Django+Layui background layout introduction

Layui background layout:
1. Top sidebar of background layout
<div class="layui-header">
<div class="layui-logo">layui 后台布局</div>
<!-- 头部区域(可配合layui已有的水平导航) -->
<ul class="layui-nav layui-layout-left">
<li class="layui-nav-item"><a href="">控制台</a></li>
<li class="layui-nav-item"><a href="">商品管理</a></li>
<li class="layui-nav-item"><a href="">用户</a></li>
<li class="layui-nav-item">
<a href="javascript:;">其它系统</a>
<dl class="layui-nav-child">
<dd><a href="">邮件管理</a></dd>
<dd><a href="">消息管理</a></dd>
<dd><a href="">授权管理</a></dd>
</dl>
</li>
</ul>
<ul class="layui-nav layui-layout-right">
<li class="layui-nav-item">
<a href="javascript:;">
<img class="layui-nav-img lazy" src="/static/imghw/default1.png" data-src="http://t.cn/RCzsdCq" alt="Django+Layui background layout introduction" >
{{request.user.username}}
</a>
<dl class="layui-nav-child">
<dd><a href="">基本资料</a></dd>
<dd><a href="">安全设置</a></dd>
</dl>
</li>
<li class="layui-nav-item"><a href="">退了</a></li>
</ul>
</div>The line with orange background in the code is the current login passed in Django The user's username.
The final effect is as follows:

2. Sidebar of background layout
The sidebar needs to dynamically load nodes and sub-nodes. Therefore, you need to first establish the model of nodes and sub-nodes in Django. The model code is as follows:
# 节点类
class NavigationProfile(models.Model):
name=models.CharField(max_length=20,verbose_name='节点名称')
url=models.CharField(max_length=50,verbose_name='链接地址')
iconCls=models.CharField(max_length=50,verbose_name='图标icon')
class Meta:
verbose_name='节点名称'
verbose_name_plural=verbose_name
def __str__(self):
return self.name
# 子节点类
class NavigationSubProfile(models.Model):
name=models.CharField(max_length=20,verbose_name='子节点名称')
url=models.CharField(max_length=50,verbose_name='链接地址')
iconCls=models.CharField(max_length=50,verbose_name='图标icon')
parent=models.ForeignKey(NavigationProfile,on_delete=models.CASCADE,verbose_name='父节点')
class Meta:
verbose_name='子节点名称'
verbose_name_plural=verbose_name
def __str__(self):
return self.nameThe code in Django views is as follows:
def open_index(request):
if request.user.is_authenticated == False:
return HttpResponseRedirect('/account/login/')
else:
navigation = NavigationProfile.objects.all()
dict = []
for nav in navigation:
dic = {}
id = nav.id
dic['id'] = nav.id
dic['text'] = nav.name
dic['url'] = nav.url
dic['iconCls'] = nav.iconCls
dic['nid'] = 0
sub_navigation = NavigationSubProfile.objects.filter(parent_id=id)
sub_dict = []
for sub_nav in sub_navigation:
sub_dic = {}
sub_dic['id'] = sub_nav.id
sub_dic['text'] = sub_nav.name
sub_dic['url'] = sub_nav.url
sub_dic['iconCls'] = sub_nav.iconCls
sub_dic['nid'] = sub_nav.parent_id
sub_dict.append(sub_dic)
dic["children"] = sub_dict
dict.append(dic)30 return render(request,'index.html',{'dict':dict})The Django urls code is as follows:
urlpatterns = [
path('get-navigationProfile/',views.get_navigationProfile,name='get_navigationProfile'),
]The Html sidebar code is as follows:
<div class="layui-side layui-bg-black">
<div class="layui-side-scroll">
<!-- 左侧导航区域(可配合layui已有的垂直导航) -->
<ul class="layui-nav layui-nav-tree" lay-filter="test">
{% for dic in dict %}
<li class="layui-nav-item">
<a class="" href="javascript:;">{{ dic.text }}</a>
<dl class="layui-nav-child">
{% for child in dic.children %}
<dd><a href="javascript:;" data-id="{{ child.id }}"
data-url="{{ child.url }}">{{ child.text }}</a></dd>
{% endfor %}
</dl>
</li>
{% endfor %}
</ul>
</div>
</div>Final rendering
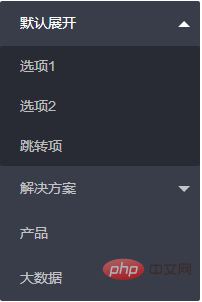
For more layui knowledge, please pay attention to the layui usage tutorial column.
The above is the detailed content of Django+Layui background layout introduction. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to set up jump on layui login page
Apr 04, 2024 am 03:12 AM
How to set up jump on layui login page
Apr 04, 2024 am 03:12 AM
Layui login page jump setting steps: Add jump code: Add judgment in the login form submit button click event, and jump to the specified page through window.location.href after successful login. Modify the form configuration: add a hidden input field to the form element of lay-filter="login", with the name "redirect" and the value being the target page address.
 How to get form data in layui
Apr 04, 2024 am 03:39 AM
How to get form data in layui
Apr 04, 2024 am 03:39 AM
layui provides a variety of methods for obtaining form data, including directly obtaining all field data of the form, obtaining the value of a single form element, using the formAPI.getVal() method to obtain the specified field value, serializing the form data and using it as an AJAX request parameter, and listening Form submission event gets data.
 What is the difference between layui and vue?
Apr 04, 2024 am 03:54 AM
What is the difference between layui and vue?
Apr 04, 2024 am 03:54 AM
The difference between layui and Vue is mainly reflected in functions and concerns. Layui focuses on rapid development of UI elements and provides prefabricated components to simplify page construction; Vue is a full-stack framework that focuses on data binding, component development and state management, and is more suitable for building complex applications. Layui is easy to learn and suitable for quickly building pages; Vue has a steep learning curve but helps build scalable and easy-to-maintain applications. Depending on the project needs and developer skill level, the appropriate framework can be selected.
 How layui implements self-adaptation
Apr 26, 2024 am 03:00 AM
How layui implements self-adaptation
Apr 26, 2024 am 03:00 AM
Adaptive layout can be achieved by using the responsive layout function of the layui framework. The steps include: referencing the layui framework. Define an adaptive layout container and set the layui-container class. Use responsive breakpoints (xs/sm/md/lg) to hide elements under specific breakpoints. Specify element width using the grid system (layui-col-). Create spacing via offset (layui-offset-). Use responsive utilities (layui-invisible/show/block/inline) to control the visibility of elements and how they appear.
 How to transfer data in layui
Apr 26, 2024 am 03:39 AM
How to transfer data in layui
Apr 26, 2024 am 03:39 AM
The method of using layui to transmit data is as follows: Use Ajax: Create the request object, set the request parameters (URL, method, data), and process the response. Use built-in methods: Simplify data transfer using built-in methods such as $.post, $.get, $.postJSON, or $.getJSON.
 What does layui mean?
Apr 04, 2024 am 04:33 AM
What does layui mean?
Apr 04, 2024 am 04:33 AM
layui is a front-end UI framework that provides a wealth of UI components, tools and functions to help developers quickly build modern, responsive and interactive web applications. Its features include: flexible and lightweight, modular design, rich components, Powerful tools and easy customization. It is widely used in the development of various web applications, including management systems, e-commerce platforms, content management systems, social networks and mobile applications.
 What language is layui framework?
Apr 04, 2024 am 04:39 AM
What language is layui framework?
Apr 04, 2024 am 04:39 AM
The layui framework is a JavaScript-based front-end framework that provides a set of easy-to-use UI components and tools to help developers quickly build responsive web applications. Its features include: modular, lightweight, responsive, and has complete documentation and community support. layui is widely used in the development of management backend systems, e-commerce websites, and mobile applications. The advantages are quick start-up, improved efficiency, and easy maintenance. The disadvantages are poor customization and slow technology updates.
 The difference between layui framework and vue framework
Apr 26, 2024 am 01:27 AM
The difference between layui framework and vue framework
Apr 26, 2024 am 01:27 AM
layui and vue are front-end frameworks. layui is a lightweight library that provides UI components and tools; vue is a comprehensive framework that provides UI components, state management, data binding, routing and other functions. layui is based on a modular architecture, and vue is based on a componentized architecture. layui has a smaller ecosystem, vue has a large and active ecosystem. The learning curve of layui is low, and the learning curve of vue is steep. Layui is suitable for small projects and rapid development of UI components, while vue is suitable for large projects and scenarios that require rich functions.






