 Backend Development
Backend Development
 C#.Net Tutorial
C#.Net Tutorial
 A brief discussion on what is Edge.js in the .NET Core development log? How to use?
A brief discussion on what is Edge.js in the .NET Core development log? How to use?
A brief discussion on what is Edge.js in the .NET Core development log? How to use?
This article brings you a brief discussion of what Edge.js is in the .NET Core development log? How to use? It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to you.
I recently encountered the need in a project: to integrate part of the business logic of the old system into a new automated process tool. The automation tool being developed uses the C# language, while the business logic of the old system is built on the front end using AngularJS. So there are two solutions in the initial consideration. One is to rewrite the original JavaScript code into C# code for integration; the other is to extract the required code and place them in a RESTful API built through Node.js, and then Call it with HttpClient in C# code.
But then I discovered the interesting class library Edge.js, so I had another choice.
The role of Edge.js is to connect the two worlds of Node.js and .NET. Through it, developers can call .NET code in the Node.js process or call Node.js code in the .NET process.
According to requirements, here we need to call Node.js in C# code, that is, JavaScript code.
If you want to know how to use this class library, you can start with the examples on the official website:
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var func = Edge.Func(@"
return function (data, callback) {
callback(null, 'Node.js welcomes ' + data);
}
");
Console.WriteLine(func(".NET").Result);
Console.Read();
}
}First, you need to introduce its class library through Nuget, Install-Package Edge.js .
Then, use the Func static method of the Edge class in EdgeJs. This method needs to be passed in the code used in Node.js and must return a JavaScript function. The function has a parameter for the external incoming data, and a callback function parameter. The first parameter in this callback function is the exception information in JavaScript, and the second is the return value. The
Edge.Func method returns the Func<object,Task<object>> delegate object, which means that the returned content can be processed asynchronously in .NET.
Next, let’s look at an example close to actual engineering.
The following code is commonly used in AngularJS. The current plan is to put the logic of the sayHello function into C# code and call it.
app.controller('myCtrl', function($scope) {
$scope.name = "World";
$scope.sayHello = function(data) {
$scope.greeting = 'Hello ' + $scope.name + ' ' + data + '!';
};
});The first step to solve is to consider how to deal with $scope. Because it is essentially an object, just define it as a global object variable.
The second step is to move the core code into the Func method parameter of Edge.
var func = Edge.Func(@"
var $scope = {};
$scope.name = 'World';
$scope.sayHello = function(data) {
$scope.greeting = 'Hello ' + $scope.name + ' ' + data + '!';
};
");The third step is to add a return method and capture exceptions that may occur in the JavaScript code.
var func = Edge.Func(@"
var $scope = {};
$scope.name = 'World';
$scope.sayHello = function(data) {
$scope.greeting = 'Hello ' + $scope.name + ' ' + data + '!';
};
return function (data, callback) {
var exception = null;
try {
$scope.sayHello(data);
} catch(err) {
exception = err;
}
callback(exception, $scope.greeting);
}
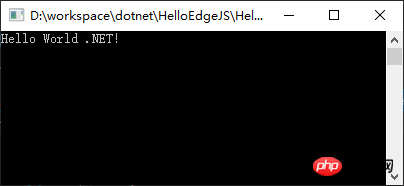
");Running the complete code can get the expected results.
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var func = Edge.Func(@"
var $scope = {};
$scope.name = 'World';
$scope.sayHello = function(data) {
$scope.greeting = 'Hello ' + $scope.name + ' ' + data + '!';
};
return function (data, callback) {
var exception = null;
try {
$scope.sayHello(data);
} catch(err) {
exception = err;
}
callback(exception, $scope.greeting);
}
");
Console.WriteLine(func(".NET").Result);
Console.Read();
}
}
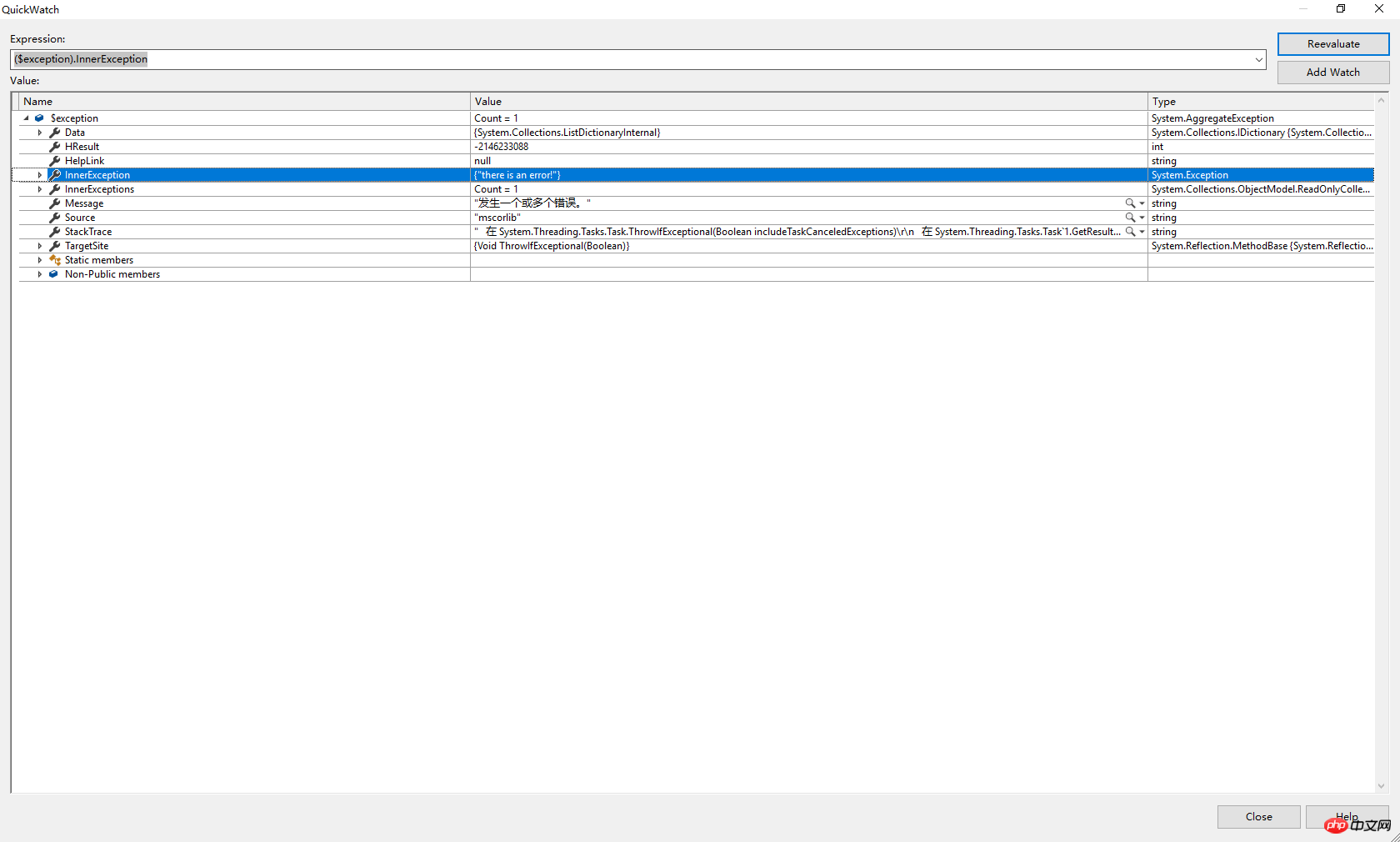
However, the above .NET code cannot handle the exceptions that may be found in JavaScript. For example, adding a throw exception statement to the sayHello function, when the code is executed An expected error will occur.
$scope.sayHello = function(data) {
$scope.greeting = 'Hello ' + $scope.name + ' ' + data + '!';
throw 'there is an error!';
};
So a better approach is to add corresponding exception handling in the .NET code.
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
try
{
var func = Edge.Func(@"
var $scope = {};
$scope.name = 'World';
$scope.sayHello = function(data) {
$scope.greeting = 'Hello ' + $scope.name + ' ' + data + '!';
throw 'there is an error!';
};
return function (data, callback) {
var exception = null;
try {
$scope.sayHello(data);
} catch(err) {
exception = err;
}
callback(exception, $scope.greeting);
}
");
Console.WriteLine(func(".NET").Result);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
// 处理异常
}
Console.Read();
}
}Using this method saves more man-hours than the solution of directly translating JavaScript code, and can avoid many bugs that may occur during the language translation process. Compared with the second way of establishing Node.js Restful API, there is less work to deploy additional services. Therefore, after comprehensive consideration, it is a solution that is very suitable for actual needs.
The only regret is that Edge.js currently does not support .NET Core in terms of .NET code calling Node.js code. I hope the coming soon mentioned on the official website will come as soon as possible. 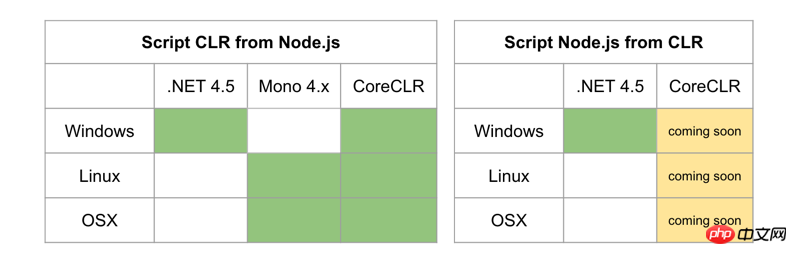
The above is the detailed content of A brief discussion on what is Edge.js in the .NET Core development log? How to use?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Detailed graphic explanation of the memory and GC of the Node V8 engine
Mar 29, 2023 pm 06:02 PM
Detailed graphic explanation of the memory and GC of the Node V8 engine
Mar 29, 2023 pm 06:02 PM
This article will give you an in-depth understanding of the memory and garbage collector (GC) of the NodeJS V8 engine. I hope it will be helpful to you!
 An article about memory control in Node
Apr 26, 2023 pm 05:37 PM
An article about memory control in Node
Apr 26, 2023 pm 05:37 PM
The Node service built based on non-blocking and event-driven has the advantage of low memory consumption and is very suitable for handling massive network requests. Under the premise of massive requests, issues related to "memory control" need to be considered. 1. V8’s garbage collection mechanism and memory limitations Js is controlled by the garbage collection machine
 Let's talk about how to choose the best Node.js Docker image?
Dec 13, 2022 pm 08:00 PM
Let's talk about how to choose the best Node.js Docker image?
Dec 13, 2022 pm 08:00 PM
Choosing a Docker image for Node may seem like a trivial matter, but the size and potential vulnerabilities of the image can have a significant impact on your CI/CD process and security. So how do we choose the best Node.js Docker image?
 Let's talk in depth about the File module in Node
Apr 24, 2023 pm 05:49 PM
Let's talk in depth about the File module in Node
Apr 24, 2023 pm 05:49 PM
The file module is an encapsulation of underlying file operations, such as file reading/writing/opening/closing/delete adding, etc. The biggest feature of the file module is that all methods provide two versions of **synchronous** and **asynchronous**, with Methods with the sync suffix are all synchronization methods, and those without are all heterogeneous methods.
 Let's talk about the event loop in Node
Apr 11, 2023 pm 07:08 PM
Let's talk about the event loop in Node
Apr 11, 2023 pm 07:08 PM
The event loop is a fundamental part of Node.js and enables asynchronous programming by ensuring that the main thread is not blocked. Understanding the event loop is crucial to building efficient applications. The following article will give you an in-depth understanding of the event loop in Node. I hope it will be helpful to you!
 What are the employment prospects of C#?
Oct 19, 2023 am 11:02 AM
What are the employment prospects of C#?
Oct 19, 2023 am 11:02 AM
Whether you are a beginner or an experienced professional, mastering C# will pave the way for your career.
 Learn more about Buffers in Node
Apr 25, 2023 pm 07:49 PM
Learn more about Buffers in Node
Apr 25, 2023 pm 07:49 PM
At the beginning, JS only ran on the browser side. It was easy to process Unicode-encoded strings, but it was difficult to process binary and non-Unicode-encoded strings. And binary is the lowest level data format of the computer, video/audio/program/network package
 What should I do if node cannot use npm command?
Feb 08, 2023 am 10:09 AM
What should I do if node cannot use npm command?
Feb 08, 2023 am 10:09 AM
The reason why node cannot use the npm command is because the environment variables are not configured correctly. The solution is: 1. Open "System Properties"; 2. Find "Environment Variables" -> "System Variables", and then edit the environment variables; 3. Find the location of nodejs folder; 4. Click "OK".





