java multithreading implementation
1. What is a thread?
Thread: A single sequential control process in a program. A relatively independent and schedulable execution unit within the process is the basic unit for the system to independently schedule and dispatch the CPU.
Multi-threading: Running multiple threads at the same time to complete different tasks in a single program is called multi-threading.
Features:
1) A lightweight process, the smallest executable unit in the program running flow. Threads do not own system resources, and multiple threads share the resources owned by the process.
2) One thread can create another thread, and multiple threads can execute concurrently.
3) When multiple threads seize resources during system operation, there will be discontinuity. What we see is parallel execution, but in fact there is a sequence.
4) A process contains at least one thread, the main thread.
2. What are the statuses of threads?
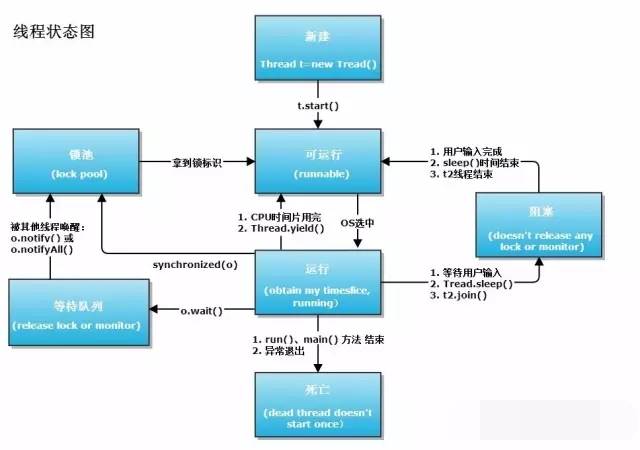
Threads have five states: new, ready, running, blocked, and terminated.
①New: The thread is created without executing any method, such as Thread th = new Thread().
②Ready: When the start method of the thread is called, the thread status will be triggered to change to the ready state, waiting for the CPU to call. Only threads in the ready state will be scheduled by the CPU, and a single CPU will not execute it immediately.
③Run: When the CPU initiates a call to this thread, it enters the running state.
④Blocking: When a thread no longer has the right to use the CPU for some reason, it will be blocked.种 The following situations are obstructed:
1) Sleep (long mills): The parameters are milliseconds, so that the thread enters the obstruction within the specified time. Once the time passes, it will be ready.
2) suspend() and resume(): suspend will cause the thread to hang, and resume must be executed to resume the thread.
3) yield(): similar to sleep(), but the user cannot specify how long to pause. It can only give the opportunity to threads of the same priority without entering blocking. Just like in a queue, the person in front switches places with the person behind, but they are still in the queue.
4) wait() and notify(): wait() puts the thread into a blocking state. There are two forms, one specifies the number of milliseconds, and the other has no parameters. The former can be evoked through notify() or automatically restored after a specified time; the latter must be evoked through notify().
5) Synchronous blocking: waiting for synchronization lock resources. When multiple threads compete for the same resource, only one thread can obtain the lock, and other threads have to wait.
⑤ Termination: The thread finishes execution, or an exception occurs, and the thread ends.
3. How to create a thread?
There are three ways to implement Java threads: inherit the Thread class, implement the Runnable interface, and use Callable and FutureTask (can have return values)
1. Override the run() method by integrating the Thread class
class MyThread extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + i ; ;
MyThread th1 = new MyThread();
MyThread th2 = new MyThread();
th1.start();
th2.start();
}
}
Output: main
Thread-1 0
Thread-0 0
Thread-1 1
Thread-1 2
...
The logic to be implemented by the thread is written in the run method, by executing the thread's start() Method to put the thread into the ready state and wait for the CPU to allocate resources.
You can see that two threads execute in parallel and get the CPU randomly.
2. Tried implementing the Runnable interface and the run() method
class MyThread implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + i);
}
}
}
public class ThreadDemo {
public static void main( String[] args) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
MyThread th = new MyThread();
Thread t1 = new Thread(th);
Thread t2 = new Thread(th);
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
Output: main
Thread-0 0
Thread-0 1
Thread- 1 0
Thread-0 2
...
Instantiate Thread by passing the MyThread instance into the Thread constructor, call the start method of Thread, and start the thread.
ps: What is the difference between inheriting Thread and implementing the Runnable interface?
1: The former is single inheritance, which has limitations, but multiple interfaces can be implemented.
2: The latter can realize resource sharing.
In multi-threaded programming, it is strongly recommended to use Runnable
3. Use Callable and Future interfaces to create threads.
Specifically, create an implementation class of the Callable interface and implement the clam() method.
And use the FutureTask class to wrap the object of the Callable implementation class, and use this FutureTask object as the target of the Thread object to create a thread.
class MyCallable implements Callable
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
return 1;
}
}
public class ThreadDemo {
public static void main (String[] args) {
Callable
FutureTask
Thread thread = new Thread (ft); // Pass the FutureTask into the Thread structure and instantiate the thread
thread.start(); // Start the thread
Integer result = ft.get(); // Get the return value
System. out.println(result);
}
}
1) Implement the call() method in the Callable interface. This is the logic to be executed by the thread.
2) The get() method of FutureTask will block until the call() method is executed and the return value is obtained.

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is
 PHP: A Key Language for Web Development
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP: A Key Language for Web Development
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP is a scripting language widely used on the server side, especially suitable for web development. 1.PHP can embed HTML, process HTTP requests and responses, and supports a variety of databases. 2.PHP is used to generate dynamic web content, process form data, access databases, etc., with strong community support and open source resources. 3. PHP is an interpreted language, and the execution process includes lexical analysis, grammatical analysis, compilation and execution. 4.PHP can be combined with MySQL for advanced applications such as user registration systems. 5. When debugging PHP, you can use functions such as error_reporting() and var_dump(). 6. Optimize PHP code to use caching mechanisms, optimize database queries and use built-in functions. 7
 TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to TimeStamp to Date in Java. Here we also discuss the introduction and how to convert timestamp to date in java along with examples.
 PHP vs. Python: Understanding the Differences
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP vs. Python: Understanding the Differences
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages, and the choice should be based on project requirements. 1.PHP is suitable for web development, with simple syntax and high execution efficiency. 2. Python is suitable for data science and machine learning, with concise syntax and rich libraries.
 Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Capsules are three-dimensional geometric figures, composed of a cylinder and a hemisphere at both ends. The volume of the capsule can be calculated by adding the volume of the cylinder and the volume of the hemisphere at both ends. This tutorial will discuss how to calculate the volume of a given capsule in Java using different methods. Capsule volume formula The formula for capsule volume is as follows: Capsule volume = Cylindrical volume Volume Two hemisphere volume in, r: The radius of the hemisphere. h: The height of the cylinder (excluding the hemisphere). Example 1 enter Radius = 5 units Height = 10 units Output Volume = 1570.8 cubic units explain Calculate volume using formula: Volume = π × r2 × h (4
 PHP vs. Other Languages: A Comparison
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP vs. Other Languages: A Comparison
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP is suitable for web development, especially in rapid development and processing dynamic content, but is not good at data science and enterprise-level applications. Compared with Python, PHP has more advantages in web development, but is not as good as Python in the field of data science; compared with Java, PHP performs worse in enterprise-level applications, but is more flexible in web development; compared with JavaScript, PHP is more concise in back-end development, but is not as good as JavaScript in front-end development.
 PHP vs. Python: Core Features and Functionality
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:16 AM
PHP vs. Python: Core Features and Functionality
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:16 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages and are suitable for different scenarios. 1.PHP is suitable for web development and provides built-in web servers and rich function libraries. 2. Python is suitable for data science and machine learning, with concise syntax and a powerful standard library. When choosing, it should be decided based on project requirements.






