Introduce what is Apache Flink

Introduction to Apache Flink:
Apache Flink is a framework and distributed processing engine for stateful processing on unbounded and bounded data streams calculation. Flink runs in all common cluster environments and can compute at memory speeds and at any scale.
(Recommended tutorial: apache)
Next, let’s introduce the important aspects of the Flink architecture.
Handling unbounded and bounded data
Any type of data can form an event stream. Credit card transactions, sensor measurements, machine logs, user interaction records on a website or mobile app, all this data forms a stream.
Data can be processed as unbounded or bounded streams.
1. Unbounded flow The beginning of the flow is defined, but the end of the flow is not defined. They generate data endlessly. The data of unbounded flow must be processed continuously, that is, the data needs to be processed immediately after being ingested. We cannot wait until all the data arrives before processing because the input is infinite and will never be completed at any time. Processing unbounded data often requires ingesting events in a specific order, such as the order in which they occur, to be able to infer the completeness of the results.
2. Bounded flow defines the beginning of the flow and the end of the flow. Bounded streams allow calculations to be performed after all data has been ingested. All data in bounded streams can be sorted, so ordered ingestion is not required. Bounded stream processing is often called batch processing.
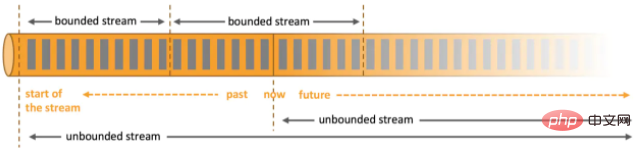
Apache Flink is good at processing unbounded and bounded data sets. Precise time control and statefulness enable Flink's runtime to run any application that handles unbounded streams. Bounded streams are processed internally by algorithms and data structures specifically designed for fixed-size data sets, resulting in excellent performance.
Deepen your understanding by exploring use cases built on top of Flink.
Deploy applications anywhere
Apache Flink is a distributed system that requires computing resources to execute applications. Flink integrates with all common cluster resource managers, such as Hadoop YARN, Apache Mesos and Kubernetes, but can also run as a standalone cluster.
Flink is designed to work well with each of the above resource managers, which is achieved through a resource-manager-specific deployment mode. Flink can interact with the current resource manager in a manner appropriate to it.
When you deploy a Flink application, Flink automatically identifies the required resources based on the application's configured parallelism and requests these resources from the resource manager. In the event of a failure, Flink replaces the failed container by requesting new resources. All communication to submit or control applications occurs through REST calls, which simplifies the integration of Flink into a variety of environments.
Run applications at any scale
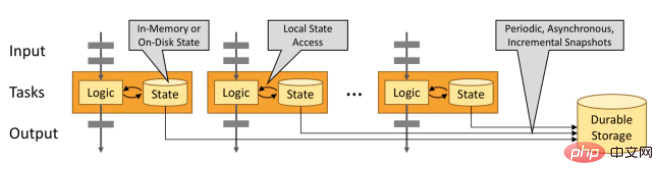
Flink is designed to run stateful streaming applications at any scale. Therefore, the application is parallelized into potentially thousands of tasks that are distributed across the cluster and executed concurrently. So applications can take advantage of endless CPU, memory, disk, and network IO. And Flink makes it easy to maintain very large application state. Its asynchronous and incremental checkpointing algorithm has minimal impact on processing latency while ensuring the consistency of exactly-once state.
Flink users have reported some impressive scalability numbers in their production environments
Processing trillions of events per day, applications maintaining terabytes of state, and applications running on data Run on thousands of cores.
Exploiting memory performance
Stateful Flink programs are optimized for local state access. The state of a task is always maintained in memory or, if the state size exceeds available memory, is saved in an on-disk data structure that can be accessed efficiently. Tasks perform all computations by accessing local (usually in-memory) state, resulting in very low processing latency. Flink ensures exact-once state consistency in failure scenarios by regularly and asynchronously persisting local state storage.
The above is the detailed content of Introduce what is Apache Flink. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to set the cgi directory in apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:18 PM
How to set the cgi directory in apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:18 PM
To set up a CGI directory in Apache, you need to perform the following steps: Create a CGI directory such as "cgi-bin", and grant Apache write permissions. Add the "ScriptAlias" directive block in the Apache configuration file to map the CGI directory to the "/cgi-bin" URL. Restart Apache.
 How to connect to the database of apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
How to connect to the database of apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
Apache connects to a database requires the following steps: Install the database driver. Configure the web.xml file to create a connection pool. Create a JDBC data source and specify the connection settings. Use the JDBC API to access the database from Java code, including getting connections, creating statements, binding parameters, executing queries or updates, and processing results.
 What to do if the apache80 port is occupied
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:24 PM
What to do if the apache80 port is occupied
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:24 PM
When the Apache 80 port is occupied, the solution is as follows: find out the process that occupies the port and close it. Check the firewall settings to make sure Apache is not blocked. If the above method does not work, please reconfigure Apache to use a different port. Restart the Apache service.
 How to view your apache version
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:15 PM
How to view your apache version
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:15 PM
There are 3 ways to view the version on the Apache server: via the command line (apachectl -v or apache2ctl -v), check the server status page (http://<server IP or domain name>/server-status), or view the Apache configuration file (ServerVersion: Apache/<version number>).
 How to view the apache version
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:00 PM
How to view the apache version
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:00 PM
How to view the Apache version? Start the Apache server: Use sudo service apache2 start to start the server. View version number: Use one of the following methods to view version: Command line: Run the apache2 -v command. Server Status Page: Access the default port of the Apache server (usually 80) in a web browser, and the version information is displayed at the bottom of the page.
 How to configure zend for apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 12:57 PM
How to configure zend for apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 12:57 PM
How to configure Zend in Apache? The steps to configure Zend Framework in an Apache Web Server are as follows: Install Zend Framework and extract it into the Web Server directory. Create a .htaccess file. Create the Zend application directory and add the index.php file. Configure the Zend application (application.ini). Restart the Apache Web server.
 How to solve the problem that apache cannot be started
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:21 PM
How to solve the problem that apache cannot be started
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:21 PM
Apache cannot start because the following reasons may be: Configuration file syntax error. Conflict with other application ports. Permissions issue. Out of memory. Process deadlock. Daemon failure. SELinux permissions issues. Firewall problem. Software conflict.
 Apache Performance Tuning: Optimizing Speed & Efficiency
Apr 04, 2025 am 12:11 AM
Apache Performance Tuning: Optimizing Speed & Efficiency
Apr 04, 2025 am 12:11 AM
Methods to improve Apache performance include: 1. Adjust KeepAlive settings, 2. Optimize multi-process/thread parameters, 3. Use mod_deflate for compression, 4. Implement cache and load balancing, 5. Optimize logging. Through these strategies, the response speed and concurrent processing capabilities of Apache servers can be significantly improved.






