Summary of Xpath positioning
1.Relative positioning and absolute positioning
// represents relative positioning. Relative positioning should be used for pages or nodes that frequently change. Search
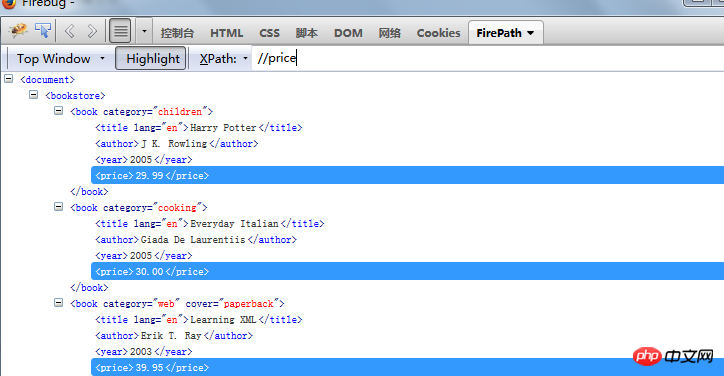
/ means absolute positioning. When remains unchanged, you can use absolute positioning to search
2.Node
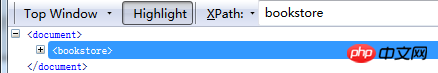
##Top node: bookstore
 Current node:“. ”
Current node:“. ”
If there are multiple current nodes, match multiple
If the current node has only 1, then match 1
Select the current node The parentnode:" ..”
For p under html/body, its parent node is body. This is done using absolute The path means that you must find the body from the html and then find p, and then match the parent node of p.
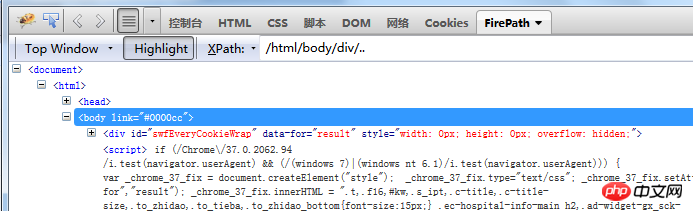
If you use a relative path to find the parent node, you can see that its absolute position is not considered starting from p, that is to say All elements starting from body that meet the conditions of the parent node will be found.
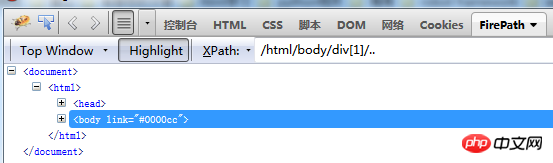
Find all elements under the current node: //book[1]/..
This is the method of node index +parent node

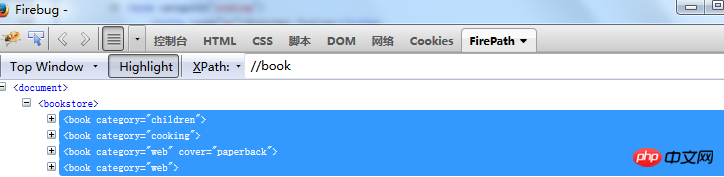
Positioning by label Element //book
: Find all tags namedbook
Attribute positioning1.
The element whose positioning attribute iscategory//book[@category='cooking'] '
[]' means search attribute
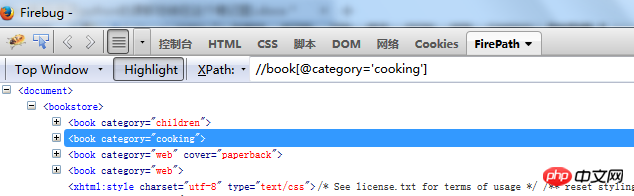 2.
2.
text text attribute for precise positioning, text can also be used instead of
Find the element with the text 30.00 under//book//price
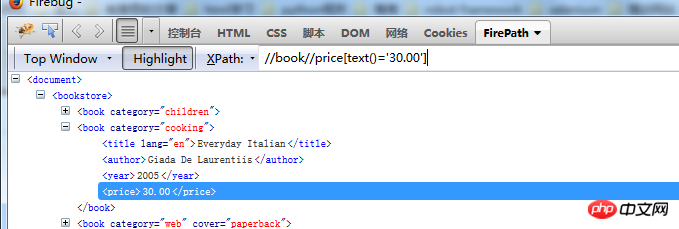
Find the element in the text in the year tag that is greater than 2004
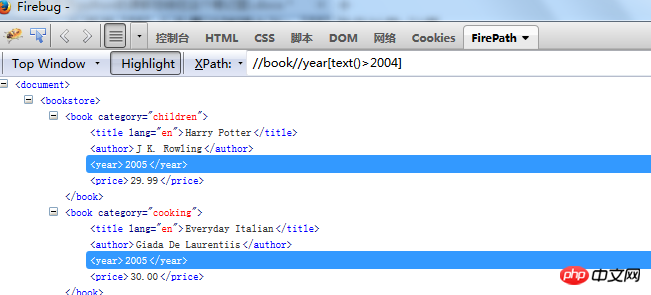
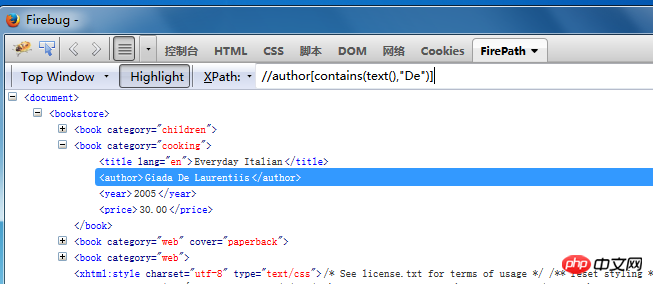
3. Use contains for fuzzy positioning. contains means containing
Fuzzy positioning searches for elements whose text information contains Potter: //title[contains(text(),"Potter")]
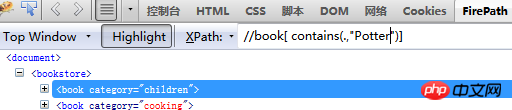
Extension Exercise
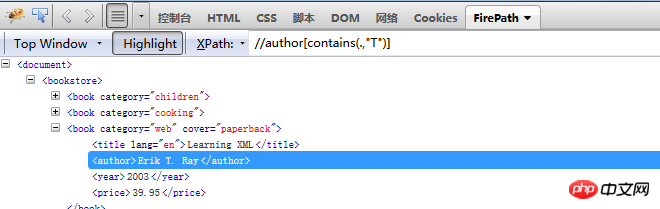
4.”*” means any Attributes All attributes
Find all attributes with attribute values://@*
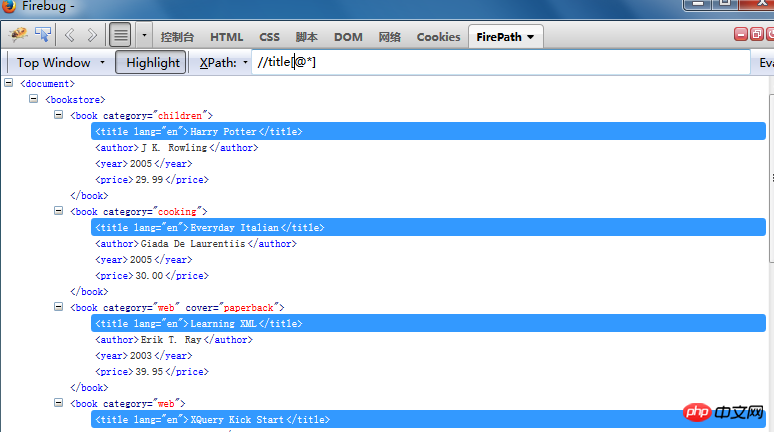

Find all elements with attributes in the tag:
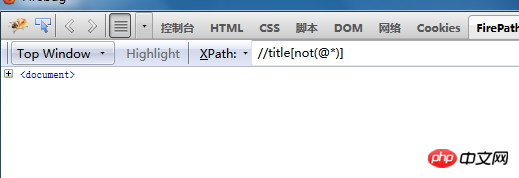
Not to negate , means to find elements that have no attributes in the title tag , there is no one here so I didn’t find it.
@*
means all attributesnot(@*)
means no attributes
5.
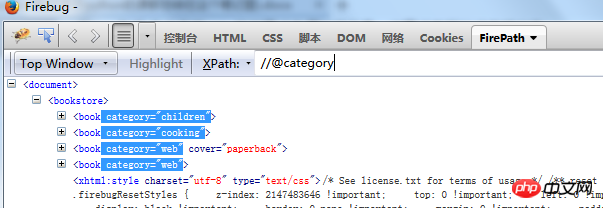
Find elements with thecategory attribute//@category
Logical operators1.
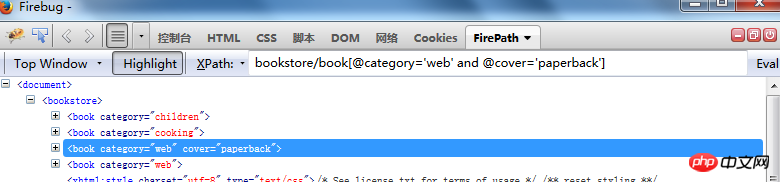
Locate elements through theand operator//book[@category="web" and @cover="paperback"]
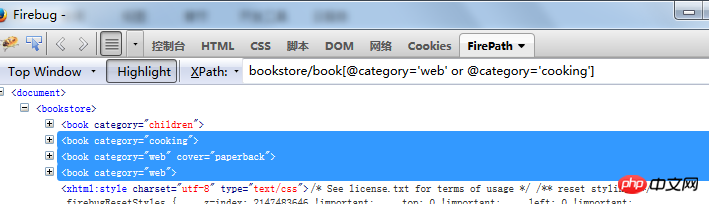
 2. Locate elements through the or operator
2. Locate elements through the or operator
 3.
3.
not operator //book[not(position()>2)]
Get the# whose position is greater than
2 in thebook tag
##//book[not(position()>2)] not negation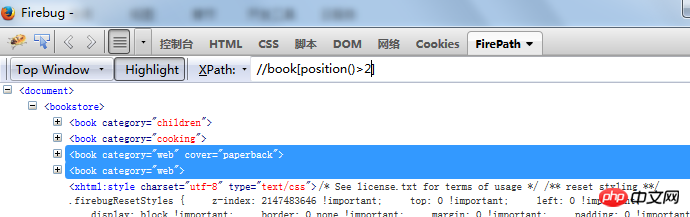
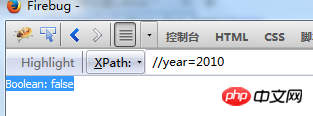
//year[not(.=2005) ] 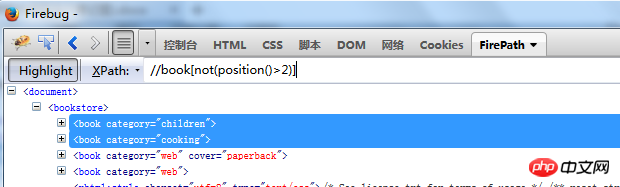 means taking the year node that is not the
means taking the year node that is not the
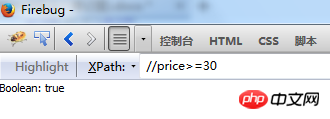
Find the element by “>=”“operator
//price>=30 Whether there is price greater than or equal to 30 Exists returns Boolean true Does not exist Returns Boolean: false
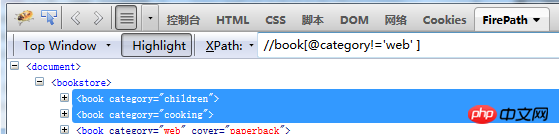
4.Locate elements through "!"operator
//book [@category!='web' ]
6.Locate elements by node index
1.Find the first element
//book[1]: Find the first # with the label book
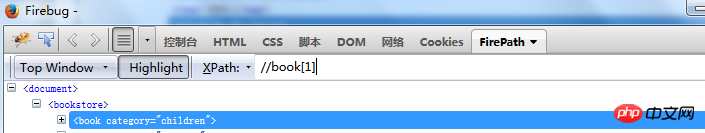
Position the th 3# through position ##Element//bookstore/book[position()=3]
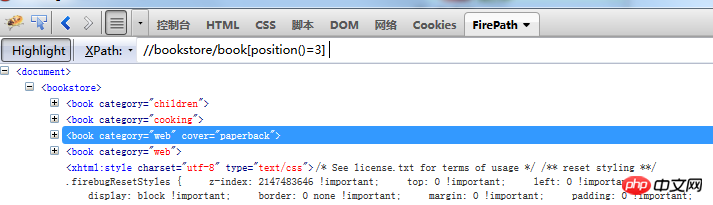
3.
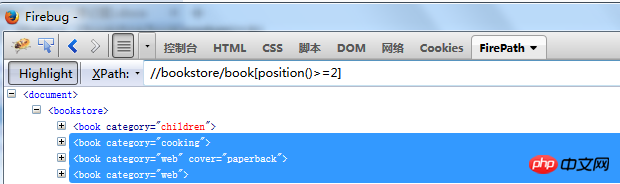
Get multiple elements throughposition//bookstore/book[position()>=2]
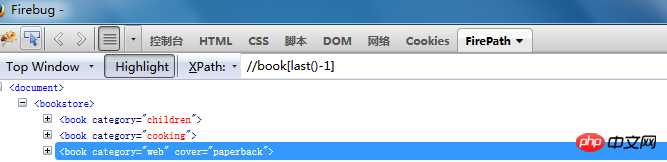
 4. Through last()
4. Through last()
//book[last()]
 5.
5.
last ()Function to find the penultimate element//book[last()-1]

7 .
Axis positioning
Find the parent element of
book[1]/title: //book [1]/title/parent::*
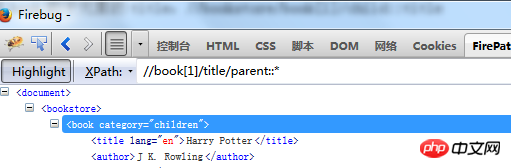
book[1]: //book[ 1]/child::*
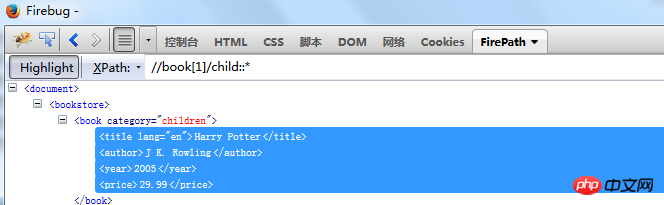 //book/child::price
//book/child::price
book tag with the tag price
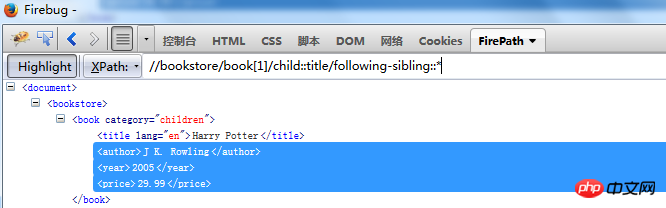 following-sibling
following-sibling
//bookstore/book[1]/child::title/following-sibling::*
Following-sibling represents all sibling node elements in the subsequent sequence of the current node
title

following-sibling::author
title The element named author
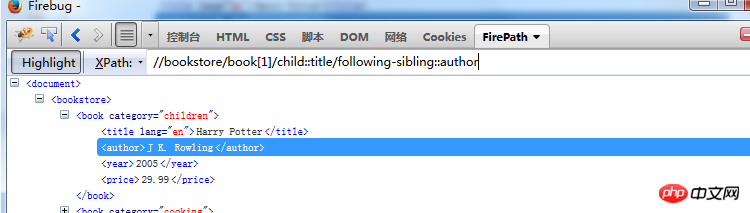 preceding-sibling::* represents all sibling node elements in front of the current node
preceding-sibling::* represents all sibling node elements in front of the current node
//bookstore /book[1]/child::price/preceding-sibling::*
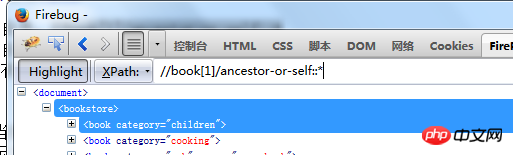
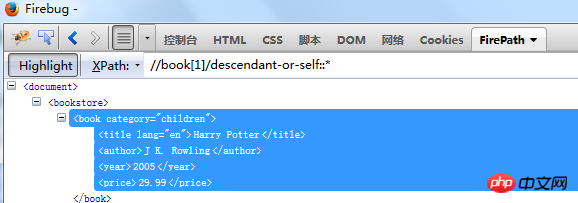
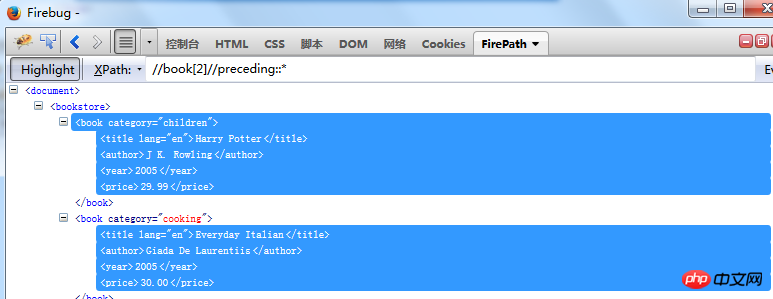
means to find all sibling elements in front of theprice node Find ancestor nodes including self: //book[1]/ancestor-or-self::* Find descendant nodes including self: //book[1]/descendant-or-self::* ##//book[2]//preceding::* will book[2] and book[2] nodes before Find all elements of
# #Axis summary: parent::* represents the parent node element of the current node child::* represents the current node The child elements of the node /A/descendant::* represent all descendant elements of A 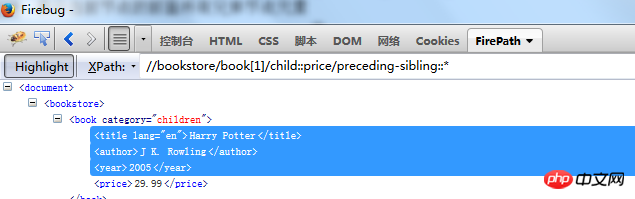
Find all elements of the current node: //book[1]/preceding::* Find all elements under the current node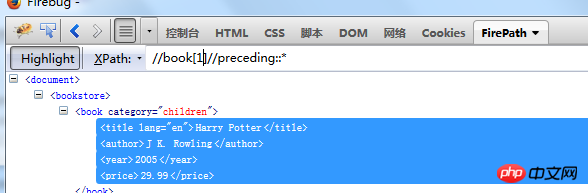
self::* represent the self elements of the current node
ancestor-or-self::* represent the current node and its ancestor nodes The element
descendant-or-self::* represents the current node and their descendant elements
following-sibling::* represents the following sibling node elements of the current node
preceding-sibling::* represents All sibling node elements in front of the current node
following::* represents all elements in the following order of the current node
preceding::* represents all elements of the current node
The above is the detailed content of Summary of Xpath positioning. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Is HTML easy to learn for beginners?
Apr 07, 2025 am 12:11 AM
Is HTML easy to learn for beginners?
Apr 07, 2025 am 12:11 AM
HTML is suitable for beginners because it is simple and easy to learn and can quickly see results. 1) The learning curve of HTML is smooth and easy to get started. 2) Just master the basic tags to start creating web pages. 3) High flexibility and can be used in combination with CSS and JavaScript. 4) Rich learning resources and modern tools support the learning process.
 The Roles of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: Core Responsibilities
Apr 08, 2025 pm 07:05 PM
The Roles of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: Core Responsibilities
Apr 08, 2025 pm 07:05 PM
HTML defines the web structure, CSS is responsible for style and layout, and JavaScript gives dynamic interaction. The three perform their duties in web development and jointly build a colorful website.
 Understanding HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: A Beginner's Guide
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:02 AM
Understanding HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: A Beginner's Guide
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:02 AM
WebdevelopmentreliesonHTML,CSS,andJavaScript:1)HTMLstructurescontent,2)CSSstylesit,and3)JavaScriptaddsinteractivity,formingthebasisofmodernwebexperiences.
 Gitee Pages static website deployment failed: How to troubleshoot and resolve single file 404 errors?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 11:54 PM
Gitee Pages static website deployment failed: How to troubleshoot and resolve single file 404 errors?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 11:54 PM
GiteePages static website deployment failed: 404 error troubleshooting and resolution when using Gitee...
 What is an example of a starting tag in HTML?
Apr 06, 2025 am 12:04 AM
What is an example of a starting tag in HTML?
Apr 06, 2025 am 12:04 AM
AnexampleofastartingtaginHTMLis,whichbeginsaparagraph.StartingtagsareessentialinHTMLastheyinitiateelements,definetheirtypes,andarecrucialforstructuringwebpagesandconstructingtheDOM.
 How to use CSS3 and JavaScript to achieve the effect of scattering and enlarging the surrounding pictures after clicking?
Apr 05, 2025 am 06:15 AM
How to use CSS3 and JavaScript to achieve the effect of scattering and enlarging the surrounding pictures after clicking?
Apr 05, 2025 am 06:15 AM
To achieve the effect of scattering and enlarging the surrounding images after clicking on the image, many web designs need to achieve an interactive effect: click on a certain image to make the surrounding...
 HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: Essential Tools for Web Developers
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:12 AM
HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: Essential Tools for Web Developers
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:12 AM
HTML, CSS and JavaScript are the three pillars of web development. 1. HTML defines the web page structure and uses tags such as, etc. 2. CSS controls the web page style, using selectors and attributes such as color, font-size, etc. 3. JavaScript realizes dynamic effects and interaction, through event monitoring and DOM operations.
 How to implement adaptive layout of Y-axis position in web annotation?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 11:30 PM
How to implement adaptive layout of Y-axis position in web annotation?
Apr 04, 2025 pm 11:30 PM
The Y-axis position adaptive algorithm for web annotation function This article will explore how to implement annotation functions similar to Word documents, especially how to deal with the interval between annotations...






