Apache server security settings

Securing your web server is very important, which means allowing others to view only some of the information and protecting the data and limiting access.
These are common things to enhance the security of your Apache web server. (Recommended learning: Apache Server)
1. Hide Apache version and operating system information. Apache displays its version and operating system name incorrectly, as shown below Screen shot shown.
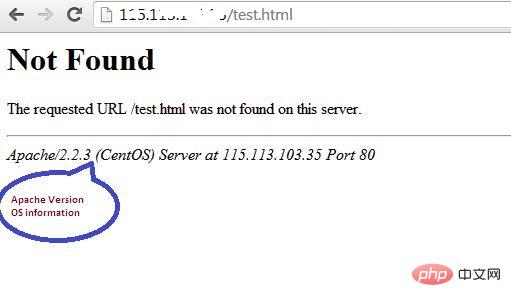
#Hackers can use this information to launch attacks using exposed vulnerabilities in specific versions of servers or operating systems. To prevent Apache webserver from displaying this information, we can modify the server signature option provided in the apache configuration file. By default it is on, set it to off.
vim /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf<br/>
The modification is:
ServerSignature Off<br/>ServerTokens Prod<br/>
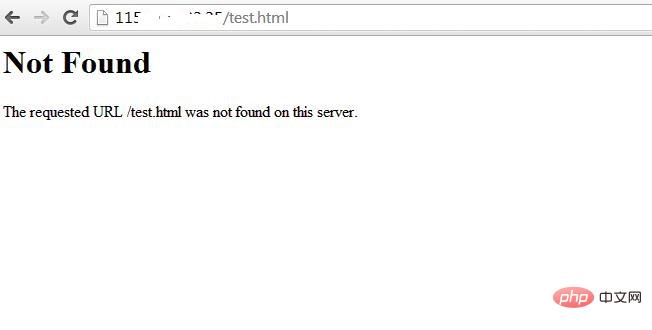
We also set up "ServerTokens Prod", which tells the web server to only return apache and prohibits operating system major and minor versions . After modifying the configuration file, the Apache web server must be restarted/reloaded for it to take effect.
service httpd restart<br/>
After modifying and restarting the Apache server, you should see similar results -
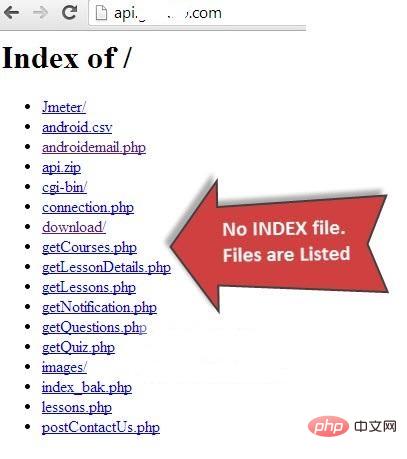
2. Disable directory listing
If there is no index file in the document root directory (such as: index.html, index.php, index.html, etc.), then by default, the apache web server will display all the contents of the document root directory.
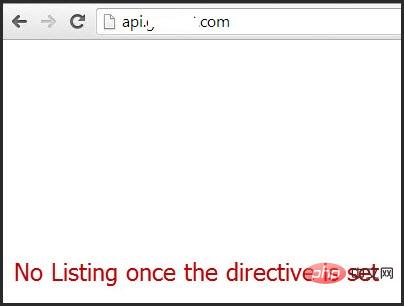
This feature can be turned off for a specific directory through the options directive provided in the Apache configuration file.
<Directory /var/www/html><br/> Options -Indexes<br/></Directory><br/>
3. Disable unnecessary modules
It is best to disable all unused unnecessary modules, you can See the list of enabled modules in the apache configuration file -
[root@amsterdam ~]#httpd –M<br/>perl_module (shared)<br/>php5_module (shared)<br/>proxy_ajp_module (shared)<br/>python_module (shared)<br/>ssl_module (shared)<br/>
Many of the listed modules can be disabled like mod_imap, mod_include, mod_info, mod_userdir, mod_autoindex as they are hardly used by any production Used by web server.
vi /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf<br/>
Then comment out -
#LoadModule auth_digest_module modules/mod_auth_digest.so<br/>
After commenting the module, save the file. Use the following command to restart the apache service.
/etc/init.d/httpd restart/<br/>
4. Use mod_evasive to counter DoS attacks
If you want to protect your web server from DoS (i.e. Denial of Service), you must enable the module mod_evasive. It is a third-party module that detects DoS attacks and prevents them from causing damage far beyond the course of their operation.
5. Limit request size
Apache does not have any limit on the total size of http requests that may lead to a DoS attack. The request size of the Apache directive LimitRequestBody can be limited using directory tags.
Depending on the requirements, this value can be set from 0 to 2GB (i.e. 2147483647 bytes).
<Directory "/var/www/html/uploads"><br/> LimitRequestBody 512000<br/></Directory><br/>
The above is the detailed content of Apache server security settings. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to set the cgi directory in apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:18 PM
How to set the cgi directory in apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:18 PM
To set up a CGI directory in Apache, you need to perform the following steps: Create a CGI directory such as "cgi-bin", and grant Apache write permissions. Add the "ScriptAlias" directive block in the Apache configuration file to map the CGI directory to the "/cgi-bin" URL. Restart Apache.
 What to do if the apache80 port is occupied
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:24 PM
What to do if the apache80 port is occupied
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:24 PM
When the Apache 80 port is occupied, the solution is as follows: find out the process that occupies the port and close it. Check the firewall settings to make sure Apache is not blocked. If the above method does not work, please reconfigure Apache to use a different port. Restart the Apache service.
 How to connect to the database of apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
How to connect to the database of apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
Apache connects to a database requires the following steps: Install the database driver. Configure the web.xml file to create a connection pool. Create a JDBC data source and specify the connection settings. Use the JDBC API to access the database from Java code, including getting connections, creating statements, binding parameters, executing queries or updates, and processing results.
 How to view your apache version
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:15 PM
How to view your apache version
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:15 PM
There are 3 ways to view the version on the Apache server: via the command line (apachectl -v or apache2ctl -v), check the server status page (http://<server IP or domain name>/server-status), or view the Apache configuration file (ServerVersion: Apache/<version number>).
 How to view the apache version
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:00 PM
How to view the apache version
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:00 PM
How to view the Apache version? Start the Apache server: Use sudo service apache2 start to start the server. View version number: Use one of the following methods to view version: Command line: Run the apache2 -v command. Server Status Page: Access the default port of the Apache server (usually 80) in a web browser, and the version information is displayed at the bottom of the page.
 How to configure zend for apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 12:57 PM
How to configure zend for apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 12:57 PM
How to configure Zend in Apache? The steps to configure Zend Framework in an Apache Web Server are as follows: Install Zend Framework and extract it into the Web Server directory. Create a .htaccess file. Create the Zend application directory and add the index.php file. Configure the Zend application (application.ini). Restart the Apache Web server.
 How to delete more than server names of apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:09 PM
How to delete more than server names of apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:09 PM
To delete an extra ServerName directive from Apache, you can take the following steps: Identify and delete the extra ServerName directive. Restart Apache to make the changes take effect. Check the configuration file to verify changes. Test the server to make sure the problem is resolved.
 How to solve the problem that apache cannot be started
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:21 PM
How to solve the problem that apache cannot be started
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:21 PM
Apache cannot start because the following reasons may be: Configuration file syntax error. Conflict with other application ports. Permissions issue. Out of memory. Process deadlock. Daemon failure. SELinux permissions issues. Firewall problem. Software conflict.






