 Backend Development
Backend Development
 C#.Net Tutorial
C#.Net Tutorial
 Does a for loop execute the loop body statement first and then evaluate the expression?
Does a for loop execute the loop body statement first and then evaluate the expression?
Does a for loop execute the loop body statement first and then evaluate the expression?
No, the for loop first judges the expression and then executes the loop body statement. The general form is "for (expression 1; expression 2; expression 3) {loop body}"; first execute "expression 1"; then execute "expression 2", if its value is true (non-0), Then execute the loop body, otherwise end the loop; execute "expression 3" after executing the loop body.

The general form of a for loop is:
for(表达式1; 表达式2; 表达式3){
语句块
}Its running process is:
1) Execute "Expression 1" first.
2) Execute "expression 2" again. If its value is true (non-0), execute the loop body, otherwise end the loop.
3) Execute "expression 3" after executing the loop body.
4) Repeat steps 2) and 3) until the value of "expression 2" is false, then end the loop.
In the above steps, 2) and 3) are a loop and will be executed repeatedly. The main function of the for statement is to continuously execute steps 2) and 3).
"Expression 1" is only executed during the first loop and will not be executed again in the future. This can be considered an initialization statement. "Expression 2" is generally a relational expression, which determines whether to continue the next loop, which is called the "loop condition". "Expression 3" is often an expression with an increment or decrement operation, so that the loop condition gradually becomes "not true".
The execution process of the for loop can be represented by the following figure:
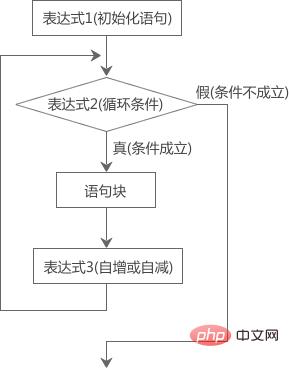
Let’s analyze the “calculation of adding from 1 to 100 and" code:
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
int i, sum=0;
for(i=1; i<=100; i++){
sum+=i;
}
printf("%d\n",sum);
return 0;
} Running result:
5050
Code analysis:
1) When executing the for statement, first assign an initial value to i 1. Determine whether i<=100 is true; because i=1 and i<=100 are true at this time, the loop body is executed. After the execution of the loop body ends (the value of sum is 1), i is calculated again.
2) During the second loop, the value of i is 2, i<=100 is established, and the loop body continues to be executed. After the execution of the loop body ends (the value of sum is 3), i is calculated again.
3) Repeat step 2) until the 101st loop. At this time, the value of i is 101, and i<=100 is not true, so the loop ends.
From this we can summarize the general form of the for loop:
for(初始化语句; 循环条件; 自增或自减){
语句块
}The three expressions in the for loop
" in the for loop "Expression 1 (initialization condition)", "Expression 2 (loop condition)" and "Expression 3 (self-increment or self-decrement)" are all optional and can be omitted (but the semicolon; must be retained).
1) Modify the code for "sum from 1 to 100" and omit "expression 1 (initialization condition)":
int i = 1, sum = 0;
for( ; i<=100; i++){
sum+=i;
}You can see that i=1 Moved outside the for loop.
2) If "expression 2 (loop condition)" is omitted, it will become an infinite loop if no other processing is done. For example:
for(i=1; ; i++) sum=sum+i;
is equivalent to:
i=1;
while(1){
sum=sum+i;
i++;
}The so-called infinite loop means that the loop condition is always true, and the loop will continue and never end. Infinite loops are very harmful to the program and must be avoided.
3) If "expression 3 (self-increment or self-decrement)" is omitted, the variables in "expression 2 (loop condition)" will not be modified. In this case, the modified variables can be added to the loop body statement. For example:
for( i=1; i<=100; ){
sum=sum+i;
i++;
}4) "Expression 1 (initialization statement)" and "Expression 3 (self-increment or self-decrement)" are omitted. For example:
for( ; i<=100 ; ){
sum=sum+i;
i++;
}is equivalent to:
while(i<=100){
sum=sum+i;
i++;
}5) 3 expressions can be omitted at the same time. For example:
for( ; ; ) 语句
is equivalent to:
while(1) 语句
6) "Expression 1" can be an initialization statement or other statements. For example:
for( sum=0; i<=100; i++ ) sum=sum+i;
7) "Expression 1" and "Expression 3" can be a simple expression or a comma expression.
for( sum=0,i=1; i<=100; i++ ) sum=sum+i;
or:
for( i=0,j=100; i<=100; i++,j-- ) k=i+j;
8) "Expression 2" is generally a relational expression or a logical expression, but it can also be a numerical value or character. As long as its value is non-zero, the loop body will be executed. . For example:
for( i=0; (c=getchar())!='\n'; i+=c );
Another example:
for( ; (c=getchar())!='\n' ; )
printf("%c",c);Related recommendations: "c Language Tutorial"
The above is the detailed content of Does a for loop execute the loop body statement first and then evaluate the expression?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to use php to find odd numbers within 100
Dec 23, 2022 pm 06:54 PM
How to use php to find odd numbers within 100
Dec 23, 2022 pm 06:54 PM
Implementation steps: 1. Use the for statement control range to traverse the numbers from 1 to 100, the syntax is "for ($i = 1; $i <= 100; $i++) {loop body code}"; 2. In the loop body, Just use the if statement and the "%" operator to obtain and output odd numbers. The syntax is "if($i % 2 != 0){echo $i." ";}".
 What is the execution order of for loop in PHP
Sep 22, 2021 pm 06:24 PM
What is the execution order of for loop in PHP
Sep 22, 2021 pm 06:24 PM
Execution sequence: 1. Execute the "initialization expression"; 2. Execute the "conditional judgment expression". If the value of the expression is true, execute the "loop body", otherwise the loop ends; 3. After executing the loop body, execute "Variable update expression"; 4. After the variable is updated, enter the next loop until the condition judgment value is false, ending the loop.
 Does mysql have a for loop?
Mar 30, 2023 pm 08:26 PM
Does mysql have a for loop?
Mar 30, 2023 pm 08:26 PM
MySQL does not have a for loop. MySQL does not support for loop statements. It only supports three loop statements: WHILE, REPEAT and LOOP. MySQL provides loop statements, allowing you to repeatedly execute a SQL code block based on conditions.
 How to use for loop in Python
Oct 25, 2023 pm 12:18 PM
How to use for loop in Python
Oct 25, 2023 pm 12:18 PM
How to use the for loop in Python Python is a simple and easy-to-use programming language, and the for loop is one of the most commonly used tools. By using for loops, we can loop through a series of data, perform effective processing and operations, and improve the efficiency of the code. Below, I will introduce how to use the for loop in Python through specific code examples. Basic for loop syntax In Python, the syntax of a for loop is as follows: for variable in iterable object:
 JS loop learning: use of for loop statements (detailed examples)
Aug 03, 2022 pm 06:45 PM
JS loop learning: use of for loop statements (detailed examples)
Aug 03, 2022 pm 06:45 PM
In the previous article "JS Loop Learning: The Use of While Loop Statements (Detailed Examples)", we briefly learned about the while loop and the do while loop, and today we will introduce another kind of loop-the for loop statement. I hope it will be useful to everyone. Helped!
 How to separate even and odd numbers in an array using for loop in C language?
Aug 25, 2023 pm 03:09 PM
How to separate even and odd numbers in an array using for loop in C language?
Aug 25, 2023 pm 03:09 PM
An array is a group of related data items stored under a single name. For example intStudent[30];//student is an array name, a collection of 30 data items containing a single variable name Operational search of array - used to find whether a specific element exists sorting - it helps to arrange the elements in the array in ascending order or descending sort. Traversal - It processes each element in the array sequentially. Insertion - It helps to insert elements in array. Delete - It helps in deleting elements from an array. elements in the array. The logic of finding even numbers in an array is as follows - for(i=0;i<size;i++){ if(a[i]%2==0){
 Handling large arrays in Go: use for range or for loop?
Jul 24, 2023 pm 02:47 PM
Handling large arrays in Go: use for range or for loop?
Jul 24, 2023 pm 02:47 PM
We know that Go’s syntax is relatively concise. It does not provide loop control syntax such as while, do...while, etc. supported by C, but only retains one statement, the for loop.
 How to use for loop to implement flip operation in Go language
Mar 24, 2024 pm 02:15 PM
How to use for loop to implement flip operation in Go language
Mar 24, 2024 pm 02:15 PM
Title: How to use for loops to implement flip operations in Go language. In Go language, you can easily flip data structures such as arrays and slices by using for loops. In this article, we will introduce how to use for loops to flip arrays and slices, and give specific code examples. Operation of flipping an array First, let's look at how to flip an array through a for loop. We define an array containing integer elements and flip it using a for loop. packagemain





