 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 How springboot and element-axios implement cross-domain requests (code)
How springboot and element-axios implement cross-domain requests (code)
How springboot and element-axios implement cross-domain requests (code)
The content of this article is about how springboot and element-axios implement cross-domain requests (code). It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to you.
1. Initialize element project
1.1: vue init webpage 'Project name'
1.2: npm i element-ui -S
1.3: In main.js Add
import ElementUI from 'element-ui' import 'element-ui/lib/theme-chalk/index.css' Vue.use(ElementUI)
2. Add axios cross-domain request
Add
/**
* 跨域设置
* @type {AxiosStatic}
*/
import axios from 'axios'
Vue.prototype.$axios = axios
Vue.config.productionTip = false
axios.defaults.withCredentials = false//这个默认即为false,如果改为true,可以传递session信息,后端要做相应修改来放行,##3. Create a page
<template>
<el-button @click="post">发送请求</el-button>
</template>
<script>
import axios from "axios";
export default {
data() {
return {
activeIndex2: '1'
};
},
methods: {
handleSelect(key, keyPath) {
console.log(key, keyPath);
},
post(){
axios.get('http://localhost:8080/test')
.then(function (response) {
console.log(response,"已经成功发送请求!");
})
.catch(function (error) {
console.log("请求失败!");
});
}
}
}
</script>4. Create a springboot project
4.1 Add a controller class
@Controller
@CrossOrigin
public class TestController {
@RequestMapping("/test")
@ResponseBody
public JsonResponseExt Test(){
System.out.println("在执行~~~~~~~~~");
return JsonResponseExt.success("执行");
}
}In addition, the @CrossOrigin annotation must be added to the controller class, otherwise the front-end return result will report an error

@Configurationpublic class CorsConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter {
@Override public void addCorsMappings(CorsRegistry registry) {
System.out.println("----------------------");
registry.addMapping("/**")
.allowedOrigins("*")
.allowCredentials(true)
.allowedMethods("GET", "POST", "DELETE", "PUT")
.maxAge(3600);
}
}5, test results
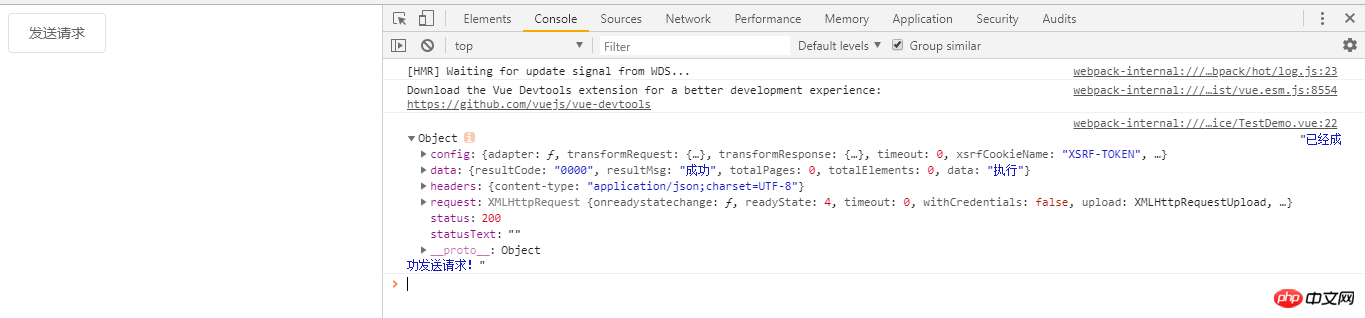 ##Related recommendations:
##Related recommendations:
The above is the detailed content of How springboot and element-axios implement cross-domain requests (code). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to use the Hyperf framework for cross-domain request processing
Oct 20, 2023 pm 01:09 PM
How to use the Hyperf framework for cross-domain request processing
Oct 20, 2023 pm 01:09 PM
How to use the Hyperf framework for cross-domain request processing Introduction: In modern network application development, cross-domain requests have become a common requirement. In order to ensure the separation of front-end and back-end development and improve user experience, it has become particularly important to use the Hyperf framework for cross-domain request processing. This article will introduce how to use the Hyperf framework for cross-domain request processing and provide specific code examples. 1. What is a cross-domain request? Cross-domain requests refer to JavaScript running on the browser through XMLHttpReques.
 How to handle cross-domain requests and security issues in C# development
Oct 08, 2023 pm 09:21 PM
How to handle cross-domain requests and security issues in C# development
Oct 08, 2023 pm 09:21 PM
How to handle cross-domain requests and security issues in C# development. In modern network application development, cross-domain requests and security issues are challenges that developers often face. In order to provide better user experience and functionality, applications often need to interact with other domains or servers. However, the browser's same-origin policy causes these cross-domain requests to be blocked, so some measures need to be taken to handle cross-domain requests. At the same time, in order to ensure data security, developers also need to consider some security issues. This article will discuss how to handle cross-domain requests in C# development
 Comparative analysis of PHP Session cross-domain and cross-site request forgery
Oct 12, 2023 pm 12:58 PM
Comparative analysis of PHP Session cross-domain and cross-site request forgery
Oct 12, 2023 pm 12:58 PM
Comparative analysis of PHPSession cross-domain and cross-site request forgery With the development of the Internet, the security of web applications has become particularly important. PHPSession is a commonly used authentication and session tracking mechanism when developing web applications, while cross-domain requests and cross-site request forgery (CSRF) are two major security threats. In order to protect the security of user data and applications, developers need to understand the difference between Session cross-domain and CSRF, and adopt
 How to use php functions to optimize cross-domain requests and security restrictions?
Oct 05, 2023 pm 12:34 PM
How to use php functions to optimize cross-domain requests and security restrictions?
Oct 05, 2023 pm 12:34 PM
How to use PHP functions to optimize cross-domain requests and security restrictions? In web development, cross-domain requests and security restrictions are common problems. Cross-domain request refers to a page under one domain name accessing resources under another domain name. Due to browser security policies, ordinary cross-domain requests are prohibited. Security restrictions refer to measures to prevent malicious attacks and protect user privacy. PHP provides some functions and methods to optimize these problems. This article will introduce how to use these functions to solve the problems of cross-domain requests and security restrictions. For cross-domain request issues
 React cross-domain request solution: how to deal with cross-domain access issues in front-end applications
Sep 26, 2023 pm 02:48 PM
React cross-domain request solution: how to deal with cross-domain access issues in front-end applications
Sep 26, 2023 pm 02:48 PM
React cross-domain request solution: How to deal with cross-domain access issues in front-end applications, specific code examples are needed. In front-end development, we often encounter cross-domain request issues. Cross-domain request means that the target address (domain name, port, protocol) of the HTTP request sent by the front-end application is inconsistent with the address of the current page. Due to the browser's same-origin policy, cross-domain requests are restricted. However, in real development, we often need to communicate with different servers, so the solution for cross-domain requests is particularly important. This article will introduce Re
 Cross-domain request processing in Go language framework
Jun 03, 2023 am 08:32 AM
Cross-domain request processing in Go language framework
Jun 03, 2023 am 08:32 AM
In web development, cross-domain requests are a common requirement. If a website needs to obtain data from another domain or call an API interface, it needs to use cross-domain requests. However, in order to ensure the security of the website, the browser will block such requests, causing cross-domain requests to fail. In order to solve this problem, we need to use some technical means to handle cross-domain requests. In this article, we will introduce the cross-domain request processing method in the Go language framework. What is a cross-domain request? In web development, front-end pages under the same domain name can
 How to deal with cross-domain request issues in PHP development
Jun 29, 2023 am 08:31 AM
How to deal with cross-domain request issues in PHP development
Jun 29, 2023 am 08:31 AM
How to deal with cross-domain request issues in PHP development In web development, cross-domain requests are a common problem. When the Javascript code in a web page initiates an HTTP request to access resources under different domain names, a cross-domain request occurs. Cross-domain requests are restricted by the browser's Same-Origin Policy, so in PHP development, we need to take some measures to deal with cross-domain request issues. Using a proxy server to forward requests is a common way to handle cross-domain
 How to use JSONP to implement cross-domain requests in Vue
Oct 15, 2023 pm 03:52 PM
How to use JSONP to implement cross-domain requests in Vue
Oct 15, 2023 pm 03:52 PM
Introduction to how to use JSONP to implement cross-domain requests in Vue. Due to the restrictions of the same-origin policy, the front-end will be hindered to a certain extent when making cross-domain requests. JSONP (JSONwithPadding) is a cross-domain request method. It uses the characteristics of the <script> tag to implement cross-domain requests by dynamically creating the <script> tag, and passes the response data back as a parameter of the callback function. This article will introduce in detail how to use JSONP in Vue





