Apache Mina study notes (4)-Session
Session is the core of Apache. Whenever a client connection arrives, a new Session will be created until the connection is closed. Session is used to save connections and various information.
Session has the following states:
Connected : the session has been created and is available Idle : the session hasn't processed any request for at least a period of time (this period is configurable) Idle for read : no read has actually been made for a period of time Idle for write : no write has actually been made for a period of time Idle for both : no read nor write for a period of time Closing : the session is being closed (the remaining messages are being flushed, cleaning up is not terminated) Closed : The session is now closed, nothing else can be done to revive it.
The following figure shows the state transition relationship of Session:
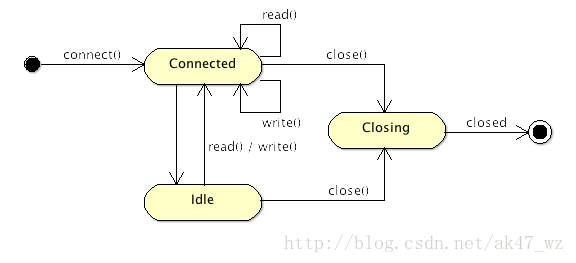
The following parameters can be used To configure Session
receive buffer size
sending buffer size
Idle time
Write timeOut
Manage user-defined attributes:
For example, if If you want to track how many requests a user has sent since the session was established, it can be easily stored in this map: just create a key and associate it with the value.
... int counterValue = session.getAttribute( "counter" ); session.setAttribute( "counter", counterValue + 1 ); ...
We use key/value pairs to store attributes in the session. This key/value pair can be read, added or deleted through the session container.
Define container
As we said, this container is a key/value container. The default is a mapping. Of course, it can also be defined as other data structures. When the Session is created we can implement an interface and a factory to create the container. The following code snippet illustrates how to create a container during Session initialization (I don’t understand, what does this mean?)
protected final void initSession(IoSession session,
IoFuture future, IoSessionInitializer sessionInitializer) {
...
try {
((AbstractIoSession) session).setAttributeMap(session.getService()
.getSessionDataStructureFactory().getAttributeMap(session));
} catch (IoSessionInitializationException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new IoSessionInitializationException(
"Failed to initialize an attributeMap.", e);
}and here is the factory interface we can implement if we want to define another kind of container:
public interface IoSessionDataStructureFactory {
/**
* Returns an {@link IoSessionAttributeMap} which is going to be associated
* with the specified <tt>session</tt>. Please note that the returned
* implementation must be thread-safe.
*/
IoSessionAttributeMap getAttributeMap(IoSession session) throws Exception;
}Filter chain
Each session will be associated with some filter chains to process incoming requests or outgoing data. Each session will have a separate filter chain specified, and in most cases we will use many of the same filter chains across sessions.
Statistics
Each session also keep a track of records about what has been done for the session : number of bytes received/sent number of messages received/sent Idle status throughput and many other useful informations. Handler
Last but not least, a Handler must be attached to a Session to handle program messages. This Handler will also send a package in response, just simply call the write method:
... session.write( <your message> ); ...
The above is the content of Apache Mina study notes (4)-Session. For more related content, please pay attention to the PHP Chinese website (www .php.cn)!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1663
1663
 14
14
 1419
1419
 52
52
 1313
1313
 25
25
 1263
1263
 29
29
 1237
1237
 24
24
 How to set the cgi directory in apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:18 PM
How to set the cgi directory in apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:18 PM
To set up a CGI directory in Apache, you need to perform the following steps: Create a CGI directory such as "cgi-bin", and grant Apache write permissions. Add the "ScriptAlias" directive block in the Apache configuration file to map the CGI directory to the "/cgi-bin" URL. Restart Apache.
 How to connect to the database of apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
How to connect to the database of apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
Apache connects to a database requires the following steps: Install the database driver. Configure the web.xml file to create a connection pool. Create a JDBC data source and specify the connection settings. Use the JDBC API to access the database from Java code, including getting connections, creating statements, binding parameters, executing queries or updates, and processing results.
 How to view your apache version
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:15 PM
How to view your apache version
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:15 PM
There are 3 ways to view the version on the Apache server: via the command line (apachectl -v or apache2ctl -v), check the server status page (http://<server IP or domain name>/server-status), or view the Apache configuration file (ServerVersion: Apache/<version number>).
 What to do if the apache80 port is occupied
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:24 PM
What to do if the apache80 port is occupied
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:24 PM
When the Apache 80 port is occupied, the solution is as follows: find out the process that occupies the port and close it. Check the firewall settings to make sure Apache is not blocked. If the above method does not work, please reconfigure Apache to use a different port. Restart the Apache service.
 How to view the apache version
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:00 PM
How to view the apache version
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:00 PM
How to view the Apache version? Start the Apache server: Use sudo service apache2 start to start the server. View version number: Use one of the following methods to view version: Command line: Run the apache2 -v command. Server Status Page: Access the default port of the Apache server (usually 80) in a web browser, and the version information is displayed at the bottom of the page.
 How to configure zend for apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 12:57 PM
How to configure zend for apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 12:57 PM
How to configure Zend in Apache? The steps to configure Zend Framework in an Apache Web Server are as follows: Install Zend Framework and extract it into the Web Server directory. Create a .htaccess file. Create the Zend application directory and add the index.php file. Configure the Zend application (application.ini). Restart the Apache Web server.
 How to solve the problem that apache cannot be started
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:21 PM
How to solve the problem that apache cannot be started
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:21 PM
Apache cannot start because the following reasons may be: Configuration file syntax error. Conflict with other application ports. Permissions issue. Out of memory. Process deadlock. Daemon failure. SELinux permissions issues. Firewall problem. Software conflict.
 How to delete more than server names of apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:09 PM
How to delete more than server names of apache
Apr 13, 2025 pm 01:09 PM
To delete an extra ServerName directive from Apache, you can take the following steps: Identify and delete the extra ServerName directive. Restart Apache to make the changes take effect. Check the configuration file to verify changes. Test the server to make sure the problem is resolved.




