Node crawler advanced - login
In the previous article node entry scenario - crawler, we have introduced the simplest node crawler implementation. This article goes one step further on the original basis and discusses how to bypass the login and crawl the data in the login area.
Contents
Theoretical basis
- ##How to maintain login status
- How does the browser do it
- node implementation
- If there is a
verification codeHow to break it
- EXTEND ##Summary
- 1. Theoretical basis
How to maintain login status
http as a A protocol without
status. The client and server will not maintain a long connection. How can the server identify which interfaces are from the same client between independent requests and responses? You can easily think of the following mechanism:
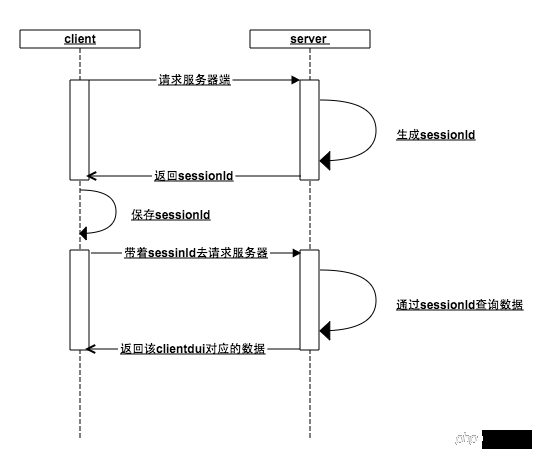
##session
The core of this mechanism is Session id (sessionId):
When the client requests the server, the server determines that the client has not passed in the sessionId. Okay, this guy is new, generate it for it A sessionId is stored in the memory, and the sessionId is returned to the client.- The client gets the sessionId from the server and saves it locally. It will bring this sessionId with the next request, and the server checks the memory. Does this sessionId exist ( If in a previous step, the user accessed the login interface, then the seesionId is already
- key
in the memory at this moment, and the user data is saved in the memory ), the server can return the data corresponding to the client based on the unique identifier of sessionId
Whether the client or the server loses the sessionId, the previous steps will be repeated. No one knows anyone anymore, start over - First the client establishes an association with the server through sessionId, and then the user establishes an association with the server through the client (key-value pair between sessionId and user data), thus maintaining the login state
How does the browser do it
In fact, does the browser follow the above What about the mechanism design? It really is!
##bs-sid.png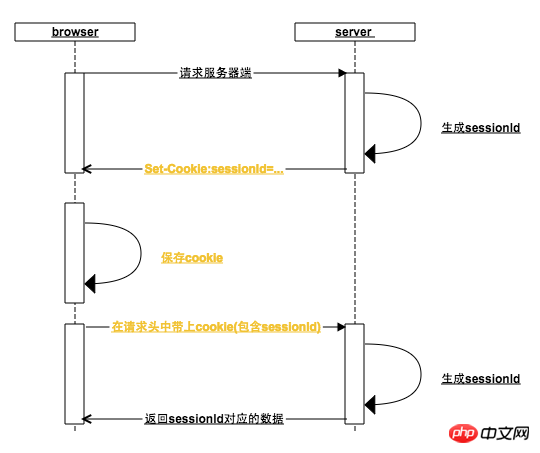
What does the browser do:
in the cookie yet. 2. The browser sets the cookie according to the
Set-Cookie in the server response header. For this reason, the server will put the generated sessionId into Set-cookie
When the browser receives the Set-Cookie instruction, it will set a local cookie with the domain name of the request address as the key. Generally, when the server returns the Set-cookie, the expiration time of the sessionId is set to the browser to close by default. It expires when the browser is opened, which is why it is a session from opening to closing the browser (some websites can also be set to stay logged in and set cookies that will not expire for a long time)
3. When the browser opens again When a request is initiated in the background, the cookie in the request header already contains the sessionId. If the user has visited the login interface before, then the user data can bequeried
based on the sessionId
There is no proof, here is an example: 1). First use the login page opened by chr
ome, and find all the files under http://www.jianshu.com in the application Cookie, enter the Network item and check preserve log (otherwise you will not be able to see the previous log after the page is redirected)Login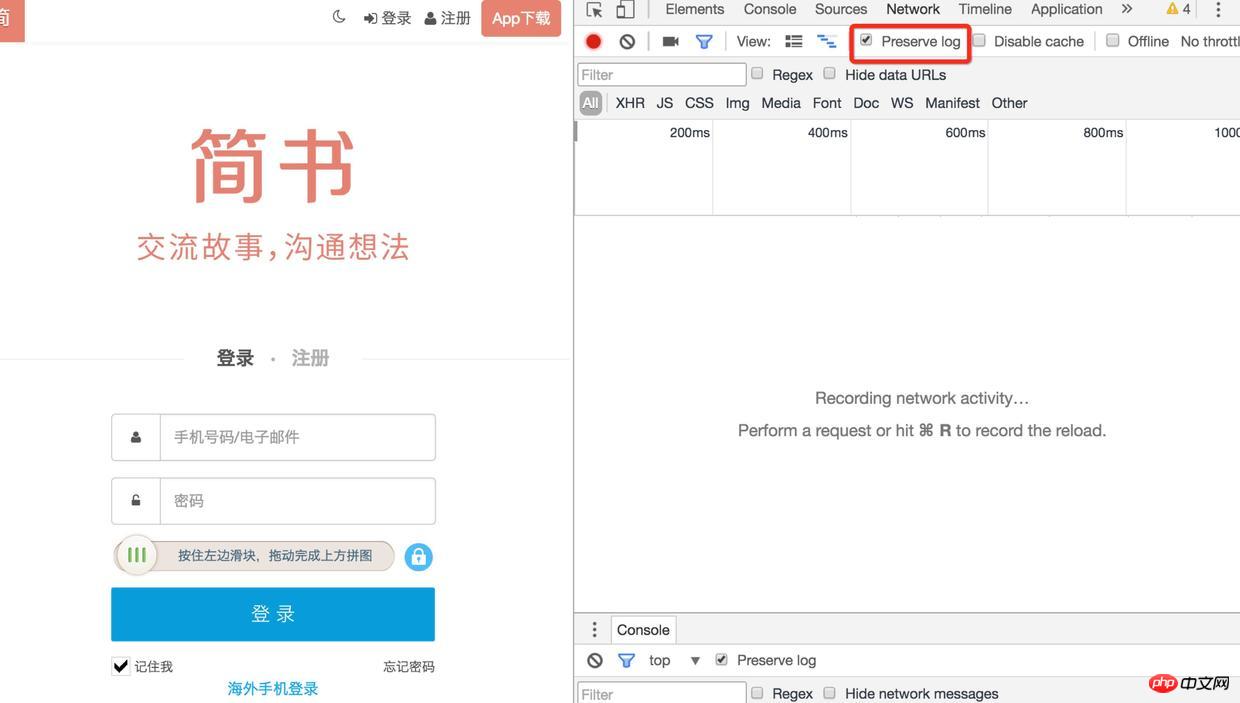
2). Then refresh the page and find the sign-in interface. There are many Set-Cookies in its response header. Are there any
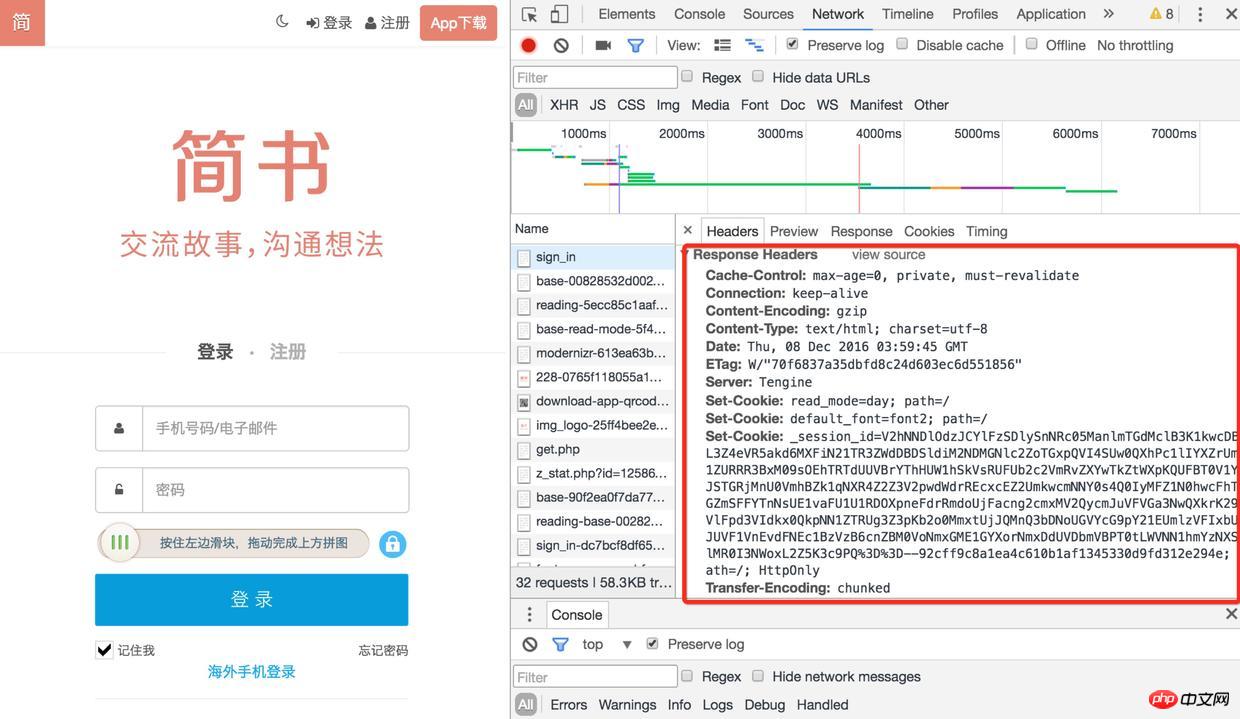
Login
3). When you check the cookie again, the session-id has been saved, and you will request others next time When accessing the interface (such as obtaining verification code, logging in), this session-id will be brought. After logging in, the user's information will also be associated with the session-id
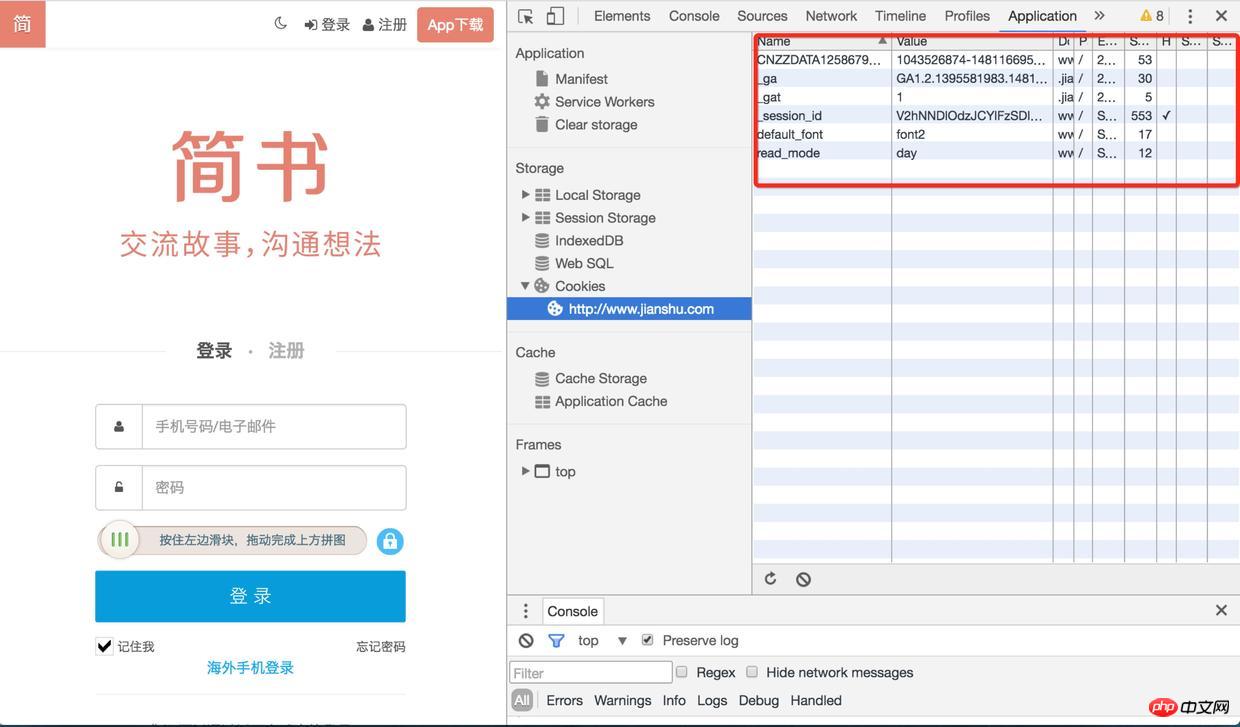
Login
2. Node implementation
We need to simulate the working mode of the browser and crawl the data in the website login area
I found one without verification Test the website with the verification code. If there is a verification code, verification code identification is involved (the login is not considered, the complexity of the verification code is impressive). The next section explains
Access the login interface to obtain cookies
// 浏览器请求报文头部部分信息
var browserMsg={
"User-Agent":"Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_10_5) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/54.0.2840.71 Safari/537.36",
'Content-Type':'application/x-www-form-urlencoded'
};
//访问登录接口获取cookie
function getLoginCookie(userid, pwd) {
userid = userid.toUpperCase();
return new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
superagent.post(url.login_url).set(browserMsg).send({
userid: userid,
pwd: pwd,
timezoneOffset: '0'
}).redirects(0).end(function (err, response) {
//获取cookie
var cookie = response.headers["set-cookie"];
resolve(cookie);
});
});
}You need to capture a request under chrome and obtain some request header information, because the server may verify these request header information. For example, on the website I experimented with, I did not pass in the User-Agent at first. The server found that the request was not from the server and returned a string of error messages, so I later set up the User-Agent and put I pretend to be a chrome browser~~
superagent is a client-side HTTP request library. You can use it to easily send requests and process cookies (call http.request yourself to operate The header field data is not so convenient. After obtaining the set-cookie, you have to assemble it into a suitable format cookie). redirects(0) is mainly set not to redirect
Request the interface in the login area
function getData(cookie) {
return new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
//传入cookie
superagent.get(url.target_url).set("Cookie",cookie).set(browserMsg).end(function(err,res) {
var $ = cheerio.load(res.text);
resolve({
cookie: cookie,
doc: $
});
});
});
}After getting the set-cookie in the previous step, pass in the getData method , after setting it into the request through the superagent (set-cookie will be formatted into a cookie), you can get the login data normally
In the actual scenario, it may not be so smooth, because it is different Websites have different security measures. For example: some websites may need to request a token first, some websites need to encrypt parameters, and some with higher security also have anti-replay mechanisms. In directional crawlers, this requires a detailed analysis of the website's processing mechanism. If it cannot be circumvented, then enough is enough~~
But it is still enough to deal with general content information websites
What is requested through the above method is only a piece of html string. Here is the old method. Use the cheerio library to load the string, and you can get a ## similar to jquery dom. #Object, you can operate dom like jquery. This is really an artifact, made with conscience!
3. How to break the verification code if there is one?How many websites can you log in to without entering the verification code? Of course, we won’t try to identify the verification code of 12306. We don’t expect such a conscientious verification code. Too young and too simple verification codes like Zhihu can still be challenged.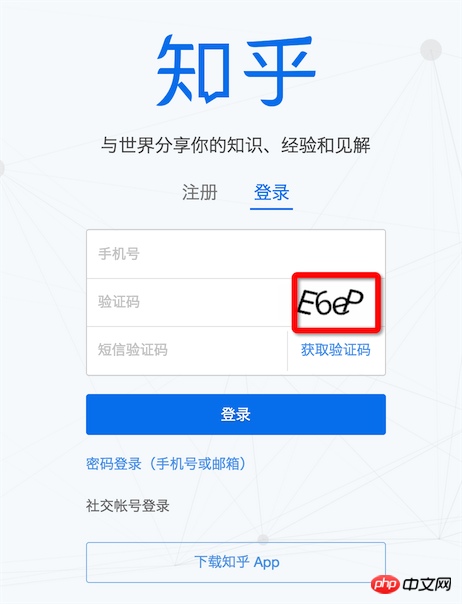
node.jsRealizing simple recognition of verification codes
However, even if graphicsmagick is used to preprocess Whether you can achieve a high recognition rate depends on your character~~~ 4. Extension There is a simpler way to bypass the login state, which is to use PhantomJS. Phantomjs is an open source server js based on webkitapi. It can be considered as a browser , but you can control it through js script.
Since it completely simulates thebehavior of the browser, you don’t need to care about set-cookie, cookie at all, you only need to simulate the user’s click operation (of course, if there is verification code, you still have to identify it)
This method is not without its shortcomings. It completely simulates the behavior of the browser, which means that it does not miss any request and needs to load js, css, and images that you may not need.Static For resources, you need to click on multiple pages to reach the destination page, which is less efficient than directly accessing the target url
Search if you are interestedSearch
phontomJS
5. Summary
Although I am talking about the login of node crawler, I have talked about a lot of principles before. The purpose is that if you want to change the language to implement it, you can do it with ease. Still the same sentence: It is important to understand the principle
Welcome to leave a message for discussion. If it is helpful to you, please leave a like~~
The above is the detailed content of Node crawler advanced - login. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to delete node in nvm
Dec 29, 2022 am 10:07 AM
How to delete node in nvm
Dec 29, 2022 am 10:07 AM
How to delete node with nvm: 1. Download "nvm-setup.zip" and install it on the C drive; 2. Configure environment variables and check the version number through the "nvm -v" command; 3. Use the "nvm install" command Install node; 4. Delete the installed node through the "nvm uninstall" command.
 How to use express to handle file upload in node project
Mar 28, 2023 pm 07:28 PM
How to use express to handle file upload in node project
Mar 28, 2023 pm 07:28 PM
How to handle file upload? The following article will introduce to you how to use express to handle file uploads in the node project. I hope it will be helpful to you!
 How to do Docker mirroring of Node service? Detailed explanation of extreme optimization
Oct 19, 2022 pm 07:38 PM
How to do Docker mirroring of Node service? Detailed explanation of extreme optimization
Oct 19, 2022 pm 07:38 PM
During this period, I was developing a HTML dynamic service that is common to all categories of Tencent documents. In order to facilitate the generation and deployment of access to various categories, and to follow the trend of cloud migration, I considered using Docker to fix service content and manage product versions in a unified manner. . This article will share the optimization experience I accumulated in the process of serving Docker for your reference.
 An in-depth analysis of Node's process management tool 'pm2”
Apr 03, 2023 pm 06:02 PM
An in-depth analysis of Node's process management tool 'pm2”
Apr 03, 2023 pm 06:02 PM
This article will share with you Node's process management tool "pm2", and talk about why pm2 is needed, how to install and use pm2, I hope it will be helpful to everyone!
 Pi Node Teaching: What is a Pi Node? How to install and set up Pi Node?
Mar 05, 2025 pm 05:57 PM
Pi Node Teaching: What is a Pi Node? How to install and set up Pi Node?
Mar 05, 2025 pm 05:57 PM
Detailed explanation and installation guide for PiNetwork nodes This article will introduce the PiNetwork ecosystem in detail - Pi nodes, a key role in the PiNetwork ecosystem, and provide complete steps for installation and configuration. After the launch of the PiNetwork blockchain test network, Pi nodes have become an important part of many pioneers actively participating in the testing, preparing for the upcoming main network release. If you don’t know PiNetwork yet, please refer to what is Picoin? What is the price for listing? Pi usage, mining and security analysis. What is PiNetwork? The PiNetwork project started in 2019 and owns its exclusive cryptocurrency Pi Coin. The project aims to create a one that everyone can participate
 What to do if npm node gyp fails
Dec 29, 2022 pm 02:42 PM
What to do if npm node gyp fails
Dec 29, 2022 pm 02:42 PM
npm node gyp fails because "node-gyp.js" does not match the version of "Node.js". The solution is: 1. Clear the node cache through "npm cache clean -f"; 2. Through "npm install -g n" Install the n module; 3. Install the "node v12.21.0" version through the "n v12.21.0" command.
 Let's talk about how to use pkg to package Node.js projects into executable files.
Dec 02, 2022 pm 09:06 PM
Let's talk about how to use pkg to package Node.js projects into executable files.
Dec 02, 2022 pm 09:06 PM
How to package nodejs executable file with pkg? The following article will introduce to you how to use pkg to package a Node project into an executable file. I hope it will be helpful to you!
 Token-based authentication with Angular and Node
Sep 01, 2023 pm 02:01 PM
Token-based authentication with Angular and Node
Sep 01, 2023 pm 02:01 PM
Authentication is one of the most important parts of any web application. This tutorial discusses token-based authentication systems and how they differ from traditional login systems. By the end of this tutorial, you will see a fully working demo written in Angular and Node.js. Traditional Authentication Systems Before moving on to token-based authentication systems, let’s take a look at traditional authentication systems. The user provides their username and password in the login form and clicks Login. After making the request, authenticate the user on the backend by querying the database. If the request is valid, a session is created using the user information obtained from the database, and the session information is returned in the response header so that the session ID is stored in the browser. Provides access to applications subject to






