Detailed example of many-to-many relationship in laravel
数据表之间是纵横交叉、相互关联的,laravel的一对一,一对多比较好理解,本文重点通过实例给大家讲解 laravel中的多对多关系,感兴趣的朋友一起看看吧
数据表之间是纵横交叉、相互关联的,laravel的一对一,一对多比较好理解,官网介绍滴很详细了,在此我就不赘述啦,重点我记下多对多的关系
一种常见的关联关系是多对多,即表A的某条记录通过中间表C与表B的多条记录关联,反之亦然。比如一个用户有多种角色,反之一个角色对应多个用户。
为了测试该关联关系,我们沿用官网的用户角色示例:
需要三张数据表:users、roles 和 role_user,role_user 表按照关联模型名的字母顺序命名(这里role_user是中间表),并且包含 user_id 和 role_id两个列。
多对多关联通过编写返回 belongsToMany 方法返回结果的方法来定义。废话不说多,直接上数据结构:
1:创建一个角色表roles,并添加一些初始化数据:
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS=0; -- ---------------------------- -- Table structure for users -- ---------------------------- DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `users`; CREATE TABLE `users` ( `id` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `name` varchar(255) COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci NOT NULL, `email` varchar(255) COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci NOT NULL, `password` varchar(60) COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci NOT NULL, `remember_token` varchar(100) COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci DEFAULT NULL, `created_at` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT '0000-00-00 00:00:00', `updated_at` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT '0000-00-00 00:00:00', PRIMARY KEY (`id`), UNIQUE KEY `users_email_unique` (`email`) USING BTREE ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=4 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COLLATE=utf8_unicode_ci; -- ---------------------------- -- Records of users -- ---------------------------- INSERT INTO `users` VALUES ('1', 'admin', 'admin@163.com', '$2y$10$J/yXqscucanrHAGZp9G6..Tu1Md.SOljX3M8WrHsUdrgat4zeSuhC', 'ilocXtjZJwhrmIdLG1cKOYegeCwQCkuyx1pYAOLuzY2PpScQFT5Ss7lBCi7i', '2016-04-21 16:26:23', '2016-12-14 09:29:59'); INSERT INTO `users` VALUES ('2', 'baidu', '10940370@qq.com', '$2y$10$2A5zJ4pnJ5uCp1DN3NX.5uj/Ap7P6O4nP2BaA55aFra8/rti1K6I2', null, '2016-04-22 06:48:10', '2016-04-22 06:48:10'); INSERT INTO `users` VALUES ('3', 'fantasy', '1009@qq.com', '', null, '2017-06-14 10:38:57', '2017-06-15 10:39:01');
2:创建一个角色表roles,并添加一些初始化数据:
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS=0; -- ---------------------------- -- Table structure for roles -- ---------------------------- DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `roles`; CREATE TABLE `roles` ( `id` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `name` varchar(255) COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci NOT NULL, `created_at` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT '0000-00-00 00:00:00', `updated_at` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT '0000-00-00 00:00:00', PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=7 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COLLATE=utf8_unicode_ci; -- ---------------------------- -- Records of roles -- ---------------------------- INSERT INTO `roles` VALUES ('1', '超级版主', '2016-04-21 16:26:23', '2016-12-14 09:29:59'); INSERT INTO `roles` VALUES ('2', '司令', '2016-04-22 06:48:10', '2016-04-22 06:48:10'); INSERT INTO `roles` VALUES ('3', '军长', '2017-06-14 10:38:57', '2017-06-15 10:39:01'); INSERT INTO `roles` VALUES ('4', '司长', '2017-06-07 10:41:41', '2017-06-15 10:41:51'); INSERT INTO `roles` VALUES ('5', '团战', '2017-06-22 10:41:44', '2017-06-28 10:41:54'); INSERT INTO `roles` VALUES ('6', '小兵', '2017-06-22 10:41:47', '2017-06-22 10:41:56');
3:创建一个中间表role_user用于记录users表与roles表的对应关系,并添加一些初始化数据:
SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS=0; -- ---------------------------- -- Table structure for role_user -- ---------------------------- DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `role_user`; CREATE TABLE `role_user` ( `id` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `user_id` int(11) DEFAULT NULL, `role_id` int(11) DEFAULT NULL, `created_at` datetime DEFAULT NULL, `updated_at` datetime DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=MyISAM AUTO_INCREMENT=8 DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1; -- ---------------------------- -- Records of role_user -- ---------------------------- INSERT INTO `role_user` VALUES ('1', '1', '2', '2017-06-07 11:42:13', '2017-06-21 11:32:16'); INSERT INTO `role_user` VALUES ('2', '1', '3', '2017-06-07 11:32:13', '2017-06-07 11:22:13'); INSERT INTO `role_user` VALUES ('3', '2', '4', '2017-06-07 11:32:13', '2017-06-07 11:12:13'); INSERT INTO `role_user` VALUES ('4', '1', '5', '2017-06-07 11:32:13', '2017-06-07 11:22:13'); INSERT INTO `role_user` VALUES ('5', '3', '6', '2017-06-07 11:32:13', '2017-06-07 11:52:13'); INSERT INTO `role_user` VALUES ('6', '3', '2', '2017-06-07 11:32:13', '2017-06-07 11:42:13'); INSERT INTO `role_user` VALUES ('7', '2', '2', '2017-06-07 11:42:13', '2017-06-07 11:52:13');
注意我们定义中间表的时候没有在结尾加s并且命名规则是按照字母表顺序,将role放在前面,user放在后面,并且用_分隔,这一切都是为了适应Eloquent模型关联的默认设置:在定义多对多关联的时候如果没有指定中间表,Eloquent默认的中间表使用这种规则拼接出来。
创建一个Role模型:
<?php
namespace App\Models;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
/**
* Class Role
* @package App\Models
* @mixin \Eloquent
*/
class Role extends Model
{
}然后我们在 User 模型上定义 roles 方法:
<?php
namespace App\Models;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
/**
* Class User
* @package App\Models
* @mixin \Eloquent
*/
class User extends Model
{
/**
* 用户角色
*/
public function roles()
{
return $this->belongsToMany('App\Models\Role');
}
}注:正如我们上面提到的,如果中间表不是role_user,那么需要将中间表作为第二个参数传入belongsToMany方法,如果中间表中的字段不是user_id和role_id,这里我们姑且将其命名为$user_id和$role_id,那么需要将$user_id作为第三个参数传入该方法,$role_id作为第四个参数传入该方法,如果关联方法名不是roles还可以将对应的关联方法名作为第五个参数传入该方法。
接下来我们在控制器中编写测试代码:
<?php $user = User::find(1); $roles = $user->roles; echo '用户'.$user->name.'所拥有的角色:'; foreach($roles as $role) echo $role->name.' '; //对应输出为:用户admin所拥有的角色:司令 军长 团战
当然,和所有其它关联关系类型一样,你可以调用roles 方法来添加条件约束到关联查询上:
User::find(1)->roles()->orderBy('name')->get();
正如前面所提到的,为了确定关联关系连接表的表名,Eloquent 以字母顺序连接两个关联模型的名字。不过,你可以重写这种约定 —— 通过传递第二个参数到 belongsToMany 方法:
return $this->belongsToMany('App\Models\Role', 'user_roles');
除了自定义连接表的表名,你还可以通过传递额外参数到 belongsToMany 方法来自定义该表中字段的列名。第三个参数是你定义关联关系模型的外键名称,第四个参数你要连接到的模型的外键名称:
return $this->belongsToMany('App\Models\Role', 'user_roles', 'user_id', 'role_id');
定义相对的关联关系
要定义与多对多关联相对的关联关系,只需在关联模型中调用一下 belongsToMany 方法即可。我们在 Role 模型中定义 users 方法:
<?php
namespace App\Models;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
/**
* Class Role
* @package App\Models
* @mixin \Eloquent
*/
class Role extends Model
{
/**
* 角色用户
*/
public function users()
{
return $this->belongsToMany('App\Models\User');
}
}正如你所看到的,定义的关联关系和与其对应的User 中定义的一模一样,只是前者引用 App\Models\Role,后者引用App\Models\User,由于我们再次使用了 belongsToMany 方法,所有的常用表和键自定义选项在定义与多对多相对的关联关系时都是可用的。
测试代码如下:
$role = Role::find(2); $users = $role->users; echo '角色#'.$role->name.'下面的用户:'; foreach ($users as $user) echo $user->name.' ';//对应输出为:角色#司令下面的用户:admin fantasy baidu
正如你看到的,处理多对多关联要求一个中间表。Eloquent 提供了一些有用的方法来与这个中间表进行交互,例如,我们假设 User 对象有很多与之关联的 Role 对象,访问这些关联关系之后,我们可以使用这些模型上的pivot 属性访问中间表字段:
$roles = User::find(1)->roles; foreach ($roles as $role) echo $role->pivot->role_id.'<br>';//对应输出为:2 3 5
注意我们获取到的每一个 Role 模型都被自动赋上了 pivot 属性。该属性包含一个代表中间表的模型,并且可以像其它 Eloquent 模型一样使用。
默认情况下,只有模型主键才能用在 pivot 对象上,如果你的 pivot 表包含额外的属性,必须在定义关联关系时进行指定:
return $this->belongsToMany('App\Models\Role')->withPivot('column1', 'column2');
比如我们修改role_user表增加一个字段 username 数据如下:
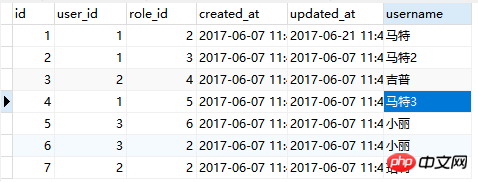
修改模型User:
<?php
namespace App\Models;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
/**
* Class User
* @package App\Models
* @mixin \Eloquent
*/
class User extends Model
{
/**
* 用户角色
*/
public function roles()
{
//return $this->belongsToMany('App\Models\Role');
return $this->belongsToMany('App\Models\Role')->withPivot('username');
}
}测试代码如下:
$user = User::find(1); foreach ($user->roles as $role) echo $role->pivot->username;//对应输出为:马特马特2马特3
如果你想要你的 pivot 表自动包含created_at 和 updated_at 时间戳,在关联关系定义时使用 withTimestamps 方法:
return $this->belongsToMany('App\Models\Role')->withTimestamps();
通过中间表字段过滤关联关系
你还可以在定义关联关系的时候使用 wherePivot 和 wherePivotIn 方法过滤belongsToMany 返回的结果集:
return $this->belongsToMany('App\Models\Role')->withPivot('username')->wherePivot('username', '马特2'); //return $this->belongsToMany('App\Models\Role')->wherePivotIn('role_id', [1, 2]);
测试代码如下:
$user = User::find(1); print_r($user->roles->toArray());
以上对应输出:
Array
(
[0] => Array
(
[id] => 3
[name] => 军长
[created_at] => 2017-06-14 10:38:57
[updated_at] => 2017-06-15 10:39:01
[pivot] => Array
(
[user_id] => 1
[role_id] => 3
[username] => 马特2
)
)
)如果你想要你的pivot表自动包含created_at和updated_at时间戳,在关联关系定义时使用withTimestamps方法:
return $this->belongsToMany('App\Models\Role')->withTimestamps();
The above is the detailed content of Detailed example of many-to-many relationship in laravel. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 PHP and Python: Comparing Two Popular Programming Languages
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:13 AM
PHP and Python: Comparing Two Popular Programming Languages
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:13 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages, and choose according to project requirements. 1.PHP is suitable for web development, especially for rapid development and maintenance of websites. 2. Python is suitable for data science, machine learning and artificial intelligence, with concise syntax and suitable for beginners.
 PHP's Current Status: A Look at Web Development Trends
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:20 AM
PHP's Current Status: A Look at Web Development Trends
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:20 AM
PHP remains important in modern web development, especially in content management and e-commerce platforms. 1) PHP has a rich ecosystem and strong framework support, such as Laravel and Symfony. 2) Performance optimization can be achieved through OPcache and Nginx. 3) PHP8.0 introduces JIT compiler to improve performance. 4) Cloud-native applications are deployed through Docker and Kubernetes to improve flexibility and scalability.
 PHP vs. Other Languages: A Comparison
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP vs. Other Languages: A Comparison
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP is suitable for web development, especially in rapid development and processing dynamic content, but is not good at data science and enterprise-level applications. Compared with Python, PHP has more advantages in web development, but is not as good as Python in the field of data science; compared with Java, PHP performs worse in enterprise-level applications, but is more flexible in web development; compared with JavaScript, PHP is more concise in back-end development, but is not as good as JavaScript in front-end development.
 The Enduring Relevance of PHP: Is It Still Alive?
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:12 AM
The Enduring Relevance of PHP: Is It Still Alive?
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:12 AM
PHP is still dynamic and still occupies an important position in the field of modern programming. 1) PHP's simplicity and powerful community support make it widely used in web development; 2) Its flexibility and stability make it outstanding in handling web forms, database operations and file processing; 3) PHP is constantly evolving and optimizing, suitable for beginners and experienced developers.
 PHP's Purpose: Building Dynamic Websites
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:18 AM
PHP's Purpose: Building Dynamic Websites
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:18 AM
PHP is used to build dynamic websites, and its core functions include: 1. Generate dynamic content and generate web pages in real time by connecting with the database; 2. Process user interaction and form submissions, verify inputs and respond to operations; 3. Manage sessions and user authentication to provide a personalized experience; 4. Optimize performance and follow best practices to improve website efficiency and security.
 PHP vs. Python: Core Features and Functionality
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:16 AM
PHP vs. Python: Core Features and Functionality
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:16 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages and are suitable for different scenarios. 1.PHP is suitable for web development and provides built-in web servers and rich function libraries. 2. Python is suitable for data science and machine learning, with concise syntax and a powerful standard library. When choosing, it should be decided based on project requirements.
 PHP in Action: Real-World Examples and Applications
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP in Action: Real-World Examples and Applications
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP is widely used in e-commerce, content management systems and API development. 1) E-commerce: used for shopping cart function and payment processing. 2) Content management system: used for dynamic content generation and user management. 3) API development: used for RESTful API development and API security. Through performance optimization and best practices, the efficiency and maintainability of PHP applications are improved.
 PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP is mainly procedural programming, but also supports object-oriented programming (OOP); Python supports a variety of paradigms, including OOP, functional and procedural programming. PHP is suitable for web development, and Python is suitable for a variety of applications such as data analysis and machine learning.






