JS and WebService large file upload code sharing
In the process of writing the front-end, it is inevitable to encounter the problem of file upload. When a user wants to upload a larger file, it will be restricted by the server and prevented from uploading. In ASP.Net, adjust the server's acceptance of files. The size configuration method is as follows:
Configure the httpRuntime of the Web.config file in ASP:
<httpRuntime executionTimeout="90" maxRequestLength="40960" useFullyQualifiedRedirectUrl="false"minFreeThreads="8" minLocalRequestFreeThreads="4" appRequestQueueLimit="100" enableVersionHeader="false"/>
The role of each parameter is:
executionTimeout : Indicates the maximum time limit allowed to execute the request, in seconds.
maxRequestLength: Indicates the maximum file upload size supported by ASP.NET. This limit can be used to prevent denial of service attacks caused by users passing large numbers of files to the server. The specified size is in KB. The default value is 4096KB (4 MB).
useFullyQualifiedRedirectUr: Indicates whether the client redirection is fully qualified (in the "http://server/path" format, which is required for some mobile controls), or whether to use a relative redirection instead Sent to client. If True, all redirects that are not fully qualified will be automatically converted to fully qualified format. false is the default option.
minFreeThreads: Indicates the minimum number of free threads allowed to execute new requests. ASP.NET keeps a specified number of threads free for requests that require additional threads to complete its processing. The default value is 8.
minLocalRequestFreeThreads: Indicates the minimum number of free threads maintained by ASP.NET that are allowed to execute new local requests. This number of threads is reserved for incoming requests from the local host in case some requests make subrequests to the local host during their processing. This avoids possible deadlocks caused by recursively re-entering the Web server.
appRequestQueueLimit: Indicates the maximum number of requests that ASP.NET will queue for the application. Requests are queued when there are not enough free threads to handle the request. When the queue exceeds the limit specified in this setting, incoming requests will be rejected with a "503 - Server Too Busy" error message. enableVersionHeader: Indicates specifying whether ASP.NET should output a version header. Microsoft Visual Studio 2005 uses this property to determine the version of ASP.NET currently in use. For production environments, this property is not required and can be disabled.
However, even if the size of the uploaded file in the server configuration is large enough, it will be restricted by IIS and cannot provide secure services to users. So is there a way to solve the problem of uploading large files?
There must be: multipart upload.
Multiple upload refers to cutting the file you want to upload into very small pieces on the front end, then passing it to the server, and then combining the file into a complete file from the server.
Let’s start with the front-end. In the process of multi-part upload, the front-end task is to divide the file into pieces. There are many ways to divide the files. For example, you can use the upload component provided by WebUpLoader for fragmentation, or you can use JS and JQ. Upload the code provided. The code example is as follows:
var BYTES_PER_CHUNK = 1024 * 1024; // 每个文件切片大小定为1MB .
var slices;
var totalSlices;
//发送请求
function sendRequest() {
var blob = document.getElementById("yourID").files[0];
var start = 0;
var end;
var index = 0;
// 计算文件切片总数
slices = Math.ceil(blob.size / BYTES_PER_CHUNK);
totalSlices= slices;
while(start < blob.size) {
end = start + BYTES_PER_CHUNK;
if(end > blob.size) {
end = blob.size;
}
uploadFile(blob, index, start, end);
start = end;
index++;
if ( index>=totalSlices )
alert("Complete!!");
}
}
//上传文件
function uploadFile(blob, index, start, end) {
var xhr;
var fd;
var chunk;
var sliceIndex=blob.name+index;
chunk =blob.slice(start,end);//切割文件
fd = new FormData();
fd.append("FileName", chunk, sliceIndex);
var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.open('POST', 'Server URL', false);//false,同步上传;ture,异步上传
xhr.send(fd);
if((xhr.status >=200 && xhr.status < 300) || xhr.status == 304){
setTimeout("",10);
}else{
uploadFile(blob, index, start, end);
}
}With the front end, of course, the acceptance and combination at the back end are indispensable. Here I use ASP.Net as an example to explain how to receive and combine files.
public void RecoveryKPJD()
{
HttpContext context = System.Web.HttpContext.Current;
context.Response.ContentType = "text/plain";
//如果进行了分片
if (context.Request.Form.AllKeys.Any(m => m == "chunk"))
{
//取得chunk和chunks
int chunk = Convert.ToInt32(context.Request.Form["chunk"]);//当前分片在上传分片中的顺序(从0开始)
int chunks = Convert.ToInt32(context.Request.Form["chunks"]);//总分片数
//根据GUID创建用该GUID命名的临时文件夹
string folder = Your Path + context.Request["guid"] + "/";
string path = folder + chunk;
//建立临时传输文件夹
if (!Directory.Exists(Path.GetDirectoryName(folder)))
{
Directory.CreateDirectory(folder);
}
FileStream addFile = new FileStream(path, FileMode.Append, FileAccess.Write);
BinaryWriter AddWriter = new BinaryWriter(addFile);
//获得上传的分片数据流
HttpPostedFile file = context.Request.Files[0];
Stream stream = file.InputStream;
BinaryReader TempReader = new BinaryReader(stream);
//将上传的分片追加到临时文件末尾
AddWriter.Write(TempReader.ReadBytes((int)stream.Length));
//关闭BinaryReader文件阅读器
TempReader.Close();
stream.Close();
AddWriter.Close();
addFile.Close();
TempReader.Dispose();
stream.Dispose();
AddWriter.Dispose();
addFile.Dispose();
if (chunk == chunks - 1)
{
//合并文件
ProcessRequest(context.Request["guid"], Path.GetExtension(file.FileName));
}
}
else//没有分片直接保存
{
string targetPath = ""; //此处写文件的保存路径
context.Request.Files[0].SaveAs(targetPath);
}
}
private void ProcessRequest(string guid, string fileExt)
{
HttpContext context = System.Web.HttpContext.Current;
context.Response.ContentType = "text/plain";
string sourcePath = Path.Combine("Your Path", guid + "/");//源数据文件夹
string targetPath = Path.Combine("Your Path", Guid.NewGuid() + fileExt);//合并后的文件
DirectoryInfo dicInfo = new DirectoryInfo(sourcePath);
if (Directory.Exists(Path.GetDirectoryName(sourcePath)))
{
FileInfo[] files = dicInfo.GetFiles();
foreach (FileInfo file in files.OrderBy(f => int.Parse(f.Name)))
{
FileStream addFile = new FileStream(targetPath, FileMode.AppenFileAccess.Write);
BinaryWriter AddWriter = new BinaryWriter(addFile);
//获得上传的分片数据流
Stream stream = file.Open(FileMode.Open);
BinaryReader TempReader = new BinaryReader(stream);
//将上传的分片追加到临时文件末尾
AddWriter.Write(TempReader.ReadBytes((int)stream.Length));
//关闭BinaryReader文件阅读器
TempReader.Close();
stream.Close();
AddWriter.Close();
addFile.Close();
TempReader.Dispose();
stream.Dispose();
AddWriter.Dispose();
addFile.Dispose();
}
}
}Related recommendations:
php file size detection and large file upload processing
Detailed explanation of Nodejs calling WebService
JS simple example of cross-domain calling WebService
The above is the detailed content of JS and WebService large file upload code sharing. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system Introduction: With the continuous development of technology, speech recognition technology has become an important part of the field of artificial intelligence. The online speech recognition system based on WebSocket and JavaScript has the characteristics of low latency, real-time and cross-platform, and has become a widely used solution. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system.
 WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: Key technologies for realizing real-time monitoring systems Introduction: With the rapid development of Internet technology, real-time monitoring systems have been widely used in various fields. One of the key technologies to achieve real-time monitoring is the combination of WebSocket and JavaScript. This article will introduce the application of WebSocket and JavaScript in real-time monitoring systems, give code examples, and explain their implementation principles in detail. 1. WebSocket technology
 How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
Introduction to how to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system: With the popularity of the Internet and the advancement of technology, more and more restaurants have begun to provide online ordering services. In order to implement a real-time online ordering system, we can use JavaScript and WebSocket technology. WebSocket is a full-duplex communication protocol based on the TCP protocol, which can realize real-time two-way communication between the client and the server. In the real-time online ordering system, when the user selects dishes and places an order
 How to implement an online reservation system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
How to implement an online reservation system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online reservation system. In today's digital era, more and more businesses and services need to provide online reservation functions. It is crucial to implement an efficient and real-time online reservation system. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online reservation system, and provide specific code examples. 1. What is WebSocket? WebSocket is a full-duplex method on a single TCP connection.
 JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecast system Introduction: Today, the accuracy of weather forecasts is of great significance to daily life and decision-making. As technology develops, we can provide more accurate and reliable weather forecasts by obtaining weather data in real time. In this article, we will learn how to use JavaScript and WebSocket technology to build an efficient real-time weather forecast system. This article will demonstrate the implementation process through specific code examples. We
 Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
JavaScript tutorial: How to get HTTP status code, specific code examples are required. Preface: In web development, data interaction with the server is often involved. When communicating with the server, we often need to obtain the returned HTTP status code to determine whether the operation is successful, and perform corresponding processing based on different status codes. This article will teach you how to use JavaScript to obtain HTTP status codes and provide some practical code examples. Using XMLHttpRequest
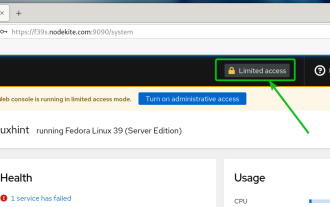 How to enable administrative access from the cockpit web UI
Mar 20, 2024 pm 06:56 PM
How to enable administrative access from the cockpit web UI
Mar 20, 2024 pm 06:56 PM
Cockpit is a web-based graphical interface for Linux servers. It is mainly intended to make managing Linux servers easier for new/expert users. In this article, we will discuss Cockpit access modes and how to switch administrative access to Cockpit from CockpitWebUI. Content Topics: Cockpit Entry Modes Finding the Current Cockpit Access Mode Enable Administrative Access for Cockpit from CockpitWebUI Disabling Administrative Access for Cockpit from CockpitWebUI Conclusion Cockpit Entry Modes The cockpit has two access modes: Restricted Access: This is the default for the cockpit access mode. In this access mode you cannot access the web user from the cockpit
 what does web mean
Jan 09, 2024 pm 04:50 PM
what does web mean
Jan 09, 2024 pm 04:50 PM
The web is a global wide area network, also known as the World Wide Web, which is an application form of the Internet. The Web is an information system based on hypertext and hypermedia, which allows users to browse and obtain information by jumping between different web pages through hyperlinks. The basis of the Web is the Internet, which uses unified and standardized protocols and languages to enable data exchange and information sharing between different computers.






