 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 CSS Tutorial
CSS Tutorial
 Some techniques for using pseudo-classes, pseudo-elements and adjacent element selectors in CSS
Some techniques for using pseudo-classes, pseudo-elements and adjacent element selectors in CSS
Some techniques for using pseudo-classes, pseudo-elements and adjacent element selectors in CSS
A few days ago, I encountered a page requirement like this:
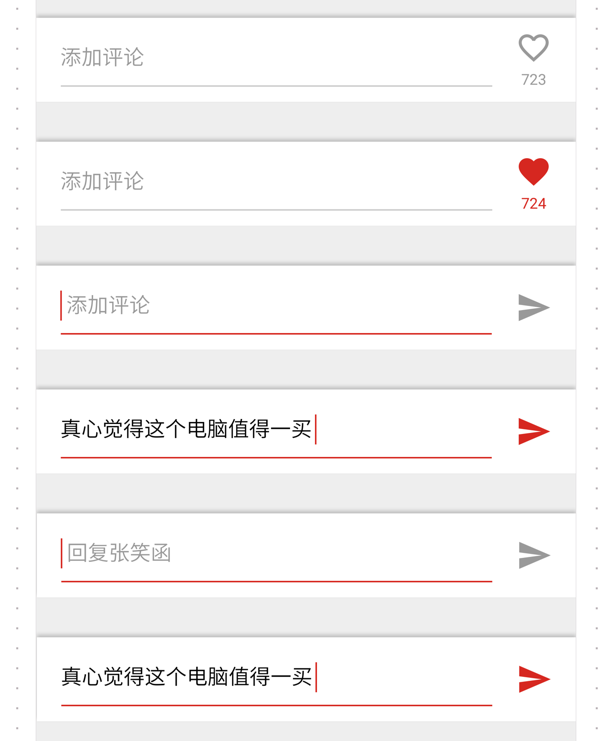
A comment box. The button behind it has two states: like or send comment. The send button is divided into clickable and comment based on whether there are words in the input box. Both states are unclickable.
Requirements:
No text, no focus - like
No text, focus - send in gray
With text - send in red
If implemented with JS, you need to monitor the change and focus events of the input box, which is more troublesome. But similar effects can be achieved using pseudo-classes in CSS.
<input type="text" class="input" required> <div class="like">点赞</div> <div class="send">发送</div>
.send {
display: none;
}
.input:focus ~ .send {
display: block;
}
.input:valid ~ .send {
display: block;
color: red;
}
.input:focus ~ .like, .input:valid ~ .like {
display: none;
}(If the comment box is implemented with a div element with the contenteditable attribute, you can use the :empty pseudo-class instead of :valid.)
So there are many pseudo-classes and pseudo-elements in CSS3, and some of them, if used cleverly, can achieve a lot Effects that originally required JS to be achieved.
Placeholder of div with contenteditable attribute
For some reasons, we sometimes use div with contenteditable attribute instead of input or textarea as input box. For example, divs can automatically adjust their height based on their content. But the div element does not support the placeholder attribute. How to display a default text when the div content is empty? You can use the :empty pseudo-class.
<div class="input" contenteditable placeholder="请输入文字"></div>
Draw a grid
This is what I saw on Meituan’s mobile page:
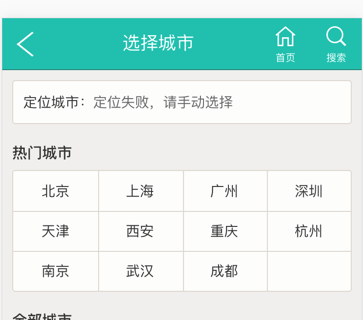
We need to draw a grid in this area of the city list. Of course, our first thought is to use the border attribute, but the designer has a requirement that if there is only one or two cities in the last row, there must be a blank grid behind it for the sake of beauty. Like this:
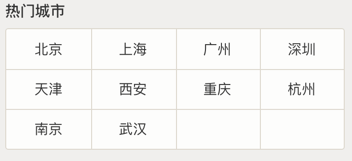
How to draw the vertical lines of the grid on Meituan’s page? It is drawn using ::after and ::before elements.
.input:empty::before {
content: attr(placeholder);
}Created two pseudo-elements with a height of 100%, using their borders as vertical lines of the table. This solution can meet the designer's requirements without adding blank page elements and destroying semantics. But the limitation is that only four vertical lines can be drawn at most, which means that the table can have up to 5 columns.
Tab switching
It is also possible to implement tab switching using pure CSS. It mainly uses the :checked pseudo-class and adjacent selector of the radio button element. Because it is a radio button, it is guaranteed that only one tab is active at the same time. If you do not require more complex effects, the tab switching effect achieved by pure CSS is much simpler and more reliable than JS.
.table:before {
content: '';
position: absolute;
width: 25%;
left: 25%;
height: 100%;
border-left: 1px solid #ddd8ce;
border-right: 1px solid #ddd8ce;
}
.table:after {
content: '';
position: absolute;
width: 10%;
left: 75%;
height: 100%;
border-left: 1px solid #ddd8ce;
border-right: none;
}<input id="tab1" type="radio" name="tabs" checked> <label for="tab1">TAB1</label> <input id="tab2" type="radio" name="tabs"> <label for="tab2">TAB2</label> <div id="content1" class="tab-content">CONTENT1<div> <div id="content2" class="tab-content">CONTENT2</div>
In addition, using pseudo-classes of form elements, label elements can be used to replace form elements such as radio buttons and check boxes themselves, because it is very difficult to define styles for the form elements themselves.
Perception of the number of child elements
This is one of the most complex techniques I have ever seen. It comes from this article. It does not rely on JS to apply different styles according to the number of child elements.
For example, this CSS:
input, .tab-content{
display: none;
}
#tab1:checked ~ #content1,
#tab2:checked ~ #content2 {
display: block;
}can achieve this effect: if the number of li elements in the .list is greater than or equal to 4, it will be displayed in red.
How is this achieved?
:nth-last-child(n+4) This selector means the fourth to last and previous elements, with ~ li added after it, which means the li element after the element that meets the previous conditions.
If the total number of elements is less than 4, there will be no elements that match:nth-last-child(n+4) (there are not four in total, so there is no fourth-to-last element), then li:nth-last-child( n+4) ~ li will not select any elements.
But if you only use ~ li, the first li will not be matched, so li:nth-last-child(n+4):first-child is added.
This also enables the application of different styles based on the number of elements.

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
Using Bootstrap in Vue.js is divided into five steps: Install Bootstrap. Import Bootstrap in main.js. Use the Bootstrap component directly in the template. Optional: Custom style. Optional: Use plug-ins.
 The Roles of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: Core Responsibilities
Apr 08, 2025 pm 07:05 PM
The Roles of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: Core Responsibilities
Apr 08, 2025 pm 07:05 PM
HTML defines the web structure, CSS is responsible for style and layout, and JavaScript gives dynamic interaction. The three perform their duties in web development and jointly build a colorful website.
 How to write split lines on bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:12 PM
How to write split lines on bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:12 PM
There are two ways to create a Bootstrap split line: using the tag, which creates a horizontal split line. Use the CSS border property to create custom style split lines.
 Understanding HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: A Beginner's Guide
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:02 AM
Understanding HTML, CSS, and JavaScript: A Beginner's Guide
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:02 AM
WebdevelopmentreliesonHTML,CSS,andJavaScript:1)HTMLstructurescontent,2)CSSstylesit,and3)JavaScriptaddsinteractivity,formingthebasisofmodernwebexperiences.
 How to set up the framework for bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:27 PM
How to set up the framework for bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:27 PM
To set up the Bootstrap framework, you need to follow these steps: 1. Reference the Bootstrap file via CDN; 2. Download and host the file on your own server; 3. Include the Bootstrap file in HTML; 4. Compile Sass/Less as needed; 5. Import a custom file (optional). Once setup is complete, you can use Bootstrap's grid systems, components, and styles to create responsive websites and applications.
 How to insert pictures on bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:30 PM
How to insert pictures on bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:30 PM
There are several ways to insert images in Bootstrap: insert images directly, using the HTML img tag. With the Bootstrap image component, you can provide responsive images and more styles. Set the image size, use the img-fluid class to make the image adaptable. Set the border, using the img-bordered class. Set the rounded corners and use the img-rounded class. Set the shadow, use the shadow class. Resize and position the image, using CSS style. Using the background image, use the background-image CSS property.
 How to use bootstrap button
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:09 PM
How to use bootstrap button
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:09 PM
How to use the Bootstrap button? Introduce Bootstrap CSS to create button elements and add Bootstrap button class to add button text
 How to resize bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:18 PM
How to resize bootstrap
Apr 07, 2025 pm 03:18 PM
To adjust the size of elements in Bootstrap, you can use the dimension class, which includes: adjusting width: .col-, .w-, .mw-adjust height: .h-, .min-h-, .max-h-





