Example of jQuery+koa2 implementing a simple Ajax request
This article mainly introduces examples of jQuery koa2 implementing simple Ajax requests. Now I share it with you and give it as a reference.
Preface
Before writing Ajax code, I only focused on the front-end implementation. I felt that this led to my insufficient understanding of Ajax requests, so I wrote this from front-end to back-end. Ajax implements a small demo, implementing simple GET and POST requests respectively, to deepen the understanding of front-end and back-end interaction.
Technology stack
koa2
jQuer
Requirements
Some logic can be processed directly on the front end. It is sent to the backend for processing here to better understand the Ajax request.
POST
Save personnel information by filling in the number and name and sending a POST request. When the information is not filled in or is filled in incorrectly, a format error reminder is given; when When the information is filled in correctly but the number already exists, a reminder that the number already exists is given; when the information is filled in correctly and the number does not exist, it displays successful saving.
GET
Query personnel information by filling in the number and sending a GET request. When the number is not filled in or is filled incorrectly, a format error reminder is given; when the number is filled in If the information is correct and the number already exists, the person information will be returned; if the information is filled in correctly but the number does not exist, an error reminder that the person does not exist will be displayed.
File list
dist
- ##index.html
- index.js
- server.js
- router.js
Front-end implementation
html page
##index.html, a simple html page, by clicking Button sends Ajax request in json format:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> <script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/jquery/3.3.1/jquery.js"></script> </head> <body> <p> <h1>Hello World</h1> <label for="person-number">编号</label> <input type="text" id="person-number"> <label for="person-name">姓名</label> <input type="text" id="person-name"> <button id="save">保存信息</button> <label for="search-number">编号</label> <input type="text" id="search-number"> <button id="search">查询信息</button> <br> <br> <p id="message"></p> </p> <!-- jQuery实现代码 --> <script src="./index.js"><script> </body> </html>
Send
GET request:
var searchButton = $('#search');
var personNumber = $('#person-number').val();
searchButton.click(() => {
var number = $('#search-number').val();
$.ajax({
type: 'GET',
url: `person/?number=${number}`
})
});Send
POST request:
var saveButton = $('#save').click(() => {
var number = $('#person-number').val();
var name = $('#person-name').val();
$.ajax({
type: 'POST',
url: 'person',
dataType: 'json',
data: {
number: number,
name: name
}
})
});Process the returned data through the
ajaxComplete event, this event can only be bound To the document object:
// Ajax完成事件
$(document).ajaxComplete(function(event, xhr, settings) {
var obj = JSON.parse(xhr.responseText);
var data = obj.data;
if(obj.success && data['number']){
$('#message').text(`姓名:${data['name']} 编号:${data['number']}`);
} else {
$('#message').text(data);
}
});web server
Implement a simple web server through
koa2. server.js:
const path = require('path'); const serve = require('koa-static'); const Koa = require('koa'); const koaBody = require('koa-body'); // 解析 multipart、urlencoded和json格式的请求体 const router = require('./router.js'); const app = new Koa(); app.use(serve(path.join(__dirname, './dist'))); // 读取前端静态页面 app.use(koaBody()); // 通过该中间件解析POST请求的请求体才能拿到数据 app.use(router.routes()); app.listen(3000); console.log('listening on port 3000');
Handling
GETRequest and return data in the form of json string. Query parameters sent through the GET request will be stored in the ctx.query attribute in the form of object literals:
router.get('/person', (ctx, next) => {
let number = ctx.query.number;
let temp = {};
// 判断编号是否存在
temp.data = /^[0-9]+$/.test(number) ? (people[number] ? people[number] : '编号不存在' ) : '编号格式错误';
temp.success = !!temp.data['number'];
ctx.body = JSON.stringify(temp); // 响应请求,发送处理后的信息给客户端
});Handle
POST requests and return data in the form of json strings. The data of the POST request is stored in the request body of the request. It needs to be automatically parsed by the koa-body middleware before the requested data can be obtained through ctx.request.body:
router.post('/person', (ctx, next) => {
let query = ctx.request.body;
let temp = {};
// 编号必须是数字并且大于0,名字必须存在
if (/^[0-9]+$/.test(query.number) && query.name && parseInt(query.number, 10) > 0) {
// 判断编号是否存在
if (!people[query.number]) {
// 保存信息
people[query.number] = {
number: parseInt(query.number, 10),
name: query.name
};
temp.success = true;
temp.data = '保存成功';
} else {
temp.success = false;
temp.data = '编号已存在';
}
} else {
temp.success = false;
temp.data = '信息格式错误';
}
ctx.body = JSON.stringify(temp);
});Complete
router.js:
const Router = require('koa-router');
const router = new Router();
// 初始的人员信息对象,信息从这里储存和读取。
const people = {
1: { number: 1, name: 'Dan Friedell' },
2: { number: 2, name: 'Anna Matteo' },
3: { number: 3, name: 'Susan Shand' },
4: { number: 4, name: 'Bryan Lynn' },
5: { number: 5, name: 'Mario Ritter' },
};
router.get('/person', (ctx, next) => {
let number = ctx.query.number;
let temp = {}; // 要返回给客户端的对象,通过success属性判断存取是否成功。
// 判断编号是否存在
temp.data = /^[0-9]+$/.test(number) ? (people[number] ? people[number] : '编号不存在' ) : '编号格式错误';
temp.success = !!temp.data['number'];
ctx.body = JSON.stringify(temp);
});
router.post('/person', (ctx, next) => {
let query = ctx.request.body;
let temp = {};
// 编号必须是数字并且大于0,名字必须存在
if (/^[0-9]+$/.test(query.number) && query.name && parseInt(query.number, 10) > 0) {
// 判断编号是否存在
if (!people[query.number]) {
// 保存信息
people[query.number] = {
number: parseInt(query.number, 10),
name: query.name
};
temp.success = true;
temp.data = '保存成功';
} else {
temp.success = false;
temp.data = '编号已存在';
}
} else {
temp.success = false;
temp.data = '信息格式错误';
}
ctx.body = JSON.stringify(temp);
});
module.exports = router;Enter
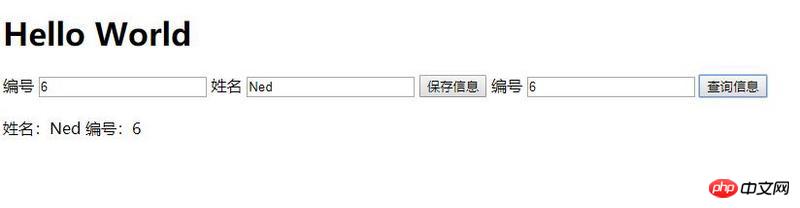
node server.js in the console and you can see that the server is running on port 3000. Open the browser and enter localhost:3000 and you can see it. A simple front-end page:
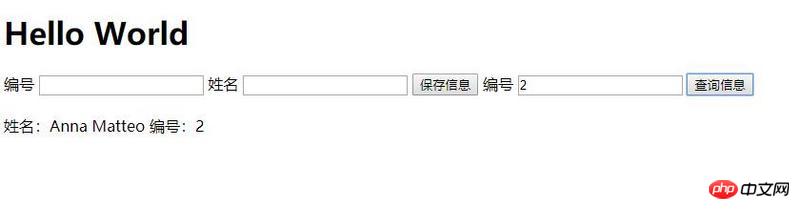
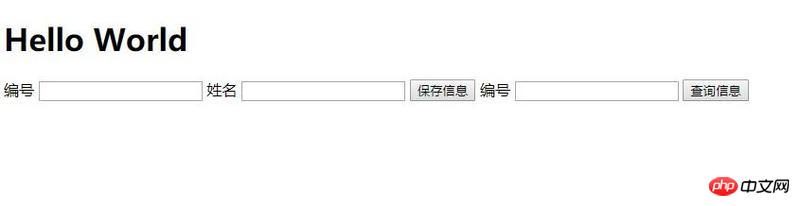 Query data:
Query data:
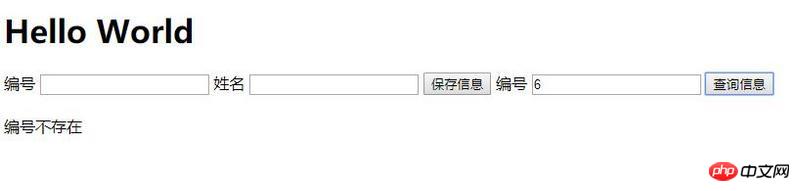 Save data :
Save data :
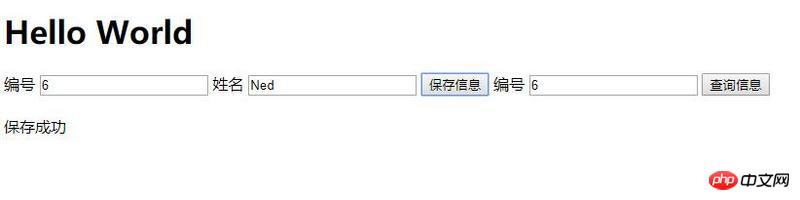 Query the data again:
Query the data again:
 The above is what I compiled for everyone. I hope it will be helpful to everyone in the future. .
The above is what I compiled for everyone. I hope it will be helpful to everyone in the future. .
Related articles:
Sample code of actual node static file servervue.js or js implements Chinese A-Z sorting The methodvue.js moves the array position and updates the view at the same timeThe above is the detailed content of Example of jQuery+koa2 implementing a simple Ajax request. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to solve the 403 error encountered by jQuery AJAX request
Feb 20, 2024 am 10:07 AM
How to solve the 403 error encountered by jQuery AJAX request
Feb 20, 2024 am 10:07 AM
Title: Methods and code examples to resolve 403 errors in jQuery AJAX requests. The 403 error refers to a request that the server prohibits access to a resource. This error usually occurs because the request lacks permissions or is rejected by the server. When making jQueryAJAX requests, you sometimes encounter this situation. This article will introduce how to solve this problem and provide code examples. Solution: Check permissions: First ensure that the requested URL address is correct and verify that you have sufficient permissions to access the resource.
 How to solve jQuery AJAX request 403 error
Feb 19, 2024 pm 05:55 PM
How to solve jQuery AJAX request 403 error
Feb 19, 2024 pm 05:55 PM
jQuery is a popular JavaScript library used to simplify client-side development. AJAX is a technology that sends asynchronous requests and interacts with the server without reloading the entire web page. However, when using jQuery to make AJAX requests, you sometimes encounter 403 errors. 403 errors are usually server-denied access errors, possibly due to security policy or permission issues. In this article, we will discuss how to resolve jQueryAJAX request encountering 403 error
 PHP and Ajax: Building an autocomplete suggestion engine
Jun 02, 2024 pm 08:39 PM
PHP and Ajax: Building an autocomplete suggestion engine
Jun 02, 2024 pm 08:39 PM
Build an autocomplete suggestion engine using PHP and Ajax: Server-side script: handles Ajax requests and returns suggestions (autocomplete.php). Client script: Send Ajax request and display suggestions (autocomplete.js). Practical case: Include script in HTML page and specify search-input element identifier.
 How to solve the problem of jQuery AJAX error 403?
Feb 23, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
How to solve the problem of jQuery AJAX error 403?
Feb 23, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
How to solve the problem of jQueryAJAX error 403? When developing web applications, jQuery is often used to send asynchronous requests. However, sometimes you may encounter error code 403 when using jQueryAJAX, indicating that access is forbidden by the server. This is usually caused by server-side security settings, but there are ways to work around it. This article will introduce how to solve the problem of jQueryAJAX error 403 and provide specific code examples. 1. to make
 How to get variables from PHP method using Ajax?
Mar 09, 2024 pm 05:36 PM
How to get variables from PHP method using Ajax?
Mar 09, 2024 pm 05:36 PM
Using Ajax to obtain variables from PHP methods is a common scenario in web development. Through Ajax, the page can be dynamically obtained without refreshing the data. In this article, we will introduce how to use Ajax to get variables from PHP methods, and provide specific code examples. First, we need to write a PHP file to handle the Ajax request and return the required variables. Here is sample code for a simple PHP file getData.php:
 PHP vs. Ajax: Solutions for creating dynamically loaded content
Jun 06, 2024 pm 01:12 PM
PHP vs. Ajax: Solutions for creating dynamically loaded content
Jun 06, 2024 pm 01:12 PM
Ajax (Asynchronous JavaScript and XML) allows adding dynamic content without reloading the page. Using PHP and Ajax, you can dynamically load a product list: HTML creates a page with a container element, and the Ajax request adds the data to that element after loading it. JavaScript uses Ajax to send a request to the server through XMLHttpRequest to obtain product data in JSON format from the server. PHP uses MySQL to query product data from the database and encode it into JSON format. JavaScript parses the JSON data and displays it in the page container. Clicking the button triggers an Ajax request to load the product list.
 PHP and Ajax: Ways to Improve Ajax Security
Jun 01, 2024 am 09:34 AM
PHP and Ajax: Ways to Improve Ajax Security
Jun 01, 2024 am 09:34 AM
In order to improve Ajax security, there are several methods: CSRF protection: generate a token and send it to the client, add it to the server side in the request for verification. XSS protection: Use htmlspecialchars() to filter input to prevent malicious script injection. Content-Security-Policy header: Restrict the loading of malicious resources and specify the sources from which scripts and style sheets are allowed to be loaded. Validate server-side input: Validate input received from Ajax requests to prevent attackers from exploiting input vulnerabilities. Use secure Ajax libraries: Take advantage of automatic CSRF protection modules provided by libraries such as jQuery.
 What are the ajax versions?
Nov 22, 2023 pm 02:00 PM
What are the ajax versions?
Nov 22, 2023 pm 02:00 PM
Ajax is not a specific version, but a technology that uses a collection of technologies to asynchronously load and update web page content. Ajax does not have a specific version number, but there are some variations or extensions of ajax: 1. jQuery AJAX; 2. Axios; 3. Fetch API; 4. JSONP; 5. XMLHttpRequest Level 2; 6. WebSockets; 7. Server-Sent Events; 8, GraphQL, etc.






