What are the redis cluster solutions?

The amount of Redis data is increasing day by day, and more and more companies are using it. It is not only used for caching, but also tends to store this piece. This will inevitably promote the development of clusters and various companies. I am also collecting cluster solutions suitable for myself. Currently, the following cluster architectures are commonly used in the industry. Most of them use sharding technology to solve a series of problems caused by the increase of single instance memory.
This article briefly introduces five solutions:
Official cluster solution
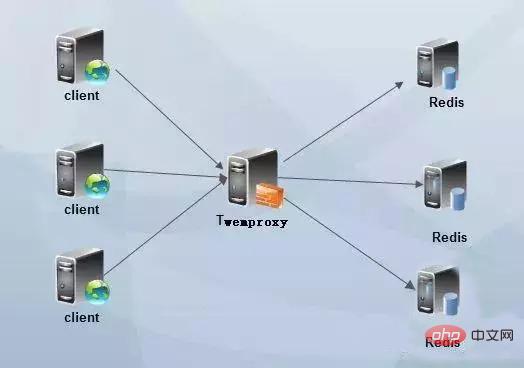
##twemproxy proxy solution
Sentinel mode
codis
Client sharding
Official cluser solution
Starting from redis version 3.0, redis-cluster cluster is supported. redis-cluster adopts a centerless structure. Each node saves data and the entire cluster status, and each node is connected to other nodes. redis-cluster is a server-side sharding technology. redis-cluster architecture diagram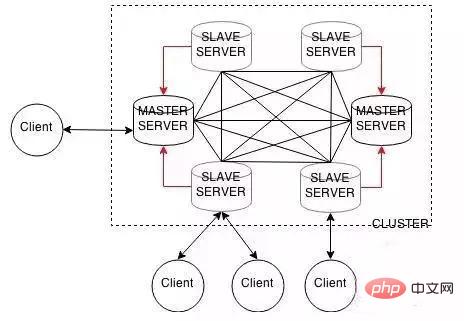
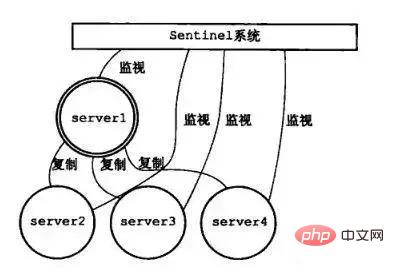

If the time since the last valid reply to the PING command for an instance exceeds the value specified by the down-after-milliseconds option, the instance will be marked as subjectively offline by Sentinel.
If a Master is marked as subjective offline, all Sentinels that are monitoring the Master must confirm once per second that the Master has indeed entered the subjective offline state.
When a sufficient number of Sentinels (greater than or equal to the value specified in the configuration file) confirm that the Master has indeed entered a subjective offline state within the specified time range, the Master will be marked as objectively offline.
Under normal circumstances, each Sentinel will send INFO commands to all Masters and Slaves it knows once every 10 seconds.
When the Master is marked as objectively offline by Sentinel, the frequency of Sentinel sending INFO commands to all slaves of the offline Master will be changed from once every 10 seconds to once every second.
If there are not enough Sentinels to agree that the Master has been offline, the Master's objective offline status will be removed. If the Master returns a valid value to Sentinel's PING command again, the Master's subjective offline status will be removed.
codis
codis is a distributed Redis solution, open sourced by Wandoujia. For upper-layer applications, there is no obvious difference between connecting to codis proxy and connecting to the native redis server. The upper-layer The application can be used like a stand-alone redis. The bottom layer of codis will handle the forwarding of requests, non-stop data migration, etc. All the subsequent things are transparent to the previous client. You can simply think that the connection behind is A redis service with unlimited memory.
Client Sharding
The logic of partitioning is implemented on the client, and the client chooses which node to request. The solution can refer to consistent hashing. This solution is usually suitable for scenarios where users have complete control over the behavior of the client.
Summary: There is no best solution, only the most suitable solution.
For more Redis-related technical articles, please visit the Redis Tutorial column to learn!
The above is the detailed content of What are the redis cluster solutions?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear Redis data: Use the FLUSHALL command to clear all key values. Use the FLUSHDB command to clear the key value of the currently selected database. Use SELECT to switch databases, and then use FLUSHDB to clear multiple databases. Use the DEL command to delete a specific key. Use the redis-cli tool to clear the data.
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
How to use the redis command
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:45 PM
Using the Redis directive requires the following steps: Open the Redis client. Enter the command (verb key value). Provides the required parameters (varies from instruction to instruction). Press Enter to execute the command. Redis returns a response indicating the result of the operation (usually OK or -ERR).
 How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
How to use redis lock
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
Using Redis to lock operations requires obtaining the lock through the SETNX command, and then using the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time. The specific steps are: (1) Use the SETNX command to try to set a key-value pair; (2) Use the EXPIRE command to set the expiration time for the lock; (3) Use the DEL command to delete the lock when the lock is no longer needed.
 How to configure Lua script execution time in centos redis
Apr 14, 2025 pm 02:12 PM
How to configure Lua script execution time in centos redis
Apr 14, 2025 pm 02:12 PM
On CentOS systems, you can limit the execution time of Lua scripts by modifying Redis configuration files or using Redis commands to prevent malicious scripts from consuming too much resources. Method 1: Modify the Redis configuration file and locate the Redis configuration file: The Redis configuration file is usually located in /etc/redis/redis.conf. Edit configuration file: Open the configuration file using a text editor (such as vi or nano): sudovi/etc/redis/redis.conf Set the Lua script execution time limit: Add or modify the following lines in the configuration file to set the maximum execution time of the Lua script (unit: milliseconds)
 How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
Use the Redis command line tool (redis-cli) to manage and operate Redis through the following steps: Connect to the server, specify the address and port. Send commands to the server using the command name and parameters. Use the HELP command to view help information for a specific command. Use the QUIT command to exit the command line tool.
 How to set the redis expiration policy
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:03 PM
How to set the redis expiration policy
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:03 PM
There are two types of Redis data expiration strategies: periodic deletion: periodic scan to delete the expired key, which can be set through expired-time-cap-remove-count and expired-time-cap-remove-delay parameters. Lazy Deletion: Check for deletion expired keys only when keys are read or written. They can be set through lazyfree-lazy-eviction, lazyfree-lazy-expire, lazyfree-lazy-user-del parameters.






