 Database
Database
 Mysql Tutorial
Mysql Tutorial
 What is the relationship between MySQL tables? Various relationships between tables
What is the relationship between MySQL tables? Various relationships between tables
What is the relationship between MySQL tables? Various relationships between tables
The content of this article is to introduce the relationship between MySQL tables and tables? Various relationships between tables. It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to you.
The relationship between tables
表1 foreign key 表2 则表1的多条记录对应表2的一条记录,即多对一 利用foreign key的原理我们可以制作两张表的多对多,一对一关系多对多: 表1的多条记录可以对应表2的一条记录 表2的多条记录也可以对应表1的一条记录 一对一: 表1的一条记录唯一对应表2的一条记录,反之亦然 分析时,我们先从按照上面的基本原理去套,然后再翻译成真实的意义,就很好理解了
1. First determine the relationship
2. Find the party with more, Write the related fields on the many side
One-to-many
Many-to-one or one-to-many (multiple records in the left table correspond to The only record in the table on the right)
Things to note:
1. Create the related table first to ensure that the fields of the related table must be unique.
2. When creating a related table, the related fields must be duplicated.
Example:
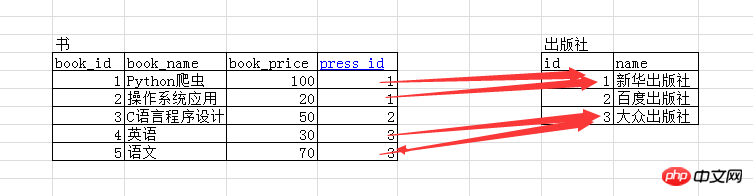
This is an example of a book and a publisher. The book should be associated with the publisher (multiple books can be published by one (a publishing house can also have many books).
Whoever associates with whomever is responsible must follow whose standards.
Create table
书要关联出版社 被关联的表 create table press(id int primary key auto_increment, name char(20)); 关联的表 create table book( book_id int primary key auto_increment, book_name varchar(20), book_price int, press_id int, constraint Fk_pressid_id foreign key(press_id) references press(id) on delete cascade on update cascade );
Insert data
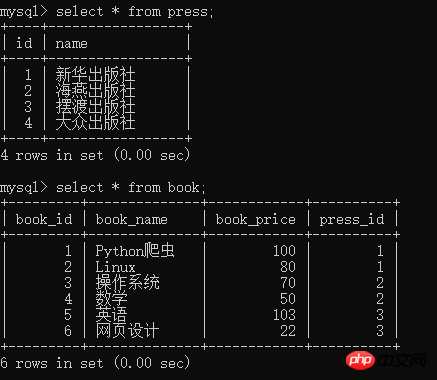
insert into press(name) values('新华出版社'), ('海燕出版社'), ('摆渡出版社'), ('大众出版社'); insert into book(book_name,book_price,press_id) values('Python爬虫',100,1), ('Linux',80,1), ('操作系统',70,2), ('数学',50,2), ('英语',103,3), ('网页设计',22,3);
Running results
One-on-one
Example 1:
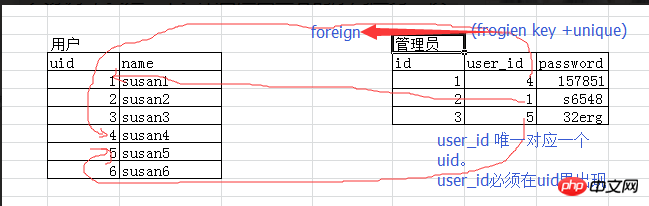
Users and administrators (only administrators can log in, one administrator corresponds to one user)
Administrator associated user
Create table
先建被关联的表 create table user( id int primary key auto_increment, #主键自增name char(10) ); 再建关联表 create table admin( id int primary key auto_increment, user_id int unique, password varchar(16), foreign key(user_id) references user(id) on delete cascade on update cascade );
Insert data
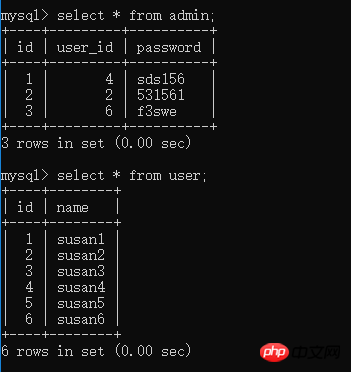
insert into user(name) values('susan1'),('susan2'),('susan3'),('susan4')('susan5'),('susan6'); insert into admin(user_id,password) values(4,'sds156'),(2,'531561'),(6,'f3swe');
Running results
Example 2:
Student table and customer table
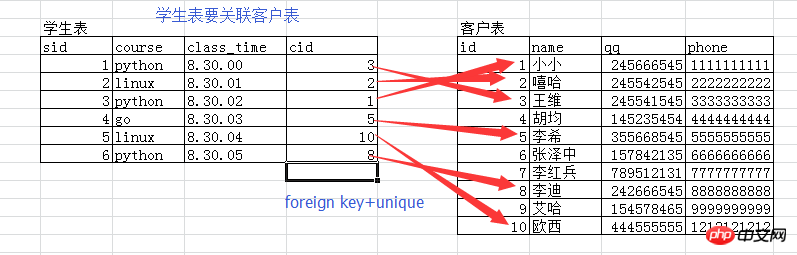
- ##Create table
create table customer( id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(10), qq int unique, phone int unique ); create table student1( sid int primary key auto_increment, course char(20), class_time time, cid int unique, foreign key(cid) references customer(id) on delete cascade on update cascade );
- Insert data
insert into customer(name,qq,phone) values('小小',13564521,11111111),('嘻哈',14758254,22222222),('王维',44545522,33333333),('胡军',545875212,4444444),('李希',145578543,5555555),('李迪',754254653,8888888),('艾哈',74545145,8712547),('啧啧',11147752,7777777); insert into student1(course,class_time,cid) values('python','08:30:00',3),('python','08:30:00',4),('linux','08:30:00',1),('linux','08:30:00',7);
- Run result
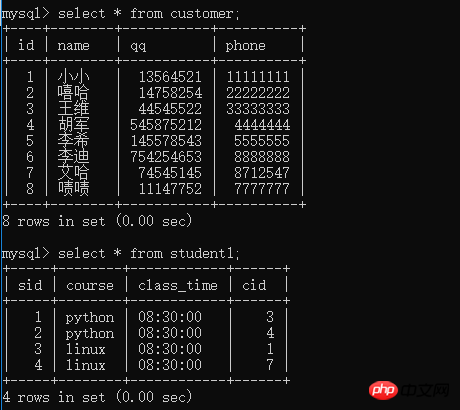
##Many-to-manyBooks and authors (we can create another table to store the relationship between the book and author tables)
To set the book_id And author_id is set to be jointly unique
Uniquely unique: unique(book_id, author_id)Joint primary key: alter table t1 add primary key(id,avg)
Many-to-many: One author can write multiple books, and one book can also have multiple authors, two-way one-to-many, that is, many pairs
Relationship method: foreign key a new table
Example: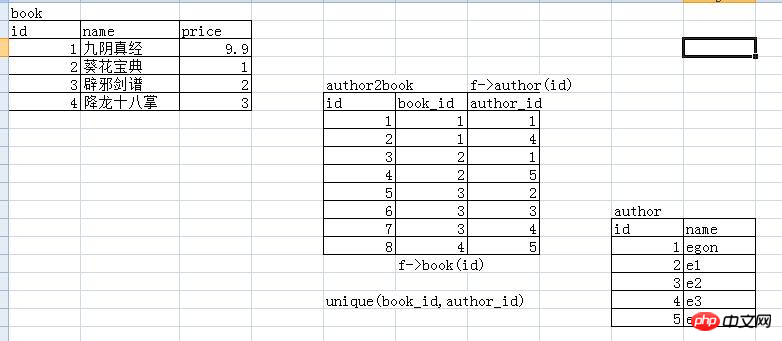

========书和作者,另外在建一张表来存书和作者的关系 #被关联的 create table book1( id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(10), price float(3,2) ); #========被关联的 create table author( id int primary key auto_increment, name char(5) ); #========关联的 create table author2book( id int primary key auto_increment, book_id int not null, author_id int not null, unique(book_id,author_id), foreign key(book_id) references book1(id) on delete cascade on update cascade, foreign key(author_id) references author(id) on delete cascade on update cascade );
Copy after login
- Many-to-many relationship example
insert into book1(name,price) values('九阳神功',9.9), ('葵花宝典',9.5), ('辟邪剑谱',5), ('降龙十巴掌',7.3); insert into author(name) values('egon'),('e1'),('e2'),('e3'),('e4'); insert into author2book(book_id,author_id) values(1,1),(1,4),(2,1),(2,5),(3,2),(3,3),(3,4),(4,5);
Copy after login
-- 用户表 create table user (id int primary key auto_increment,username varchar(20) not null,password varchar(50) not null); insert into user(username,password) values('egon','123'),('root',147),('alex',123),('haiyan',123),('yan',123); -- 用户组表 create table usergroup(id int primary key auto_increment,groupname varchar(20) not null unique); insert into usergroup(groupname) values('IT'),('Sale'),('Finance'),('boss'); -- 主机表 CREATE TABLE host(id int primary key auto_increment,ip CHAR(15) not NULL UNIQUE DEFAULT '127.0.0.1'); insert into host(ip) values('172.16.45.2'),('172.16.31.10'),('172.16.45.3'),('172.16.31.11'),('172.10.45.3'), ('172.10.45.4'),('172.10.45.5'),('192.168.1.20'),('192.168.1.21'),('192.168.1.22'),('192.168.2.23'),('192.168.2.223'), ('192.168.2.24'),('192.168.3.22'),('192.168.3.23'),('192.168.3.24');
Copy after login
-- 建立user和usergroup的关系表 create table user2usergroup( id int not NULL UNIQUE auto_increment, user_id int not null, group_id int not NULL, PRIMARY KEY(user_id,group_id), foreign key(user_id) references user(id) ON DELETE CASCADE on UPDATE CASCADE , foreign key(group_id) references usergroup(id) ON DELETE CASCADE on UPDATE CASCADE ); insert into user2usergroup(user_id,group_id) values(1,1),(1,2),(1,3),(1,4),(2,3),(2,4),(3,4); -- 建立user和host的关系 create table user2host( id int not null unique auto_increment, user_id int not null, host_id int not null, primary key(user_id,host_id), foreign key(user_id) references user(id), foreign key(host_id) references host(id) ); insert into user2host(user_id,host_id) values(1,1),(1,2),(1,3),(1,4),(1,5),(1,6),(1,7),(1,8),(1,9),(1,10),(1,11),(1,12),(1,13),(1,14),(1,15),(1,16),(2,2),(2,3),(2,4),(2,5),(3,10),(3,11),(3,12);
Copy after loginThe above is the detailed content of What is the relationship between MySQL tables? Various relationships between tables. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 MySQL: An Introduction to the World's Most Popular Database
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL: An Introduction to the World's Most Popular Database
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL is an open source relational database management system, mainly used to store and retrieve data quickly and reliably. Its working principle includes client requests, query resolution, execution of queries and return results. Examples of usage include creating tables, inserting and querying data, and advanced features such as JOIN operations. Common errors involve SQL syntax, data types, and permissions, and optimization suggestions include the use of indexes, optimized queries, and partitioning of tables.
 MySQL's Place: Databases and Programming
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL's Place: Databases and Programming
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL's position in databases and programming is very important. It is an open source relational database management system that is widely used in various application scenarios. 1) MySQL provides efficient data storage, organization and retrieval functions, supporting Web, mobile and enterprise-level systems. 2) It uses a client-server architecture, supports multiple storage engines and index optimization. 3) Basic usages include creating tables and inserting data, and advanced usages involve multi-table JOINs and complex queries. 4) Frequently asked questions such as SQL syntax errors and performance issues can be debugged through the EXPLAIN command and slow query log. 5) Performance optimization methods include rational use of indexes, optimized query and use of caches. Best practices include using transactions and PreparedStatemen
 Why Use MySQL? Benefits and Advantages
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:17 AM
Why Use MySQL? Benefits and Advantages
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:17 AM
MySQL is chosen for its performance, reliability, ease of use, and community support. 1.MySQL provides efficient data storage and retrieval functions, supporting multiple data types and advanced query operations. 2. Adopt client-server architecture and multiple storage engines to support transaction and query optimization. 3. Easy to use, supports a variety of operating systems and programming languages. 4. Have strong community support and provide rich resources and solutions.
 How to connect to the database of apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
How to connect to the database of apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
Apache connects to a database requires the following steps: Install the database driver. Configure the web.xml file to create a connection pool. Create a JDBC data source and specify the connection settings. Use the JDBC API to access the database from Java code, including getting connections, creating statements, binding parameters, executing queries or updates, and processing results.
 How to start mysql by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
How to start mysql by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
The process of starting MySQL in Docker consists of the following steps: Pull the MySQL image to create and start the container, set the root user password, and map the port verification connection Create the database and the user grants all permissions to the database
 MySQL's Role: Databases in Web Applications
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:23 AM
MySQL's Role: Databases in Web Applications
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:23 AM
The main role of MySQL in web applications is to store and manage data. 1.MySQL efficiently processes user information, product catalogs, transaction records and other data. 2. Through SQL query, developers can extract information from the database to generate dynamic content. 3.MySQL works based on the client-server model to ensure acceptable query speed.
 Laravel Introduction Example
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:45 PM
Laravel Introduction Example
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:45 PM
Laravel is a PHP framework for easy building of web applications. It provides a range of powerful features including: Installation: Install the Laravel CLI globally with Composer and create applications in the project directory. Routing: Define the relationship between the URL and the handler in routes/web.php. View: Create a view in resources/views to render the application's interface. Database Integration: Provides out-of-the-box integration with databases such as MySQL and uses migration to create and modify tables. Model and Controller: The model represents the database entity and the controller processes HTTP requests.
 How to install mysql in centos7
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:30 PM
How to install mysql in centos7
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:30 PM
The key to installing MySQL elegantly is to add the official MySQL repository. The specific steps are as follows: Download the MySQL official GPG key to prevent phishing attacks. Add MySQL repository file: rpm -Uvh https://dev.mysql.com/get/mysql80-community-release-el7-3.noarch.rpm Update yum repository cache: yum update installation MySQL: yum install mysql-server startup MySQL service: systemctl start mysqld set up booting





