Application examples of flask in python (code)
The content of this article is about the application examples (code) of flask in python. It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to you.
Bind user login information to the database
Requires the user's login information to be sent to the background for comparison with the database to determine whether the user can log in
#config.py文件,用来创建远程连接的类 class DB: HOST = '192.168.1.227' USER= 'root' PASSWD = 'sheen' PORT = 3306 DBNAME = 'test'
# 主程序
import pymysql
from config import DB
# 1. 创建连接
conn = pymysql.connect(
host=DB.HOST,
user=DB.USER,
passwd=DB.PASSWD,
port=DB.PORT,
db=DB.DBNAME,
)
cur = conn.cursor()
def isUserExist(username):
"""判断用户名是否存在"""
sqli = "select * from users where name='%s'" %(username)
res = cur.execute(sqli)
# res返回的是sql语句查询结果的个数;
# 如果为0, 没有查到。
if res == 0:
return False
else:
return True
def isPasswdOk(username, passwd):
sqli = "select * from users where name='%s' and passwd='%s'" %(
username, passwd)
res = cur.execute(sqli)
if res == 0 :
return False
else:
return True
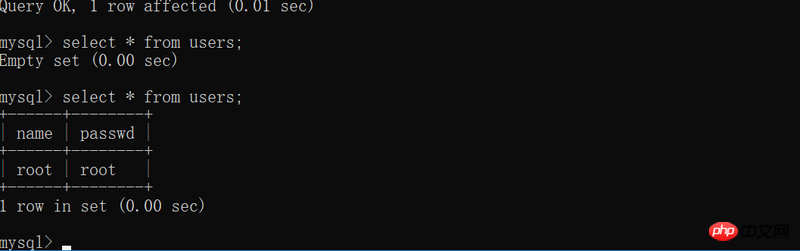
def addUser(username, passwd):
"""用户注册时, 添加信息到数据库中"""
sqli = "insert into users(name, passwd) values('%s', '%s')" %(
username, passwd)
try:
res = cur.execute(sqli)
conn.commit()
except Exception as e:
conn.rollback()
return e
# cur.close()
# conn.close()
if __name__ == "__main__":
addUser('root', 'root')
print(isUserExist('root'))
print(isPasswdOk('root', 'root'))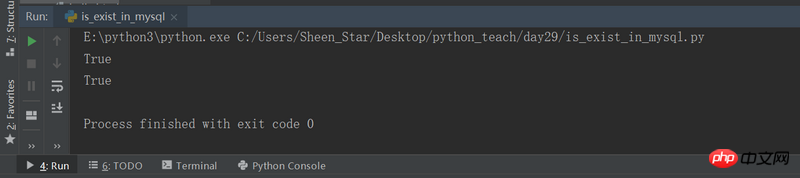
Determine whether the user is logged in
Parts of certain websites The content is only displayed to users who have logged in. At this time, we need to determine whether the user is logged in
import random
import os
from datetime import datetime
import psutil
from flask import Flask, request, render_template, redirect, url_for, abort, session
from models import isPasswdOk, isUserExist, addUser
import platform
app = Flask(__name__)
app.config['SECRET_KEY'] = random._urandom(24)
import functools
def is_login(f):
"""判断用户是否登陆的装饰器"""
@functools.wraps(f)
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
# run函数代码里面, 如果登陆, session加入user, passwd两个key值;
# run函数代码里面, 如果注销, session删除user, passwd两个key值;
# 如果没有登陆成功, 则跳转到登陆界面
if 'user' not in session:
return redirect('/login/')
# 如果用户是登陆状态, 则访问哪个路由, 就执行哪个路由对应的视图函数;
return f(*args, **kwargs)
return wrapper
# 用户主页
@app.route('/')
def index():
return render_template('index.html')
# 用户登陆按钮
@app.route('/login/', methods=['GET', 'POST'])
def login():
if request.method == 'POST':
print(request.form)
# 1. 如何获取到用户提交的信息呢?
user = request.form['user']
passwd = request.form['passwd']
# 2. 判断用户名和密码是否正确
if isPasswdOk(user, passwd):
# 将用户名和密码信息存储到session中;
session['user'] = user
session['passwd'] = passwd
# 如果登陆成功, 跳转到主页;
return redirect(url_for('index'))
else:
# 如果登陆失败, 重新登陆;
return render_template('login.html', message="用户名或者密码错误")
else:
# 用户是GET请求, 返回登陆的html页面
# 1. 读取login.html文件的内容
# 2. 将读取的内容返回给用户界面
return render_template('login.html')
# 用户注销
@app.route('/logout/')
def logout():
session.pop('user', None)
session.pop('passwd', None)
# 注销即删除用户的session信息, 注销成功, 跳转到首页;
return redirect(url_for('index'))
# return redirect('/')
# 用户注册# http方法: get, post(需要提交用户名和密码信息)
@app.route('/register/', methods=['GET', 'POST'])
def register():
# 判断是否提交注册信息;
if request.method == 'POST':
user = request.form['user']
passwd = request.form['passwd']
if isUserExist(user):
message = "用户已经存在"
return render_template('register.html', message=message)
else:
addUser(user, passwd)
return redirect(url_for('login'))
else:
return render_template('register.html')
# 系统监控
@app.route('/sysinfo/')
@is_login
def sysinfo():
info = platform.uname()
# 获取开机时间的时间戳, 需要安装psutil模块;
boot_time = psutil.boot_time()
# 将时间戳转换为字符串格式, 两种方法, 任选一种l
# print(time.ctime(boot_time))
boot_time = datetime.fromtimestamp(boot_time)
# 获取当前时间
now_time = datetime.now()
# 获取时间差
delta_time = now_time - boot_time
delta_time = str(delta_time).split('.')[0]
return render_template('sysinfo.html',
hostname = info.node,
sysname = info.system,
release = info.release,
machine = info.machine,
now_time = now_time,
boot_time = boot_time,
delta_time = delta_time
)
# 404异常处理: 类似于捕获异常
@app.errorhandler(404)
def not_found(e):
return render_template('404.html')
# 抛出异常
@app.route('/user/<user_id>/')
def user(user_id):
if 0<int app.run><p><img src="/static/imghw/default1.png" data-src="https://img.php.cn//upload/image/567/623/726/1542263688275968.png" class="lazy" title="1542263688275968.png" alt="Application examples of flask in python (code)"></p>
<p class="comments-box-content"></p></int></user_id>The above is the detailed content of Application examples of flask in python (code). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Laravel Introduction Example
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:45 PM
Laravel Introduction Example
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:45 PM
Laravel is a PHP framework for easy building of web applications. It provides a range of powerful features including: Installation: Install the Laravel CLI globally with Composer and create applications in the project directory. Routing: Define the relationship between the URL and the handler in routes/web.php. View: Create a view in resources/views to render the application's interface. Database Integration: Provides out-of-the-box integration with databases such as MySQL and uses migration to create and modify tables. Model and Controller: The model represents the database entity and the controller processes HTTP requests.
 Laravel framework installation method
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:54 PM
Laravel framework installation method
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:54 PM
Article summary: This article provides detailed step-by-step instructions to guide readers on how to easily install the Laravel framework. Laravel is a powerful PHP framework that speeds up the development process of web applications. This tutorial covers the installation process from system requirements to configuring databases and setting up routing. By following these steps, readers can quickly and efficiently lay a solid foundation for their Laravel project.
 MySQL vs. Other Programming Languages: A Comparison
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:22 AM
MySQL vs. Other Programming Languages: A Comparison
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:22 AM
Compared with other programming languages, MySQL is mainly used to store and manage data, while other languages such as Python, Java, and C are used for logical processing and application development. MySQL is known for its high performance, scalability and cross-platform support, suitable for data management needs, while other languages have advantages in their respective fields such as data analytics, enterprise applications, and system programming.
 Golang vs. Python: Performance and Scalability
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Golang vs. Python: Performance and Scalability
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Golang is better than Python in terms of performance and scalability. 1) Golang's compilation-type characteristics and efficient concurrency model make it perform well in high concurrency scenarios. 2) Python, as an interpreted language, executes slowly, but can optimize performance through tools such as Cython.
 Python vs. C : Learning Curves and Ease of Use
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python vs. C : Learning Curves and Ease of Use
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python is easier to learn and use, while C is more powerful but complex. 1. Python syntax is concise and suitable for beginners. Dynamic typing and automatic memory management make it easy to use, but may cause runtime errors. 2.C provides low-level control and advanced features, suitable for high-performance applications, but has a high learning threshold and requires manual memory and type safety management.
 MySQL and phpMyAdmin: Core Features and Functions
Apr 22, 2025 am 12:12 AM
MySQL and phpMyAdmin: Core Features and Functions
Apr 22, 2025 am 12:12 AM
MySQL and phpMyAdmin are powerful database management tools. 1) MySQL is used to create databases and tables, and to execute DML and SQL queries. 2) phpMyAdmin provides an intuitive interface for database management, table structure management, data operations and user permission management.
 Does Python projects need to be layered?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
Does Python projects need to be layered?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
Discussion on Hierarchical Structure in Python Projects In the process of learning Python, many beginners will come into contact with some open source projects, especially projects using the Django framework...
 How to safely store JavaScript objects containing functions and regular expressions to a database and restore?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:09 PM
How to safely store JavaScript objects containing functions and regular expressions to a database and restore?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:09 PM
Safely handle functions and regular expressions in JSON In front-end development, JavaScript is often required...






