Detailed explanation of the use of process and child_process
This time I will bring you a detailed explanation of the use of process and child_process. What are the precautions when using process and child_process? Here are practical cases, let’s take a look.
After struggling with the process for a week, I finally understood the obscure and difficult document, and am ready to share my understanding with everyone. I also hope that everyone can point out some opinions
Process The concept of
InNode.jseach application is an instance object of the process class.
Use the process object to represent the application. This is a global object through which you can obtain the properties of the Node.jsy application and the user and environment running the program. methods and events.
Several important attributes in the process
stdin standard input readable stream
stdout standard input writable stream
stderr standard error output stream
argv terminal input parameter array
env operating system environment information
pid application process id
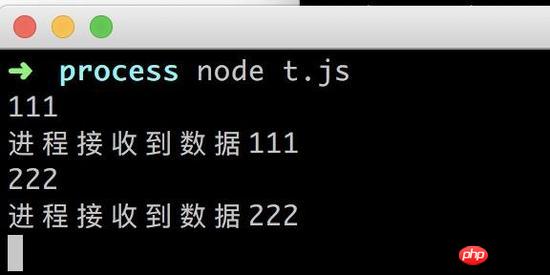
stdin and stdout
process.stdin.on('data', (chunk) => {
process.stdout.write('进程接收到数据' + chunk)
})Run result
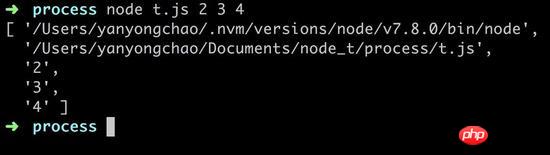
argv
console.log(process.env)
console.log(process.env.NODE_ENV) //develop
- process.memoryUsage() View memory usage information
- process.nextTick() Current Execution after eventloop is executed
- Callback function process.chdir() The chdir method is used to modify the current working directory used in Node.js applications
- process.cwd() The current working directory of the process
- process.kill() Kill the process
- process. uncaught
- Exception
() Triggers the uncaughtException event of the process object when the application throws an uncaught exception
say() //方法不存在 process.on('uncaughtException',function(err){ console.log('捕获到一个未被处理的错误:',err); });Copy after login
Child process is the focus of today’s talk. I also don’t understand some of it. I hope I can communicate with you more.
The background of child_processIn Node In .js, only one thread performs all operations. If an operation requires a large amount of CPU resources, subsequent operations will need to wait.
In Node.js, a child_process module is provided, through which multiple child processes can be started, memory space can be shared between multiple child processes, and information exchange can be achieved through mutual communication of child processes.
The child_process module gives node the ability to create child processes at will. The official document of node gives four methods for the child_proces module. Mapping to the operating system actually creates child processes. But for developers only, the APIs of these methods are a little different
child_process.exec(command[, options][, callback]) starts the
child process to execute the shell command, which can be done through the callback parameter Get the script shell execution result
child_process.execfile(file[, args][, options][, callback])
child_process.spawn(command[, args][, options]) only executes a shell command and does not need to obtain the execution results
child_process.fork(modulePath[, args][, options] ]) You can use node
to execute the .js file, and there is no need to obtain the execution results. The child process coming out of fork must be the node processSyntax: child_process.spawn(command, [args], [options])
- command Parameters that must be specified, specify the command that needs to be executed
- args array, which stores all the parameters required to run the command
options 参数为一个对象,用于指定开启子进程时使用的选项
const { spawn } = require('child_process')
const path = require('path')
let child1 = spawn('node', ['test1.js', 'yanyongchao'], {
stdio: ['pipe', 'pipe', 'pipe'], // 三个元素数组 下面会详解
cwd: dirname, 子进程工作目录
env: process.env, 环境变量
detached: true // 如果为true,当父进程不存在时也可以独立存在
})其实上面都好理解除了sdtio数组,下面来一起分析stdio
stdio
stdio是一个数组,用来设置标准输入,标准输出,错误输出。个人理解
pipe:父进程和子进程之间建立一个管道
主进程代码
const path = require('path')
const { spawn } = require('child_process')
let p = spawn('node', ['childs_t.js'], {
cwd: path.join(dirname, 'childs'),
stdio: ['pipe', 'pipe', process.stderr]
})
p.stdout.on('data', (data) => {
console.log(data.toString())
})
// 这里用stdout原因: 子进程的数据流与常规理解的数据流方向相反,
// stdin:写入流,stdout、stderr:读取流。子进程代码
process.stdout.write('asd')如果在stdio中放一个流,process.stdout,process.stdin
主进程代码
const { spawn } = require('child_process')
const path = require('path')
// 如果放的是一个流,则意味着父进程和子进程共享一个流
const p = spawn('node', ['child_t.js'], {
cwd: path.join(dirname, 'childs'),
stdio: [process.stdin, process.stdout, process.stderr]
})子进程代码
process.stdout.write('asd') //控制台会输出asdipc
主进程代码
const path = require('path')
const { spawn } = require('child_process')
let p = spawn('node', ['child_t.js'], {
cwd: path.join(dirname, 'childs'),
stdio: ['ipc', 'pipe', 'pipe']
})
p.on('message', (msg) => {
console.log(msg)
})
p.send('hello chhild_process')子进程代码
process.on('message', (msg) => {
process.send('子进程' + msg)
})
// child.send(message,[sendHandle]);//在父进程中向子进程发送消息
// process.send(message,[sendHandle]);//在子进程中向主进程发送消息detached模式
const { spawn } = require('child_process')
const fs = require('fs')
const path = require('path')
let out = fs.openSync(path.join(dirname, 'childs/msg.txt'), 'w', 0o666)
let p = spawn('node', ['test4.js'], {
detached: true, //保证父进程结束,子进程仍然可以运行
stdio: 'ignore',
cwd: path.join(dirname, 'childs')
})
p.unref()
p.on('close', function() {
console.log('子进程关闭')
})
p.on('exit', function() {
console.log('子进程退出')
})
p.on('error', function(err) {
console.log('子进程1开启失败' + err)
})fork开启一个子进程
衍生一个新的 Node.js 进程,并通过建立一个 IPC 通讯通道来调用一个指定的模块,该通道允许父进程与子进程之间相互发送信息
fork方法返回一个隐式创建的代表子进程的ChildProcess对象
子进程的输入/输出操作执行完毕后,子进程不会自动退出,必须使用process.exit()方法显式退出
子进程代码
const { fork } = require('child_process')
const path = require('path')
let child = fork(path.join(dirname, 'childs/fork1.js'))
child.on('message', (data) => {
console.log('父进程接收到消息' + data)
})
child.send('hello fork')
child.on('error', (err) => {
console.error(err)
})子进程代码
process.on('message', (m, setHandle) => {
console.log('子进程接收到消息' + m)
process.send(m) //sendHandle是一个 net.Socket 或 net.Server 对象
})exec开启子进程
// exec同步执行一个shell命令
let { exec } = require('child_process')
let path = require('path')
// 用于使用shell执行命令, 同步方法
let p1 = exec('node exec.js a b c', {cwd: path.join(dirname, 'childs')}, function(err, stdout, stderr) {
console.log(stdout)
})execFile开启子进程
let { execFile } = require('child_process')
let path = require('path')
let p1 = execFile('node', ['exec.js', 'a', 'b', 'c'], {
cwd: path.join(dirname, 'childs')
}, function(err, stdout, stderr) {
console.log(stdout)
})相信看了本文案例你已经掌握了方法,更多精彩请关注php中文网其它相关文章!
推荐阅读:
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of the use of process and child_process. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Detailed explanation of obtaining administrator rights in Win11
Mar 08, 2024 pm 03:06 PM
Detailed explanation of obtaining administrator rights in Win11
Mar 08, 2024 pm 03:06 PM
Windows operating system is one of the most popular operating systems in the world, and its new version Win11 has attracted much attention. In the Win11 system, obtaining administrator rights is an important operation. Administrator rights allow users to perform more operations and settings on the system. This article will introduce in detail how to obtain administrator permissions in Win11 system and how to effectively manage permissions. In the Win11 system, administrator rights are divided into two types: local administrator and domain administrator. A local administrator has full administrative rights to the local computer
 Detailed explanation of the mode function in C++
Nov 18, 2023 pm 03:08 PM
Detailed explanation of the mode function in C++
Nov 18, 2023 pm 03:08 PM
Detailed explanation of the mode function in C++ In statistics, the mode refers to the value that appears most frequently in a set of data. In C++ language, we can find the mode in any set of data by writing a mode function. The mode function can be implemented in many different ways, two of the commonly used methods will be introduced in detail below. The first method is to use a hash table to count the number of occurrences of each number. First, we need to define a hash table with each number as the key and the number of occurrences as the value. Then, for a given data set, we run
 Detailed explanation of division operation in Oracle SQL
Mar 10, 2024 am 09:51 AM
Detailed explanation of division operation in Oracle SQL
Mar 10, 2024 am 09:51 AM
Detailed explanation of division operation in OracleSQL In OracleSQL, division operation is a common and important mathematical operation, used to calculate the result of dividing two numbers. Division is often used in database queries, so understanding the division operation and its usage in OracleSQL is one of the essential skills for database developers. This article will discuss the relevant knowledge of division operations in OracleSQL in detail and provide specific code examples for readers' reference. 1. Division operation in OracleSQL
 Detailed explanation of remainder function in C++
Nov 18, 2023 pm 02:41 PM
Detailed explanation of remainder function in C++
Nov 18, 2023 pm 02:41 PM
Detailed explanation of the remainder function in C++ In C++, the remainder operator (%) is used to calculate the remainder of the division of two numbers. It is a binary operator whose operands can be any integer type (including char, short, int, long, etc.) or a floating-point number type (such as float, double). The remainder operator returns a result with the same sign as the dividend. For example, for the remainder operation of integers, we can use the following code to implement: inta=10;intb=3;
 Detailed explanation of the usage of Vue.nextTick function and its application in asynchronous updates
Jul 26, 2023 am 08:57 AM
Detailed explanation of the usage of Vue.nextTick function and its application in asynchronous updates
Jul 26, 2023 am 08:57 AM
Detailed explanation of the usage of Vue.nextTick function and its application in asynchronous updates. In Vue development, we often encounter situations where data needs to be updated asynchronously. For example, data needs to be updated immediately after modifying the DOM or related operations need to be performed immediately after the data is updated. The .nextTick function provided by Vue emerged to solve this type of problem. This article will introduce the usage of the Vue.nextTick function in detail, and combine it with code examples to illustrate its application in asynchronous updates. 1. Vue.nex
 Detailed explanation of php-fpm tuning method
Jul 08, 2023 pm 04:31 PM
Detailed explanation of php-fpm tuning method
Jul 08, 2023 pm 04:31 PM
PHP-FPM is a commonly used PHP process manager used to provide better PHP performance and stability. However, in a high-load environment, the default configuration of PHP-FPM may not meet the needs, so we need to tune it. This article will introduce the tuning method of PHP-FPM in detail and give some code examples. 1. Increase the number of processes. By default, PHP-FPM only starts a small number of processes to handle requests. In a high-load environment, we can improve the concurrency of PHP-FPM by increasing the number of processes
 Detailed explanation of the role and usage of PHP modulo operator
Mar 19, 2024 pm 04:33 PM
Detailed explanation of the role and usage of PHP modulo operator
Mar 19, 2024 pm 04:33 PM
The modulo operator (%) in PHP is used to obtain the remainder of the division of two numbers. In this article, we will discuss the role and usage of the modulo operator in detail, and provide specific code examples to help readers better understand. 1. The role of the modulo operator In mathematics, when we divide an integer by another integer, we get a quotient and a remainder. For example, when we divide 10 by 3, the quotient is 3 and the remainder is 1. The modulo operator is used to obtain this remainder. 2. Usage of the modulo operator In PHP, use the % symbol to represent the modulus
 Detailed explanation of the linux system call system() function
Feb 22, 2024 pm 08:21 PM
Detailed explanation of the linux system call system() function
Feb 22, 2024 pm 08:21 PM
Detailed explanation of Linux system call system() function System call is a very important part of the Linux operating system. It provides a way to interact with the system kernel. Among them, the system() function is one of the commonly used system call functions. This article will introduce the use of the system() function in detail and provide corresponding code examples. Basic Concepts of System Calls System calls are a way for user programs to interact with the operating system kernel. User programs request the operating system by calling system call functions






