 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
 Python geographic data processing analysis uses GR for vectors
Python geographic data processing analysis uses GR for vectors
Python geographic data processing analysis uses GR for vectors

Free learning recommendations: python video tutorial
1. Overlay analysis
Overlay analysis operation: 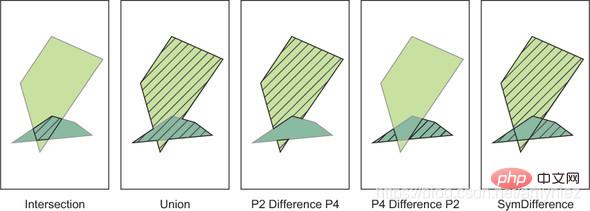
Plot color: 'r' red, 'g' green, 'b' Blue, 'c' cyan, 'y' yellow, 'm' magenta, 'k' black, 'w' white.
Simple map of New Orleans city boundaries, water bodies and wetlands: ## sync
synopsis 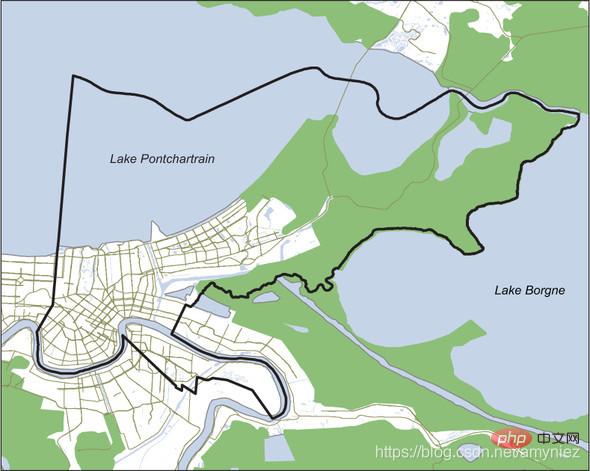 1. Analysis of urban swamp areas in New Orleans:
1. Analysis of urban swamp areas in New Orleans: import osfrom osgeo import ogrfrom ospybook.vectorplotter import VectorPlotter
data_dir = r'E:\Google chrome\Download\gis with python\osgeopy data'# 得到新奥尔良附近的一个特定的沼泽特征vp = VectorPlotter(True)water_ds = ogr.Open(os.path.join(data_dir, 'US', 'wtrbdyp010.shp'))water_lyr = water_ds.GetLayer(0)water_lyr.SetAttributeFilter('WaterbdyID = 1011327')marsh_feat = water_lyr.GetNextFeature()marsh_geom = marsh_feat.geometry().Clone()vp.plot(marsh_geom, 'c')# 获得新奥尔良边城市边界nola_ds = ogr.Open(os.path.join(data_dir, 'Louisiana', 'NOLA.shp'))nola_lyr = nola_ds.GetLayer(0)nola_feat = nola_lyr.GetNextFeature()nola_geom = nola_feat.geometry().Clone()vp.plot(nola_geom, fill=False, ec='red', ls='dashed', lw=3)# 相交沼泽和边界多边形得到沼泽的部分# 位于新奥尔良城市边界内intersection = marsh_geom.Intersection(nola_geom)vp.plot(intersection, 'yellow', hatch='x')vp.draw()
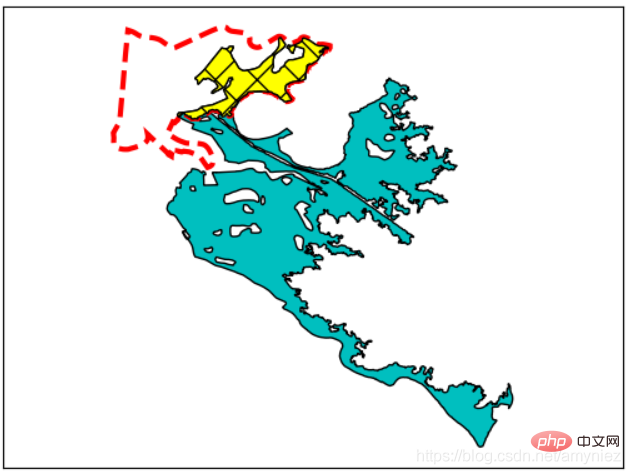 2. Calculate the wetland area of the city: Filtering out unnecessary features can significantly reduce processing time.
2. Calculate the wetland area of the city: Filtering out unnecessary features can significantly reduce processing time.
3. Intersection of two layers:
# 获得城市内的湿地多边形# 将多边形的面积进行累加# 除以城市面积water_lyr.SetAttributeFilter("Feature != 'Lake'") # 限定对象water_lyr.SetSpatialFilter(nola_geom)wetlands_area = 0# 累加多边形面积for feat in water_lyr:
intersect = feat.geometry().Intersection(nola_geom)
wetlands_area += intersect.GetArea()pcnt = wetlands_area / nola_geom.GetArea()print('{:.1%} of New Orleans is wetland'.format(pcnt))28.7% of New Orleans is wetland
OGR includes two proximity analysis tools: measuring distances between geometric features and creating buffers.
1. Determine how many cities in the United States are within 10 miles of a volcano.A problematic way to determine the number of cities near a volcano:
# 将湖泊数据排除# 在内存中创建一个临时图层# 将图层相交,将结果储存在临时图层中water_lyr.SetAttributeFilter("Feature != 'Lake'")water_lyr.SetSpatialFilter(nola_geom)wetlands_area = 0for feat in water_lyr:
intersect = feat.geometry().Intersection(nola_geom) # 求交
wetlands_area += intersect.GetArea()pcnt = wetlands_area / nola_geom.GetArea()print('{:.1%} of New Orleans is wetland'.format(pcnt))water_lyr.SetSpatialFilter(None)water_lyr.SetAttributeFilter("Feature != 'Lake'")memory_driver = ogr.GetDriverByName('Memory')temp_ds = memory_driver.CreateDataSource('temp')temp_lyr = temp_ds.CreateLayer('temp')nola_lyr.Intersection(water_lyr, temp_lyr)sql = 'SELECT SUM(OGR_GEOM_AREA) AS area FROM temp'lyr = temp_ds.ExecuteSQL(sql)pcnt = lyr.GetFeature(0).GetField('area') / nola_geom.GetArea()print('{:.1%} of New Orleans is wetland'.format(pcnt))28.7% of New Orleans is wetland
2. A better way to determine the number of cities near a volcano:
from osgeo import ogr
shp_ds = ogr.Open(r'E:\Google chrome\Download\gis with python\osgeopy data\US')volcano_lyr = shp_ds.GetLayer('us_volcanos_albers')cities_lyr = shp_ds.GetLayer('cities_albers')# 在内存中创建一个临时层来存储缓冲区memory_driver = ogr.GetDriverByName('memory')memory_ds = memory_driver.CreateDataSource('temp')buff_lyr = memory_ds.CreateLayer('buffer')buff_feat = ogr.Feature(buff_lyr.GetLayerDefn())# 缓缓冲每一个火山点,将结果添加到缓冲图层中for volcano_feat in volcano_lyr:
buff_geom = volcano_feat.geometry().Buffer(16000)
tmp = buff_feat.SetGeometry(buff_geom)
tmp = buff_lyr.CreateFeature(buff_feat)# 将城市图层与火山缓冲区图层相交result_lyr = memory_ds.CreateLayer('result')buff_lyr.Intersection(cities_lyr, result_lyr)print('Cities: {}'.format(result_lyr.GetFeatureCount()))Cities: 83
In the first example, whenever a city is within the volcano buffer, it will be copied to the output result. Note that a city located within multiple 16,000-meter buffer zones will be included more than once. # synchronization
##from osgeo import ogr
shp_ds = ogr.Open(r'E:\Google chrome\Download\gis with python\osgeopy data\US')volcano_lyr = shp_ds.GetLayer('us_volcanos_albers')cities_lyr = shp_ds.GetLayer('cities_albers')# 将缓冲区添加到一个复合多边形,而不是一个临时图层multipoly = ogr.Geometry(ogr.wkbMultiPolygon)for volcano_feat in volcano_lyr:
buff_geom = volcano_feat.geometry().Buffer(16000)
multipoly.AddGeometry(buff_geom)# 将所有的缓冲区联合在一起得到一个可以使用的多边形作为空间过滤器cities_lyr.SetSpatialFilter(multipoly.UnionCascaded())print('Cities: {}'.format(cities_lyr.GetFeatureCount()))Cities: 78
import osfrom osgeo import ogrfrom ospybook.vectorplotter import VectorPlotter
data_dir = r'E:\Google chrome\Download\gis with python\osgeopy data'shp_ds = ogr.Open(os.path.join(data_dir, 'US'))volcano_lyr = shp_ds.GetLayer('us_volcanos_albers')cities_lyr = shp_ds.GetLayer('cities_albers')# 西雅图到雷尼尔山的距离volcano_lyr.SetAttributeFilter("NAME = 'Rainier'")feat = volcano_lyr.GetNextFeature()rainier = feat.geometry().Clone()cities_lyr.SetSpatialFilter(None)cities_lyr.SetAttributeFilter("NAME = 'Seattle'")feat = cities_lyr.GetNextFeature()seattle = feat.geometry().Clone()meters = round(rainier.Distance(seattle))miles = meters / 1600print('{} meters ({} miles)'.format(meters, miles))92656 meters (57.91 miles)
Taking the elevation Z value into account, the true distance is 5. # 2Dpt1_2d = ogr.Geometry(ogr.wkbPoint)pt1_2d.AddPoint(15, 15)pt2_2d = ogr.Geometry(ogr.wkbPoint)pt2_2d.AddPoint(15, 19)print(pt1_2d.Distance(pt2_2d))
4.0
# 2.5Dpt1_25d = ogr.Geometry(ogr.wkbPoint25D)pt1_25d.AddPoint(15, 15, 0)pt2_25d = ogr.Geometry(ogr.wkbPoint25D)pt2_25d.AddPoint(15, 19, 3)print(pt1_25d.Distance(pt2_25d))
4.0
# 用2D计算面积ring = ogr.Geometry(ogr.wkbLinearRing)ring.AddPoint(10, 10)ring.AddPoint(10, 20)ring.AddPoint(20, 20)ring.AddPoint(20, 10)poly_2d = ogr.Geometry(ogr.wkbPolygon)poly_2d.AddGeometry(ring)poly_2d.CloseRings()print(poly_2d.GetArea())
Related free learning recommendations:
python tutorial
(Video)The above is the detailed content of Python geographic data processing analysis uses GR for vectors. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP is mainly procedural programming, but also supports object-oriented programming (OOP); Python supports a variety of paradigms, including OOP, functional and procedural programming. PHP is suitable for web development, and Python is suitable for a variety of applications such as data analysis and machine learning.
 Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
PHP is suitable for web development and rapid prototyping, and Python is suitable for data science and machine learning. 1.PHP is used for dynamic web development, with simple syntax and suitable for rapid development. 2. Python has concise syntax, is suitable for multiple fields, and has a strong library ecosystem.
 PHP and Python: A Deep Dive into Their History
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP and Python: A Deep Dive into Their History
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP originated in 1994 and was developed by RasmusLerdorf. It was originally used to track website visitors and gradually evolved into a server-side scripting language and was widely used in web development. Python was developed by Guidovan Rossum in the late 1980s and was first released in 1991. It emphasizes code readability and simplicity, and is suitable for scientific computing, data analysis and other fields.
 Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python is more suitable for beginners, with a smooth learning curve and concise syntax; JavaScript is suitable for front-end development, with a steep learning curve and flexible syntax. 1. Python syntax is intuitive and suitable for data science and back-end development. 2. JavaScript is flexible and widely used in front-end and server-side programming.
 How to run sublime code python
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:48 AM
How to run sublime code python
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:48 AM
To run Python code in Sublime Text, you need to install the Python plug-in first, then create a .py file and write the code, and finally press Ctrl B to run the code, and the output will be displayed in the console.
 Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
VS Code can run on Windows 8, but the experience may not be great. First make sure the system has been updated to the latest patch, then download the VS Code installation package that matches the system architecture and install it as prompted. After installation, be aware that some extensions may be incompatible with Windows 8 and need to look for alternative extensions or use newer Windows systems in a virtual machine. Install the necessary extensions to check whether they work properly. Although VS Code is feasible on Windows 8, it is recommended to upgrade to a newer Windows system for a better development experience and security.
 Where to write code in vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
Where to write code in vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
Writing code in Visual Studio Code (VSCode) is simple and easy to use. Just install VSCode, create a project, select a language, create a file, write code, save and run it. The advantages of VSCode include cross-platform, free and open source, powerful features, rich extensions, and lightweight and fast.
 Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
VS Code can be used to write Python and provides many features that make it an ideal tool for developing Python applications. It allows users to: install Python extensions to get functions such as code completion, syntax highlighting, and debugging. Use the debugger to track code step by step, find and fix errors. Integrate Git for version control. Use code formatting tools to maintain code consistency. Use the Linting tool to spot potential problems ahead of time.





