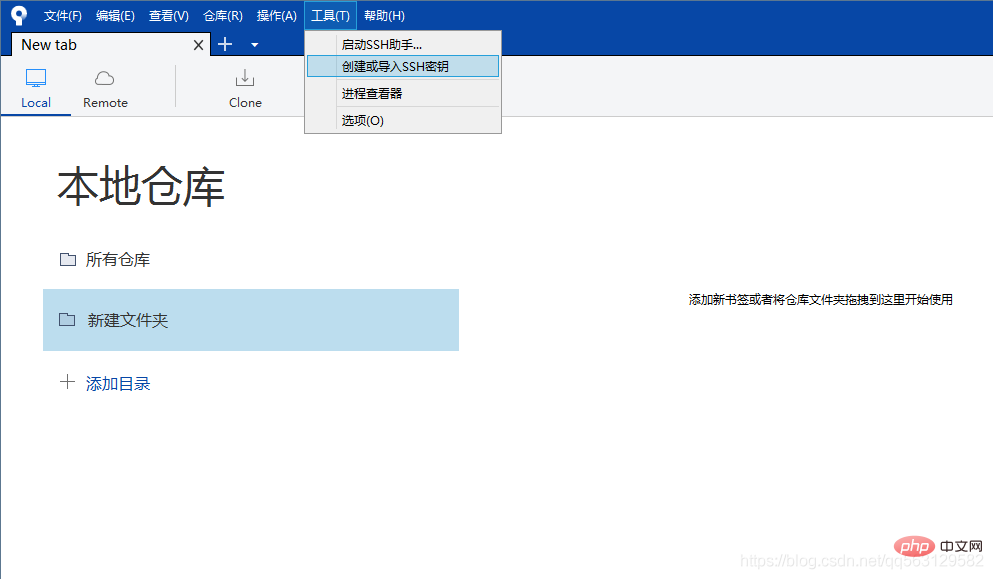 ## Open the PuTTY tool generator
## Open the PuTTY tool generator
Use Generate to directly generate the public key and private key
If you already have the key, you can click Load to load it and select the id_rsa file. 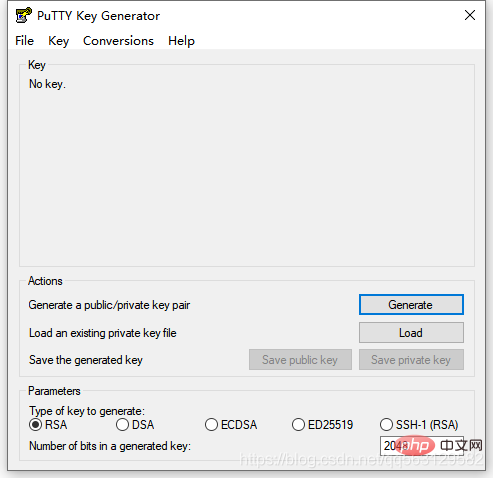
. Save[ppk file]**, (It is best to put these files together, under the user/.ssh file)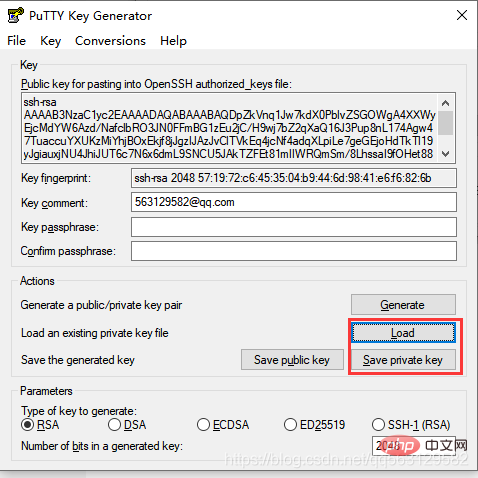 After saving, you can close the window
After saving, you can close the window
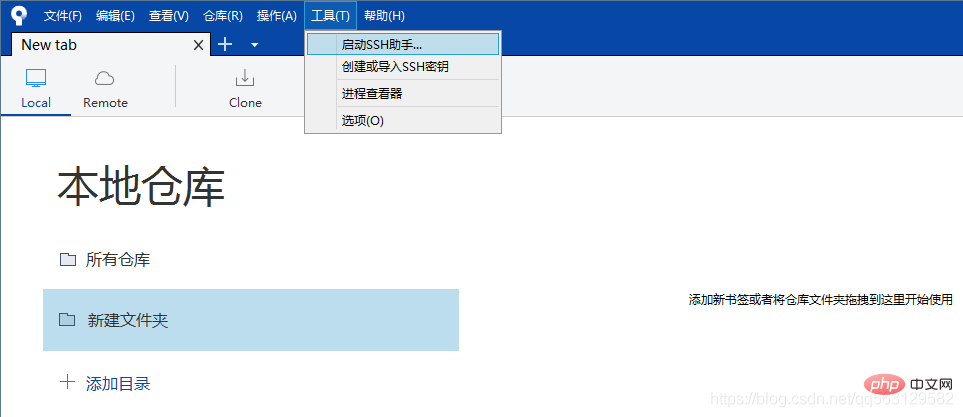 After opening, it may be hidden in the task panel below, just find it and open it
After opening, it may be hidden in the task panel below, just find it and open it
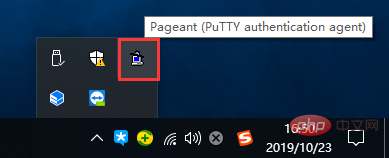 Click the **[Add Key]
Click the **[Add Key]
button and select the ppk file just generated**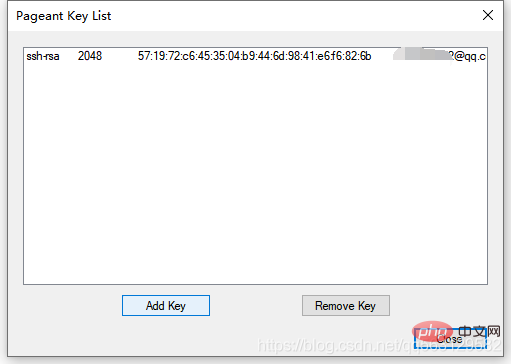 The configuration is complete and you can close it
The configuration is complete and you can close it
Next, sourceTree can read and write remote warehouses through ssh.
The above is the detailed content of Learn Git to configure SSH (common to github, gitee, and gitlab). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to download git projects to local
Apr 17, 2025 pm 04:36 PM
How to download git projects to local
Apr 17, 2025 pm 04:36 PM
To download projects locally via Git, follow these steps: Install Git. Navigate to the project directory. cloning the remote repository using the following command: git clone https://github.com/username/repository-name.git
 How to update code in git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 04:45 PM
How to update code in git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 04:45 PM
Steps to update git code: Check out code: git clone https://github.com/username/repo.git Get the latest changes: git fetch merge changes: git merge origin/master push changes (optional): git push origin master
 How to merge code in git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 04:39 PM
How to merge code in git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 04:39 PM
Git code merge process: Pull the latest changes to avoid conflicts. Switch to the branch you want to merge. Initiate a merge, specifying the branch to merge. Resolve merge conflicts (if any). Staging and commit merge, providing commit message.
 What to do if the git download is not active
Apr 17, 2025 pm 04:54 PM
What to do if the git download is not active
Apr 17, 2025 pm 04:54 PM
Resolve: When Git download speed is slow, you can take the following steps: Check the network connection and try to switch the connection method. Optimize Git configuration: Increase the POST buffer size (git config --global http.postBuffer 524288000), and reduce the low-speed limit (git config --global http.lowSpeedLimit 1000). Use a Git proxy (such as git-proxy or git-lfs-proxy). Try using a different Git client (such as Sourcetree or Github Desktop). Check for fire protection
 How to use git commit
Apr 17, 2025 pm 03:57 PM
How to use git commit
Apr 17, 2025 pm 03:57 PM
Git Commit is a command that records file changes to a Git repository to save a snapshot of the current state of the project. How to use it is as follows: Add changes to the temporary storage area Write a concise and informative submission message to save and exit the submission message to complete the submission optionally: Add a signature for the submission Use git log to view the submission content
 How to solve the efficient search problem in PHP projects? Typesense helps you achieve it!
Apr 17, 2025 pm 08:15 PM
How to solve the efficient search problem in PHP projects? Typesense helps you achieve it!
Apr 17, 2025 pm 08:15 PM
When developing an e-commerce website, I encountered a difficult problem: How to achieve efficient search functions in large amounts of product data? Traditional database searches are inefficient and have poor user experience. After some research, I discovered the search engine Typesense and solved this problem through its official PHP client typesense/typesense-php, which greatly improved the search performance.
 How to update local code in git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 04:48 PM
How to update local code in git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 04:48 PM
How to update local Git code? Use git fetch to pull the latest changes from the remote repository. Merge remote changes to the local branch using git merge origin/<remote branch name>. Resolve conflicts arising from mergers. Use git commit -m "Merge branch <Remote branch name>" to submit merge changes and apply updates.
 How to delete a repository by git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 04:03 PM
How to delete a repository by git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 04:03 PM
To delete a Git repository, follow these steps: Confirm the repository you want to delete. Local deletion of repository: Use the rm -rf command to delete its folder. Remotely delete a warehouse: Navigate to the warehouse settings, find the "Delete Warehouse" option, and confirm the operation.







