python logging module logging
Module level function
logging.getLogger([name]): Returns a logger object. If no name is specified, the root logger will be returned
logging.debug(), logging.info( ), logging.warning(), logging.error(), logging.critical(): Set the log level of the root logger
logging.basicConfig(): Use the default Formatter to create a StreamHandler for the log system, set Basic configuration and added to the root logger
Logger
logging.getLogger([name])
Returns a logger instance. If name is not specified, returns the root logger.
Each program must obtain a Logger before outputting information. Logger usually corresponds to the module name of the program. For example, the graphical interface module of a chat tool can obtain its Logger like this:
LOG=logging.getLogger("chat.gui")
And the core module It can be like this:
LOG=logging.getLogger("chat.kernel")
Logger.setLevel(logging.WARNING): Specify the lowest log level, lower than The level of WARNING will be ignored
Logger.addFilter(filt), Logger.removeFilter(filt): Add or remove the specified filter
Logger.addHandler(hdlr), Logger.removeHandler(hdlr ): Add or delete the specified handler
Handlers
The handler object is responsible for sending relevant information to the specified destination. It can be a file, screen, network, socket, etc.
Handler.setLevel(lel): Specifies the level of information to be processed, information below the lel level will be ignored
Handler.setFormatter() : Select an output format for this handler
Handler.addFilter(filt), Handler.removeFilter(filt): Add or delete a filter object
The log is printed to Screen
import logging
logging.debug('This is debug message')
logging.info('This is info message')
logging.warning('This is warning message')
返回:
WARNING:root:This is warning message
打印到屏幕By default, logging prints logs to the screen, and the log level is WARNING;
The log level size relationship is: CRITICAL > ERROR > WARNING > INFO > DEBUG > NOTSET, Of course, you can also define the log level yourself.
Format log output
Parameters of logging.basicConfig function:
filename: Specify the log file name
filemode: The same meaning as the file function, specify The opening mode of the log file, 'w' or 'a'
format: Specify the output format and content. format can output a lot of useful information, as shown in the above example:
import logging
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.DEBUG,
format='%(asctime)s %(filename)s[line:%(lineno)d] %(levelname)s %(message)s',
datefmt='%a, %d %b %Y %H:%M:%S',
filename='myapp.log',
filemode='w')
logging.debug('This is debug message')
logging.info('This is info message')
logging.warning('This is warning message')
./myapp.log文件中内容为:
Sun, 24 May 2009 21:48:54 demo2.py[line:11] DEBUG This is debug message
Sun, 24 May 2009 21:48:54 demo2.py[line:12] INFO This is info message
Sun, 24 May 2009 21:48:54 demo2.py[line:13] WARNING This is warning message
修改输出格式Log format variable
%(levelno)s: 打印日志级别的数值 %(levelname)s: 打印日志级别名称 %(pathname)s: 打印当前执行程序的路径,其实就是sys.argv[0] %(filename)s: 打印当前执行程序名 %(funcName)s: 打印日志的当前函数 %(lineno)d: 打印日志的当前行号 %(asctime)s: 打印日志的时间 %(thread)d: 打印线程ID %(threadName)s: 打印线程名称 %(process)d: 打印进程ID %(message)s: 打印日志信息 datefmt: 指定时间格式,同time.strftime() level: 设置日志级别,默认为logging.WARNING stream: 指定将日志的输出流,可以指定输出到sys.stderr,sys.stdout或者文件,默认输出到sys.stderr,当stream和filename同时指定时,stream被忽略 日志格式
logging method
logging.StreamHandler: 日志输出到流,可以是sys.stderr、sys.stdout或者文件 logging.FileHandler: 日志输出到文件 日志回滚方式,实际使用时用RotatingFileHandler和TimedRotatingFileHandler logging.handlers.BaseRotatingHandler logging.handlers.RotatingFileHandler logging.handlers.TimedRotatingFileHandler logging.handlers.SocketHandler: 远程输出日志到TCP/IP sockets logging.handlers.DatagramHandler: 远程输出日志到UDP sockets logging.handlers.SMTPHandler: 远程输出日志到邮件地址 logging.handlers.SysLogHandler: 日志输出到syslog logging.handlers.NTEventLogHandler: 远程输出日志到Windows NT/2000/XP的事件日志 logging.handlers.MemoryHandler: 日志输出到内存中的制定buffer logging.handlers.HTTPHandler: 通过"GET"或"POST"远程输出到HTTP服务器 logging方法
Since StreamHandler and FileHandler are commonly used log processing methods, they are directly included in the logging module, while other methods are included in the logging.handlers module
In Log module defined in the program
import logging
# create logger
def logger(log_type):
logger = logging.getLogger(log_type) # 创建Logger对象,类型是'TEST-LOG'
logger.setLevel(logging.WARNING) # 设置最低的日志级别,此级别覆盖ch and fh的级别
# 创建输出到控制台处理程序,并设置级别为DEBUG
ch = logging.StreamHandler()
ch.setLevel(logging.DEBUG) # 控制输出到屏幕的级别
# 创建输出到文件的处理程序,并设置级别
fh = logging.FileHandler("access.log")
fh.setLevel(logging.WARNING)
# 创建日志格式
formatter_Stream = logging.Formatter('%(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s')
formatter_File = logging.Formatter('%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s')
# add formatter to ch and fh
ch.setFormatter(formatter_Stream)
fh.setFormatter(formatter_File)
# add ch and fh to logger
logger.addHandler(ch)
logger.addHandler(fh)
return logger
eee = logger('EEE')
rrr = logger('RRR')
rrr.debug('debug message')
rrr.info('info message')
rrr.warning('warn message')
eee.error('error message')
eee.critical('critical message')
代码Screen display content
RRR - INFO - info message
RRR - WARNING - warn message
EEE - ERROR - error message
EEE - CRITICAL - critical message
Contents in the file
2017-02-21 21:35:05,700 - RRR - WARNING - warn message
2017-02-21 21:35:05,700 - EEE - ERROR - error message
2017-02-21 21:35:05,700 - EEE - CRITICAL - critical message
Filter
The format of the parameters when calling logging.getLogger() is similar to "A.B.C". This format is used to configure the filter. After adding a filter, the log will be output after being processed by the filter.
The filter "AAA.BBB" only allows loggers whose names start with "AAA.BBB" to output information.
Multiple filters can be added, as long as one filter rejects, the log will not be output
import logging
def logger(log_type):
logger = logging.getLogger(log_type) # 创建Logger对象,类型是'TEST-LOG'
logger.setLevel(logging.DEBUG) # 此级别覆盖ch and fh的级别
# 创建输出到控制台处理程序,并设置级别为DEBUG
ch = logging.StreamHandler()
ch.setLevel(logging.DEBUG) # 控制输出到屏幕的级别
# 设置过滤器
filter = logging.Filter('AAA.BBB.CCC')
ch.addFilter(filter)
formatter_Stream = logging.Formatter('%(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s')
ch.setFormatter(formatter_Stream)
logger.addHandler(ch) # ch加入logger
return logger
eee = logger('AAA.BBB.CCC')
rrr = logger('AAA.BBB.DDD')
rrr.error('debug message')
rrr.error('info message')
eee.error('critical message')
eee.error('critical message')
代码Cutting log
Cut by size
import logging
from logging import handlers
# create logger
def logger(log_type):
logger = logging.getLogger(log_type)
logger.setLevel(logging.DEBUG)
fh = logging.FileHandler("access.log")
fh.setLevel(logging.WARNING)
# 按时间切割日志文件
fh = handlers.TimedRotatingFileHandler(filename='access.log', when='s', interval=10 )
formatter_File = logging.Formatter('%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s')
fh.setFormatter(formatter_File)
logger.addHandler(fh)
return logger
rrr = logger('AAA.BBB.DDD')
rrr.error('debug message')
rrr.error('info message')
rrr.error('warn message')
代码interval: time interval
when: Time unit S seconds M minutes H hours D days W every week (interval==0 represents Monday) midnight every morning
About the root logger and the parent-child relationship of the logger
I mentioned the root logger many times before. In fact, there is a parent-child relationship between logger instances. The root logger is at the top level. logger, which is the ancestor of all loggers. As shown below: root logger is the default logger. If you do not create a logger instance and directly call the functions such as logging.debug(), logging.info(), logging.warning(), logging.error(), and logging.critical(), then use The logger is the root logger, which can be created automatically and is also a single instance.
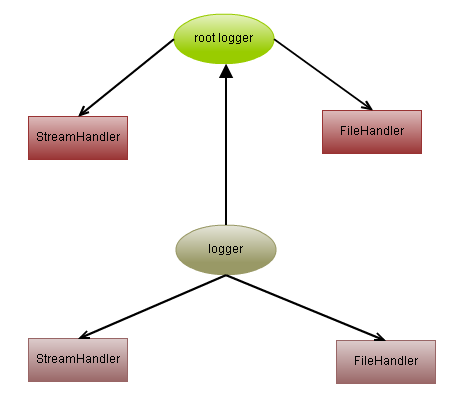
How to get the root logger Get the root logger instance through logging.getLogger() or logging.getLogger("").
The default level of the levelroot logger is logging.WARNING
How to express the parent-child relationship. The naming method of the logger name can express the parent-child relationship between loggers. For example: parent_logger = logging.getLogger('foo')child_logger = logging.getLogger('foo.bar')
What is effective level? Logger has a concept called effective level. If a logger does not set level explicitly, it uses the parent's level. If the father does not set the level explicitly, the level of the father's father will be used, and so on... Finally, when we reach the root logger, the level must have been set. The default is logging.WARNING. After child loggers get the message, it not only distributes the message to its handler for processing, but also passes it to all ancestor loggers for processing.
Please pay attention to more python log module logging related articles PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP is mainly procedural programming, but also supports object-oriented programming (OOP); Python supports a variety of paradigms, including OOP, functional and procedural programming. PHP is suitable for web development, and Python is suitable for a variety of applications such as data analysis and machine learning.
 Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
PHP is suitable for web development and rapid prototyping, and Python is suitable for data science and machine learning. 1.PHP is used for dynamic web development, with simple syntax and suitable for rapid development. 2. Python has concise syntax, is suitable for multiple fields, and has a strong library ecosystem.
 Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python is more suitable for beginners, with a smooth learning curve and concise syntax; JavaScript is suitable for front-end development, with a steep learning curve and flexible syntax. 1. Python syntax is intuitive and suitable for data science and back-end development. 2. JavaScript is flexible and widely used in front-end and server-side programming.
 PHP and Python: A Deep Dive into Their History
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP and Python: A Deep Dive into Their History
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP originated in 1994 and was developed by RasmusLerdorf. It was originally used to track website visitors and gradually evolved into a server-side scripting language and was widely used in web development. Python was developed by Guidovan Rossum in the late 1980s and was first released in 1991. It emphasizes code readability and simplicity, and is suitable for scientific computing, data analysis and other fields.
 Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
VS Code can run on Windows 8, but the experience may not be great. First make sure the system has been updated to the latest patch, then download the VS Code installation package that matches the system architecture and install it as prompted. After installation, be aware that some extensions may be incompatible with Windows 8 and need to look for alternative extensions or use newer Windows systems in a virtual machine. Install the necessary extensions to check whether they work properly. Although VS Code is feasible on Windows 8, it is recommended to upgrade to a newer Windows system for a better development experience and security.
 Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
VS Code can be used to write Python and provides many features that make it an ideal tool for developing Python applications. It allows users to: install Python extensions to get functions such as code completion, syntax highlighting, and debugging. Use the debugger to track code step by step, find and fix errors. Integrate Git for version control. Use code formatting tools to maintain code consistency. Use the Linting tool to spot potential problems ahead of time.
 How to run python with notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:33 PM
How to run python with notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:33 PM
Running Python code in Notepad requires the Python executable and NppExec plug-in to be installed. After installing Python and adding PATH to it, configure the command "python" and the parameter "{CURRENT_DIRECTORY}{FILE_NAME}" in the NppExec plug-in to run Python code in Notepad through the shortcut key "F6".
 How to run sublime code python
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:48 AM
How to run sublime code python
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:48 AM
To run Python code in Sublime Text, you need to install the Python plug-in first, then create a .py file and write the code, and finally press Ctrl B to run the code, and the output will be displayed in the console.






