Detailed explanation of XML-JAXP technology-DOM parsing
DOM解析的基本思路:
1、将整个XML文件一次性读入内存
2、将整个XML看做一棵树
3、XML中的每一个标签,属性,文本都看做是树上的一个结点
4、然后可以对结点进行增删改查的操作
话不多说,上代码。
1、首先我在D:\ABC中新建了一个文本文件,重命名为stus.xml,以下是文件中的内容
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "GBK" ?> <stus class = "S160401A"> <stu num = "001" > <name>张三</name> <age>20</age> <sex>男</sex> </stu> <stu num = "002"> <name>李四</name> <age>21</age> <sex>女</sex> </stu> <stu num = "003"> <name>王五</name> <age>22</age> <sex>男</sex> </stu> </stus>
在第一行是XML声明,version表示版本号,encoding表示编码方式,微软的记事本用的是国标的编码方式,如果要用UTF-8,则要在另存为窗口中修改编码方式为UTF-8。
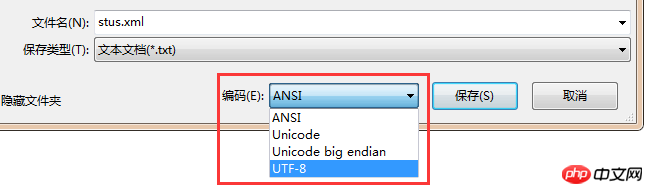
必须且只能有一对根标签,我写的根标签是
2、这是一个学生类,定义了一些属性和get、set方法
<span style="max-width:90%">public class Student {
public static String Class;
private String name;
private int num;
private int age;
private char sex;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getNum() {
return num;
}
public void setNum(int num) {
this.num = num;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public char getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(char sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
}</span>3、这是用DOM解析的类,看这个类之前还要了解一下。
DocumentBuilderFactory DOM解析器工厂
DocumentBuilder DOM解析器
Document 文档对象
Node 结点【接口】
Element 元素结点【标签结点】
Attr 属性结点
Text 文本结点
Node 是Document,Element,Attr,Text的父接口
NodeList 结点列表
NamedNodeMap 一个结点的所有属性
<span style="font-size: 16px;">import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilder;
import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilderFactory;
import org.w3c.dom.Attr;
import org.w3c.dom.Document;
import org.w3c.dom.Element;
import org.w3c.dom.NamedNodeMap;
import org.w3c.dom.Node;
import org.w3c.dom.NodeList;
import bean.Student;
public class DOMParser {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 得到解析器工厂对象
DocumentBuilderFactory factory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
// 生产一个解析器对象
DocumentBuilder builder = factory.newDocumentBuilder();
// 开始解析XML文件,得到解析的结果,是一个Document对象
// Document对象叫做文档树对象
Document dom = builder.parse("D:\\ABC\\stus.xml");
// 通过Document对象提取数据
// Document对象的第一个子节点是根节点[根标签]
Node root = dom.getFirstChild();
// 获得标签的名字
String str = root.getNodeName();
// 获得根节点的属性
NamedNodeMap attrs = root.getAttributes();
// 强转成Attr类型 属性类
Attr attr = (Attr) attrs.getNamedItem("class");
// 获得属性里的值
String v = attr.getValue();
System.out.println(v);
// 获得所有的学生-------------------------------------
NodeList list = root.getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < list.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = list.item(i);
// 判断是否是标签结点
if (node instanceof Element) {
Element e = (Element) node;
// 获得标签结点里属性的值
String num = e.getAttribute("num");
System.out.println(num);
// 输出标签中的文本
// System.out.println(e.getTextContent());
// 继续获得stu的子节点
NodeList nodeList = e.getChildNodes();
for (int j = 0; j < nodeList.getLength(); j++) {
Node n = nodeList.item(j);
if (n instanceof Element) {
Element ele = (Element) n;
// 获得元素结点的标签名字
String nodeName = ele.getNodeName();
// 获得元素结点标签中的文本
String value = ele.getTextContent();
if (nodeName.equals("name")) {
System.out.println("姓名:" + value);
} else if (nodeName.equals("age")) {
System.out.println("年龄:" + value);
} else if (nodeName.equals("sex")) {
System.out.println("性别:" + value);
}
}
}
}
}
}
}</span>自己在其中总结了一些方法:
DocumentBuilderFactory类:
public static DocumentBuilderFactory newInstance(); //得到解析器工厂对象 public abstract DocumentBuilder newDocumentBuilder(); //生产一个解析器对象
DocumentBuilder类:
public Document parse(String uri); //解析路径为uri的XML文件,得到解析的结果是一个Document对象
Node类:
public Node getFirstChild(); //得到Document对象的第一个子结点,也就是根结点、或者叫根标签,在上面的代码中得到的是stus,看上面的第1点中的XML文件的内容。 public NamedNodeMap getAttributes();//获得结点的属性 public NodeList getChildNodes();//获得所有子结点 public String getNodeName();//获得标签的名字 public String getTextContent() throws DOMException;//获得标签结点中的文本
NamedNodeMap类:
public Node getNamedItem(String name);//返回所有名字为name的结点
Attr类:
public String getValue();//获得属性里的值
NodeList类:
public Node item(int index);//返回第index个结点
Element类:
public String getAttribute(String name);//获得标签结点里属性name的值
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of XML-JAXP technology-DOM parsing. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Can I open an XML file using PowerPoint?
Feb 19, 2024 pm 09:06 PM
Can I open an XML file using PowerPoint?
Feb 19, 2024 pm 09:06 PM
Can XML files be opened with PPT? XML, Extensible Markup Language (Extensible Markup Language), is a universal markup language that is widely used in data exchange and data storage. Compared with HTML, XML is more flexible and can define its own tags and data structures, making the storage and exchange of data more convenient and unified. PPT, or PowerPoint, is a software developed by Microsoft for creating presentations. It provides a comprehensive way of
 Convert XML data to CSV format in Python
Aug 11, 2023 pm 07:41 PM
Convert XML data to CSV format in Python
Aug 11, 2023 pm 07:41 PM
Convert XML data in Python to CSV format XML (ExtensibleMarkupLanguage) is an extensible markup language commonly used for data storage and transmission. CSV (CommaSeparatedValues) is a comma-delimited text file format commonly used for data import and export. When processing data, sometimes it is necessary to convert XML data to CSV format for easy analysis and processing. Python is a powerful
 Python implements conversion between XML and JSON
Aug 07, 2023 pm 07:10 PM
Python implements conversion between XML and JSON
Aug 07, 2023 pm 07:10 PM
Python implements conversion between XML and JSON Introduction: In the daily development process, we often need to convert data between different formats. XML and JSON are common data exchange formats. In Python, we can use various libraries to convert between XML and JSON. This article will introduce several commonly used methods, with code examples. 1. To convert XML to JSON in Python, we can use the xml.etree.ElementTree module
 Handling errors and exceptions in XML using Python
Aug 08, 2023 pm 12:25 PM
Handling errors and exceptions in XML using Python
Aug 08, 2023 pm 12:25 PM
Handling Errors and Exceptions in XML Using Python XML is a commonly used data format used to store and represent structured data. When we use Python to process XML, sometimes we may encounter some errors and exceptions. In this article, I will introduce how to use Python to handle errors and exceptions in XML, and provide some sample code for reference. Use try-except statement to catch XML parsing errors When we use Python to parse XML, sometimes we may encounter some
 Python parsing special characters and escape sequences in XML
Aug 08, 2023 pm 12:46 PM
Python parsing special characters and escape sequences in XML
Aug 08, 2023 pm 12:46 PM
Python parses special characters and escape sequences in XML XML (eXtensibleMarkupLanguage) is a commonly used data exchange format used to transfer and store data between different systems. When processing XML files, you often encounter situations that contain special characters and escape sequences, which may cause parsing errors or misinterpretation of the data. Therefore, when parsing XML files using Python, we need to understand how to handle these special characters and escape sequences. 1. Special characters and
 How to handle XML and JSON data formats in C# development
Oct 09, 2023 pm 06:15 PM
How to handle XML and JSON data formats in C# development
Oct 09, 2023 pm 06:15 PM
How to handle XML and JSON data formats in C# development requires specific code examples. In modern software development, XML and JSON are two widely used data formats. XML (Extensible Markup Language) is a markup language used to store and transmit data, while JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) is a lightweight data exchange format. In C# development, we often need to process and operate XML and JSON data. This article will focus on how to use C# to process these two data formats, and attach
 Using Python to implement data verification in XML
Aug 10, 2023 pm 01:37 PM
Using Python to implement data verification in XML
Aug 10, 2023 pm 01:37 PM
Using Python to implement data validation in XML Introduction: In real life, we often deal with a variety of data, among which XML (Extensible Markup Language) is a commonly used data format. XML has good readability and scalability, and is widely used in various fields, such as data exchange, configuration files, etc. When processing XML data, we often need to verify the data to ensure the integrity and correctness of the data. This article will introduce how to use Python to implement data verification in XML and give the corresponding
 How to use PHP functions to process XML data?
May 05, 2024 am 09:15 AM
How to use PHP functions to process XML data?
May 05, 2024 am 09:15 AM
Use PHPXML functions to process XML data: Parse XML data: simplexml_load_file() and simplexml_load_string() load XML files or strings. Access XML data: Use the properties and methods of the SimpleXML object to obtain element names, attribute values, and subelements. Modify XML data: add new elements and attributes using the addChild() and addAttribute() methods. Serialized XML data: The asXML() method converts a SimpleXML object into an XML string. Practical example: parse product feed XML, extract product information, transform and store it into a database.






