Modify docker default gateway

Article background:
When we use Docker in a LAN, one of the most common confusions we encounter is that sometimes the network is blocked across network segments. The reason is that the gateway generated by Docker by default sometimes conflicts with our LAN segment. For example, if Docker is deployed on a machine in the 172.16 network segment, and the resulting docker0 bridge is the 172.17 network segment, then it is the same as the one used in the real environment. There is a conflict between machines in the network segment (that is, the machine in the 172.17 network segment cannot be pinged).
(Recommended tutorial: docker tutorial)
In order to avoid conflicts, the first thing that comes to mind is to change the gateway. The example is as follows (taking Centos as an example):
service docker stop # 删除docker防火墙过滤规则 iptables -t nat -F POSTROUTING # 删除docker默认网关配置 ip link set dev docker0 down ip addr del 172.17.0.1/16 dev docker0 # 增加新的docker网关配置 ip addr add 192.168.2.1/24 dev docker0 ip link set dev docker0 up # 检测是否配置成功,如果输出信息中有 192.168.5.1,则表明成功 ip addr show docker0 service docker start # 验证docker防火墙过滤规则
After this modification, will it be reliable? The answer is no, because after docker restarts, docker0 may still be rebuilt, overwriting the modifications we made. It shows that Docker’s IP rules are hard-coded and we are not allowed to change them at will. But let’s change our thinking and kill docker0 directly and rebuild a new bridge:
First we need to install the bridge creation tool brctl:
sudo yum install -y bridge-utils
Start the creation operation:
# 1.停止 Docker 服务
service docker stop
# 2.创建新的网桥(新的网段)
brctl addbr bridge0
ip addr add 192.168.2.1/24 dev bridge0
ip link set dev bridge0 up
# 3.确认网桥信息
ip addr show bridge0
# 4.修改配置文件
/etc/docker/daemon.json(如不存在则创建一个 touch daemon.json),使Docker启动时使用自定义网桥
{
"bridge": "bridge0"
}
# 5.重启 Docker
service docker start
# 确认 NAT 网络路由
iptables -t nat -L -n
# 6.删除不再使用的网桥
ip link set dev docker0 down
brctl delbr docker0
iptables -t nat -F POSTROUTINGRegarding the modified configuration made in step 4, it is to reference the new network bridge. In fact, you can also reference the new network bridge in the docker configuration file:
echo 'DOCKER_OPTS="-b=bridge0"' >> /etc/sysconfig/docker sudo service docker start
But it does not mean that we will definitely be able to see the docker custom configuration. file, if there is no default/docker or sysconfig/docker, it will be more troublesome. The solution is as follows:
$ vi /lib/systemd/system/docker.service #添加一行 $ EnvironmentFile=-/etc/default/docker 或者 $ EnvironmentFile=-/etc/sysconfig/docker #-代表ignore error #并修改 $ ExecStart=/usr/bin/docker daemon -H fd:// #改成 $ ExecStart=/usr/bin/docker daemon -H fd:// $DOCKER_OPTS #这样才能使用/etc/default/docker里定义的DOCKER_OPTS参数 $ systemctl daemon-reload 重载 $ sudo service docker restart
After completing the creation of bridge0 and transitioning from docker0 to bridge0, we can route it to confirm whether we The 172.17 network segment that we don’t want to see:
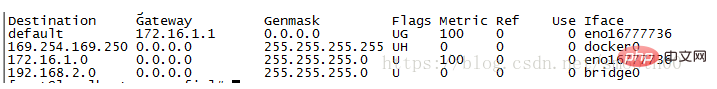
As long as it is not there, then we will not only be connected to the machines in the 172.17 network segment. If there is still one, then use ip addr del 172.17.0.1/16 dev docker0 until it is cleared (because a new docker bridge has been established, deleting the old one will not affect the use of docker).
If the network bridge created by brctl may be lost after restarting the machine, then we can write the following command into the Linux self-start script and execute it every time it restarts:
brctl addbr bridge0 ip addr add 192.168.2.1/24 dev bridge0 ip link set dev bridge0 up
Self-start Scripts can be added by adding executable statements (such as sh /opt/script.sh &) in the /etc/rc.local file. In this way, basically every time the machine is restarted, bridge0 can be guaranteed to be created and the docker service can start normally.
In addition: If you just want to solve the IP network segment conflict and are unwilling to operate the above complicated process, you can actually just change /etc/docker/daemon.json by adding the content "bip": "ip/ netmask" to change the network segment of the docker0 bridge, as follows:
[root@iZ2ze278r1bks3c1m6jdznZ ~]# cat /etc/docker/daemon.json
{
"bip":"192.168.2.1/24"
}The above is the detailed content of Modify docker default gateway. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to exit the container by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:15 PM
How to exit the container by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:15 PM
Four ways to exit Docker container: Use Ctrl D in the container terminal Enter exit command in the container terminal Use docker stop <container_name> Command Use docker kill <container_name> command in the host terminal (force exit)
 How to copy files in docker to outside
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:12 PM
How to copy files in docker to outside
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:12 PM
Methods for copying files to external hosts in Docker: Use the docker cp command: Execute docker cp [Options] <Container Path> <Host Path>. Using data volumes: Create a directory on the host, and use the -v parameter to mount the directory into the container when creating the container to achieve bidirectional file synchronization.
 How to check the name of the docker container
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
How to check the name of the docker container
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
You can query the Docker container name by following the steps: List all containers (docker ps). Filter the container list (using the grep command). Gets the container name (located in the "NAMES" column).
 How to restart docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:06 PM
How to restart docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:06 PM
How to restart the Docker container: get the container ID (docker ps); stop the container (docker stop <container_id>); start the container (docker start <container_id>); verify that the restart is successful (docker ps). Other methods: Docker Compose (docker-compose restart) or Docker API (see Docker documentation).
 How to start mysql by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
How to start mysql by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
The process of starting MySQL in Docker consists of the following steps: Pull the MySQL image to create and start the container, set the root user password, and map the port verification connection Create the database and the user grants all permissions to the database
 How to update the image of docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:03 PM
How to update the image of docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:03 PM
The steps to update a Docker image are as follows: Pull the latest image tag New image Delete the old image for a specific tag (optional) Restart the container (if needed)
 How to view the docker process
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:48 AM
How to view the docker process
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:48 AM
Docker process viewing method: 1. Docker CLI command: docker ps; 2. Systemd CLI command: systemctl status docker; 3. Docker Compose CLI command: docker-compose ps; 4. Process Explorer (Windows); 5. /proc directory (Linux).
 How to create containers for docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:18 PM
How to create containers for docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:18 PM
Create a container in Docker: 1. Pull the image: docker pull [mirror name] 2. Create a container: docker run [Options] [mirror name] [Command] 3. Start the container: docker start [Container name]






