How to use Flask blueprint in python (with code)
The content of this article is about how to use Flask blueprint in python (with code). It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to you.
Blueprint
We have learned some basic usage of Flask through code before. Now a problem arises. We have more and more functions to do. Is routing Should it be placed in the run file? For example, we have defined some routes in different files. If we want to access them, do we need to open many different services?
Blueprints are provided in Flask, specifically used for modularization of Flask.
Flask uses the concept of blueprints to make application components and support common patterns within or across applications. Blueprints can greatly simplify how large applications work and provide a central means for Flask extensions to register actions on the application. The Blueprint object works similarly to the Flask application object, but it is not actually an application. Rather, it is a blueprint for how to structure or extend an application.
In short, blueprints can make our program more modular. Routes for different functions can be placed under different modules, and finally concentrated into the startup class.
First, create a new flask project file and create a file structure as shown below:
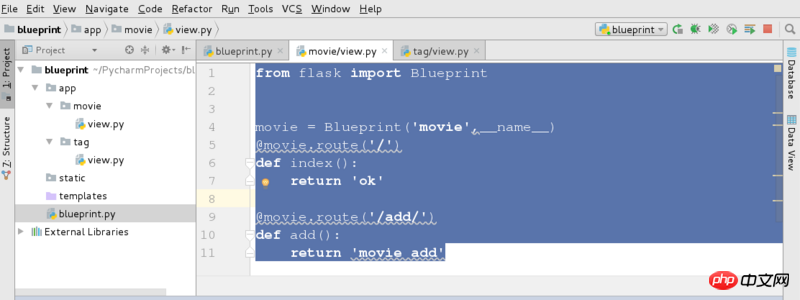
Main running file
from app.movie.view import movie as movie_bp from app.tag.view import tag as tag_bp from flask import Flask if __name__ == '__main__': app = Flask(__name__) app.register_blueprint(tag_bp,url_prefix='/tag') app.register_blueprint(movie_bp,url_prefix='/movie') app.run(port=9099)
Module One: Tag
All routing and view functions are still written in a separate file, named here view.py
from flask import Blueprint
tag = Blueprint('tag',__name__)
@tag.route('/')
def index():
return 'ok'
@tag.route('/add/')
def add():
return 'tag add'Module Two: Movie
All routing and view functions are still written in a separate file, named here view.py
from flask import Blueprint
movie = Blueprint('movie',__name__)
@movie.route('/')
def index():
return 'ok'
@movie.route('/add/')
def add():
return 'movie add'Running results
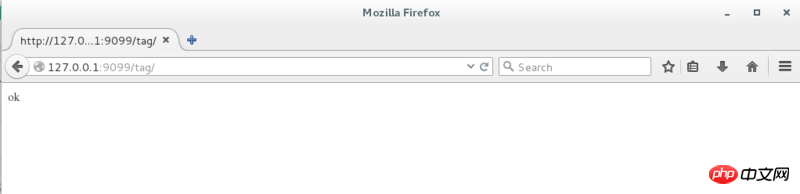
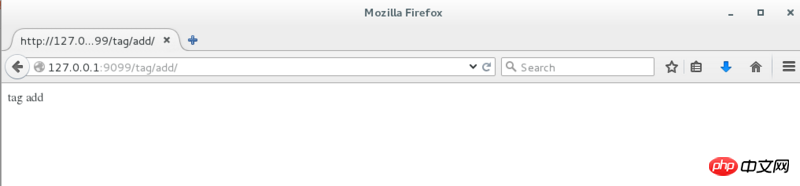
The above is the detailed content of How to use Flask blueprint in python (with code). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP is mainly procedural programming, but also supports object-oriented programming (OOP); Python supports a variety of paradigms, including OOP, functional and procedural programming. PHP is suitable for web development, and Python is suitable for a variety of applications such as data analysis and machine learning.
 Laravel Introduction Example
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:45 PM
Laravel Introduction Example
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:45 PM
Laravel is a PHP framework for easy building of web applications. It provides a range of powerful features including: Installation: Install the Laravel CLI globally with Composer and create applications in the project directory. Routing: Define the relationship between the URL and the handler in routes/web.php. View: Create a view in resources/views to render the application's interface. Database Integration: Provides out-of-the-box integration with databases such as MySQL and uses migration to create and modify tables. Model and Controller: The model represents the database entity and the controller processes HTTP requests.
 Linux Architecture: Unveiling the 5 Basic Components
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Linux Architecture: Unveiling the 5 Basic Components
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:04 AM
The five basic components of the Linux system are: 1. Kernel, 2. System library, 3. System utilities, 4. Graphical user interface, 5. Applications. The kernel manages hardware resources, the system library provides precompiled functions, system utilities are used for system management, the GUI provides visual interaction, and applications use these components to implement functions.
 PHP and Python: A Deep Dive into Their History
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP and Python: A Deep Dive into Their History
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP originated in 1994 and was developed by RasmusLerdorf. It was originally used to track website visitors and gradually evolved into a server-side scripting language and was widely used in web development. Python was developed by Guidovan Rossum in the late 1980s and was first released in 1991. It emphasizes code readability and simplicity, and is suitable for scientific computing, data analysis and other fields.
 Solve database connection problem: a practical case of using minii/db library
Apr 18, 2025 am 07:09 AM
Solve database connection problem: a practical case of using minii/db library
Apr 18, 2025 am 07:09 AM
I encountered a tricky problem when developing a small application: the need to quickly integrate a lightweight database operation library. After trying multiple libraries, I found that they either have too much functionality or are not very compatible. Eventually, I found minii/db, a simplified version based on Yii2 that solved my problem perfectly.
 Laravel framework installation method
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:54 PM
Laravel framework installation method
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:54 PM
Article summary: This article provides detailed step-by-step instructions to guide readers on how to easily install the Laravel framework. Laravel is a powerful PHP framework that speeds up the development process of web applications. This tutorial covers the installation process from system requirements to configuring databases and setting up routing. By following these steps, readers can quickly and efficiently lay a solid foundation for their Laravel project.
 MySQL vs. Other Programming Languages: A Comparison
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:22 AM
MySQL vs. Other Programming Languages: A Comparison
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:22 AM
Compared with other programming languages, MySQL is mainly used to store and manage data, while other languages such as Python, Java, and C are used for logical processing and application development. MySQL is known for its high performance, scalability and cross-platform support, suitable for data management needs, while other languages have advantages in their respective fields such as data analytics, enterprise applications, and system programming.
 Python vs. C : Learning Curves and Ease of Use
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python vs. C : Learning Curves and Ease of Use
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python is easier to learn and use, while C is more powerful but complex. 1. Python syntax is concise and suitable for beginners. Dynamic typing and automatic memory management make it easy to use, but may cause runtime errors. 2.C provides low-level control and advanced features, suitable for high-performance applications, but has a high learning threshold and requires manual memory and type safety management.






