 PHP Framework
PHP Framework
 Laravel
Laravel
 Design process of configuration management system under Laravel framework (with code)
Design process of configuration management system under Laravel framework (with code)
Design process of configuration management system under Laravel framework (with code)
本篇文章给大家带来的内容是关于Laravel框架下的配置管理系统的设计过程(附代码),有一定的参考价值,有需要的朋友可以参考一下,希望对你有所帮助。
项目背景
硬件架构采用Nginx + SLB,应用程式使用 Laravel 的 .env 进行配置管理 ,随着业务的迭代越来越多的配置被写入 .env 文件,变得越来越臃肿,管理起来也不方便。
按照集群设计,支持分布式扩展,配置中心不可用要保证不影响业务,客户端使用Redis + File的方式保存 配置 信息。
使用 supervisor 守护进程,支持秒级获取配置,后续可扩展为消息订阅。按照集群设计,支持分布式扩展,配置中心不可用要保证不影响业务,客户端使用Redis + File的方式保存 配置 信息。
使用 supervisor 守护进程,支持秒级获取配置,后续可扩展为消息订阅。
架构图
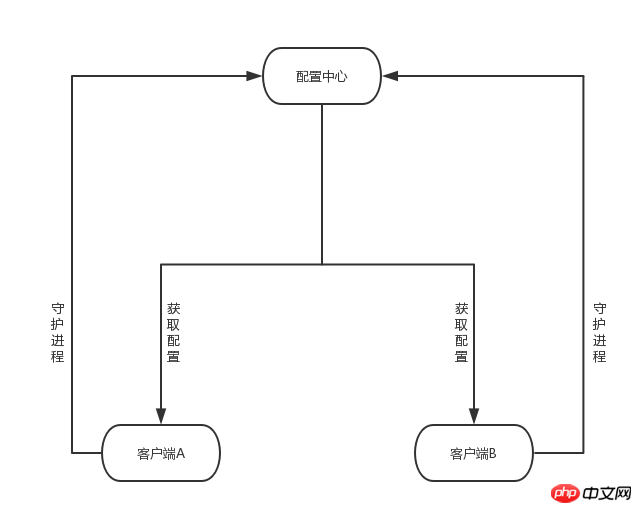
基于composer开发扩展,配置中心与客户端通信基于RESTful,系统拆分为2个composer,server 包 + client 包。
server 负责配置管理,client 负责API封装
UI界面
配置管理
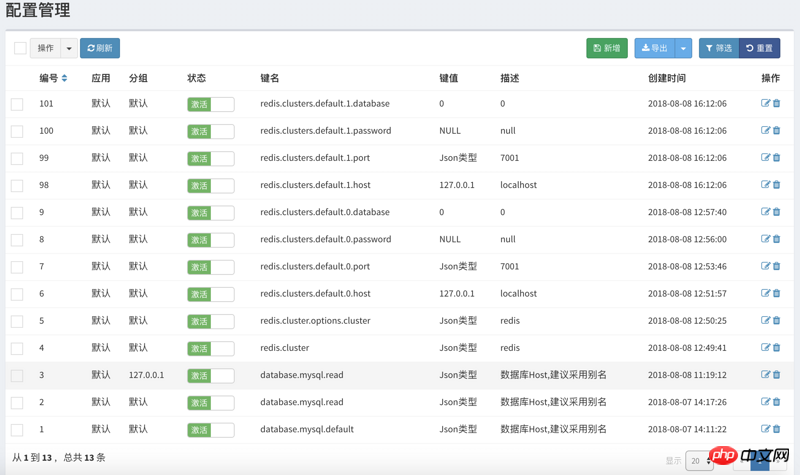
数组支持用.号,支持键值使用json
接口数据
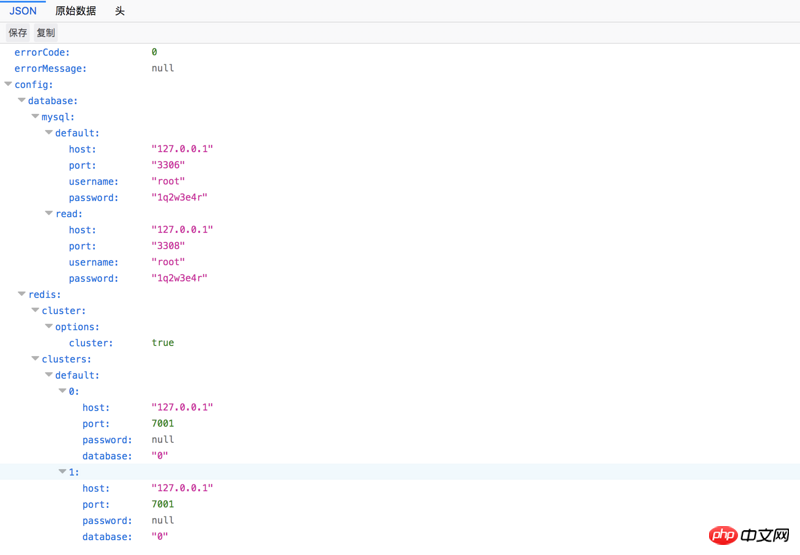
客户端请求接口,最终转被换成PHP数组。
表设计
多应用
CREATE TABLE `tms_configure_client` ( `id` bigint(20) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `is_active` tinyint(1) NOT NULL DEFAULT '1' COMMENT '状态', `app_id` varchar(32) COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci NOT NULL COMMENT 'APPID', `title` varchar(50) COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci NOT NULL COMMENT '名称', `intro` varchar(50) COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci NOT NULL COMMENT '描述', `created_at` timestamp NULL DEFAULT NULL, `updated_at` timestamp NULL DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`), KEY `configure_client_app_id_index` (`app_id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=2 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_unicode_ci;
给每个应用分配一个APPID是很有必要的。
配置分组
CREATE TABLE `tms_configure_group` ( `id` bigint(20) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `ip` varchar(30) COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci NOT NULL COMMENT 'ip地址', `title` varchar(50) COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci NOT NULL COMMENT '标题', `intro` varchar(200) COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci NOT NULL COMMENT '描述', `created_at` timestamp NULL DEFAULT NULL, `updated_at` timestamp NULL DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=3 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_unicode_ci;
暂时仅支持定义到 APPID + IP 级别配置
配置节点
CREATE TABLE `tms_configure_node` ( `id` bigint(20) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `app_id` bigint(20) unsigned NOT NULL COMMENT 'APPID', `is_active` tinyint(3) unsigned NOT NULL DEFAULT '1', `version_id` varchar(20) COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci NOT NULL, `group_id` bigint(20) unsigned NOT NULL, `skey` varchar(50) COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci NOT NULL, `svalue` varchar(2000) COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci NOT NULL, `remark` varchar(50) COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci DEFAULT NULL, `created_at` timestamp NULL DEFAULT NULL, `updated_at` timestamp NULL DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`), KEY `idx_acitve` (`is_active`,`group_id`), KEY `idx_skey` (`skey`), KEY `configure_node_app_id_is_active_group_id_index` (`app_id`,`is_active`,`group_id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=102 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_unicode_ci;
这里我们支持 mysql.port 这种采用.号key的形式,后面最终转化为php数组。
Composer包
服务端
{
"name": "xxx/xxx",
"type": "library",
"keywords": ["laravel","php","configure"],
"description": "configure-server module",
"homepage": "https://github.com/xxx",
"license": "MIT",
"authors": [
{
"name": "OkamiChen",
"email": "x25125x@126.com"
}
],
"require": {
"php": ">=7.1.0"
},
"autoload": {
"psr-4": {
"OkamiChen\\ConfigureServer\\":"src/"
}
},
"extra": {
"laravel": {
"providers": [
"OkamiChen\\ConfigureServer\\ServerServiceProvider"
]
}
}
}客户端
{
"name": "xxx/xxx",
"type": "library",
"keywords": ["laravel","php","configure"],
"description": "configure-client module",
"homepage": "https://github.com/xxx",
"license": "MIT",
"authors": [
{
"name": "OkamiChen",
"email": "x25125x@126.com"
}
],
"require": {
"php": ">=7.1.0"
},
"autoload": {
"psr-4": {
"OkamiChen\\ConfigureClient\\":"src/"
},
"files": [
"src/helper.php"
]
},
"extra": {
"laravel": {
"providers": [
"OkamiChen\\ConfigureClient\\ClientServiceProvider"
]
}
}
}相关文章推荐:
The above is the detailed content of Design process of configuration management system under Laravel framework (with code). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 PHP's Purpose: Building Dynamic Websites
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:18 AM
PHP's Purpose: Building Dynamic Websites
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:18 AM
PHP is used to build dynamic websites, and its core functions include: 1. Generate dynamic content and generate web pages in real time by connecting with the database; 2. Process user interaction and form submissions, verify inputs and respond to operations; 3. Manage sessions and user authentication to provide a personalized experience; 4. Optimize performance and follow best practices to improve website efficiency and security.
 PHP in Action: Real-World Examples and Applications
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP in Action: Real-World Examples and Applications
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP is widely used in e-commerce, content management systems and API development. 1) E-commerce: used for shopping cart function and payment processing. 2) Content management system: used for dynamic content generation and user management. 3) API development: used for RESTful API development and API security. Through performance optimization and best practices, the efficiency and maintainability of PHP applications are improved.
 PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP is mainly procedural programming, but also supports object-oriented programming (OOP); Python supports a variety of paradigms, including OOP, functional and procedural programming. PHP is suitable for web development, and Python is suitable for a variety of applications such as data analysis and machine learning.
 PHP and Python: Code Examples and Comparison
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP and Python: Code Examples and Comparison
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP and Python have their own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice depends on project needs and personal preferences. 1.PHP is suitable for rapid development and maintenance of large-scale web applications. 2. Python dominates the field of data science and machine learning.
 Why Use PHP? Advantages and Benefits Explained
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Why Use PHP? Advantages and Benefits Explained
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:16 AM
The core benefits of PHP include ease of learning, strong web development support, rich libraries and frameworks, high performance and scalability, cross-platform compatibility, and cost-effectiveness. 1) Easy to learn and use, suitable for beginners; 2) Good integration with web servers and supports multiple databases; 3) Have powerful frameworks such as Laravel; 4) High performance can be achieved through optimization; 5) Support multiple operating systems; 6) Open source to reduce development costs.
 PHP: Handling Databases and Server-Side Logic
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP: Handling Databases and Server-Side Logic
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP uses MySQLi and PDO extensions to interact in database operations and server-side logic processing, and processes server-side logic through functions such as session management. 1) Use MySQLi or PDO to connect to the database and execute SQL queries. 2) Handle HTTP requests and user status through session management and other functions. 3) Use transactions to ensure the atomicity of database operations. 4) Prevent SQL injection, use exception handling and closing connections for debugging. 5) Optimize performance through indexing and cache, write highly readable code and perform error handling.
 Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
PHP is suitable for web development and rapid prototyping, and Python is suitable for data science and machine learning. 1.PHP is used for dynamic web development, with simple syntax and suitable for rapid development. 2. Python has concise syntax, is suitable for multiple fields, and has a strong library ecosystem.
 Laravel Introduction Example
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:45 PM
Laravel Introduction Example
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:45 PM
Laravel is a PHP framework for easy building of web applications. It provides a range of powerful features including: Installation: Install the Laravel CLI globally with Composer and create applications in the project directory. Routing: Define the relationship between the URL and the handler in routes/web.php. View: Create a view in resources/views to render the application's interface. Database Integration: Provides out-of-the-box integration with databases such as MySQL and uses migration to create and modify tables. Model and Controller: The model represents the database entity and the controller processes HTTP requests.





