 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
 Python zero-based introduction to seven variables and built-in functions
Python zero-based introduction to seven variables and built-in functions
Python zero-based introduction to seven variables and built-in functions
1. Global variables and local variables
These two variables are the same as variables in other languages. Global variables are simply variables that can be used throughout the code. Its scope is the entire function, and Local variables have a limited scope, often within a code area.
It should be noted that if you just call the value of the global variable in the function without changing its value, there is no problem at all, but if you want to change the value of the global variable in the function without special processing, The Python language handles this situation by automatically generating a local variable with the same name as the called global variable, which means that the global variable is shielded, and operations on the variable will not affect the value of the global variable. (Although it looks like it has changed)
For example, in the following program, although the value of count is changed in the function, the value of count printed outside the function is still 5.
count=5def Myfun():
count=10
print(count)
Myfun()
print(count)
If you have to modify the value of a global variable inside the function, you can use the keyword global to modify the variable inside the function. This means that the operation is an operation on the global variable, rather than generating an Global variables are the same as local variables.
print("======使用global之后的变量======")
count=5def Myfun():
global count#声明与赋值不能一块进行
count=10
print(count)
Myfun()
print(count)2. Embedded (internal) function
In short, an embedded function is a function defined inside the function
It is worth noting that the internal function can only be called outside of it Function call, but cannot be called outside. In other words, who has the right to use it within who owns it.
print("======内部函数的使用======")def fun1():
print("fun1()正在被调用") def fun2():
print("fun2()正在被调用")
fun2()
fun1()3. Closure
A closure is the parameter used by an embedded function to call its external function.
You need to pay special attention when calling this function.
def funX(x):
def funY(y):
return x*y return funY
print(funX(5)(8))4. Variable problems in closures
The following code will report an error when executed. Because the parameters of the external function are called inside the embedded function, and the parameter x is a global variable for the function Fun2(), due to the shielding effect, the function error occurs.
def Fun1():
x=5
def Fun2():
x*=x return x return Fun2()#Fun1()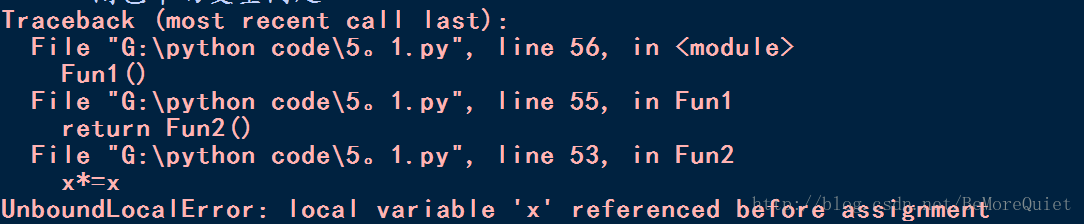
There are two ways to solve the above problem:
One is to use non-stack data structure to solve the problem
The second is to use the nonlocal keyword to solve the problem
#一种解决办法就是使用非栈存储,使用序列等来存储def Fun1():
x=[5] def Fun2():
x[0]*=x[0] return x[0] return Fun2()
print(Fun1(),"\n")#在一种解决办法就是使用nonlocal关键字def Fun3():
x=5
def Fun4():
nonlocal x
x*=x return x return Fun4()
print(Fun3())
You need to think carefully about the variables in the function. After all, there are some differences from what you learned before.
The above is the content of the seven variables and built-in functions of Python's zero-based introduction. For more related content, please pay attention to the PHP Chinese website (www.php.cn)!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP is mainly procedural programming, but also supports object-oriented programming (OOP); Python supports a variety of paradigms, including OOP, functional and procedural programming. PHP is suitable for web development, and Python is suitable for a variety of applications such as data analysis and machine learning.
 Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
PHP is suitable for web development and rapid prototyping, and Python is suitable for data science and machine learning. 1.PHP is used for dynamic web development, with simple syntax and suitable for rapid development. 2. Python has concise syntax, is suitable for multiple fields, and has a strong library ecosystem.
 Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python is more suitable for beginners, with a smooth learning curve and concise syntax; JavaScript is suitable for front-end development, with a steep learning curve and flexible syntax. 1. Python syntax is intuitive and suitable for data science and back-end development. 2. JavaScript is flexible and widely used in front-end and server-side programming.
 PHP and Python: A Deep Dive into Their History
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP and Python: A Deep Dive into Their History
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP originated in 1994 and was developed by RasmusLerdorf. It was originally used to track website visitors and gradually evolved into a server-side scripting language and was widely used in web development. Python was developed by Guidovan Rossum in the late 1980s and was first released in 1991. It emphasizes code readability and simplicity, and is suitable for scientific computing, data analysis and other fields.
 Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
VS Code can run on Windows 8, but the experience may not be great. First make sure the system has been updated to the latest patch, then download the VS Code installation package that matches the system architecture and install it as prompted. After installation, be aware that some extensions may be incompatible with Windows 8 and need to look for alternative extensions or use newer Windows systems in a virtual machine. Install the necessary extensions to check whether they work properly. Although VS Code is feasible on Windows 8, it is recommended to upgrade to a newer Windows system for a better development experience and security.
 Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
VS Code can be used to write Python and provides many features that make it an ideal tool for developing Python applications. It allows users to: install Python extensions to get functions such as code completion, syntax highlighting, and debugging. Use the debugger to track code step by step, find and fix errors. Integrate Git for version control. Use code formatting tools to maintain code consistency. Use the Linting tool to spot potential problems ahead of time.
 How to run python with notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:33 PM
How to run python with notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:33 PM
Running Python code in Notepad requires the Python executable and NppExec plug-in to be installed. After installing Python and adding PATH to it, configure the command "python" and the parameter "{CURRENT_DIRECTORY}{FILE_NAME}" in the NppExec plug-in to run Python code in Notepad through the shortcut key "F6".
 How to run sublime code python
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:48 AM
How to run sublime code python
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:48 AM
To run Python code in Sublime Text, you need to install the Python plug-in first, then create a .py file and write the code, and finally press Ctrl B to run the code, and the output will be displayed in the console.





