 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 Understand the setTimeout and setInterval_javascript techniques in javascript timers
Understand the setTimeout and setInterval_javascript techniques in javascript timers
Understand the setTimeout and setInterval_javascript techniques in javascript timers
1. Explanation
1. Overview
setTimeout: Call a function or execute a code fragment after the specified delay time
setInterval: Periodically call a function or execute a piece of code.
2. Grammar
setTimeout:
var timeoutID = window.setTimeout(func, delay, [param1, param2, ...]); var timeoutID = window.setTimeout(code, delay);
- timeoutID is the numeric ID of the delay operation. This ID can then be used as a parameter of the window.clearTimeout method
- func is the function you want to execute after delay milliseconds
- code In the second syntax, it refers to the code you want to execute after delay milliseconds
- delay is the number of milliseconds of delay (one second is equal to 1000 milliseconds). The function call will occur after this delay. But the actual delay time may be slightly longer
- Standard browsers and IE10 support the function of passing extra parameters to the delayed function in the first syntax
setInterval
var intervalID = window.setInterval(func, delay[, param1, param2, ...]); var intervalID = window.setInterval(code, delay);
- intervalID is the unique identifier of this repeated operation and can be passed as a parameter to clearInterval().
- func is the function you want to call repeatedly.
- code is another syntax application, which refers to a code consisting of a string that you want to execute repeatedly
- delay is the number of milliseconds of each delay (one second equals 1000 milliseconds), after which each call to the function will occur. Like setTimeout, the actual delay may be slightly longer.
- Standard browsers and IE10 support the function of passing extra parameters to the delayed function in the first syntax
<script type="text/javascript">
setTimeout( function(param){ alert(param)} , 100, 'ok');
</script> 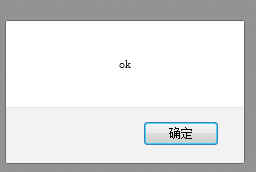
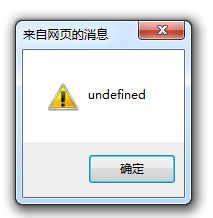
I briefly tested the fifth item, using firefox and IE9 on my computer. The former can pop up ok smoothly, while the latter pops up undefined.
2. “this” question
The code called by setTimeout() runs in an execution environment completely separate from the function in which it is located. This will cause the this keyword contained in these codes to point to the window (global object) object, which is different from the expected this The values are not the same. The situation with setInterval is similar.
<script type="text/javascript">
//this指向window
function shape(name) {
this.name = name;
this.timer = function(){alert('my shape is '+this.name)};
setTimeout(this.timer, 50);
}
new shape('rectangle');
</script>
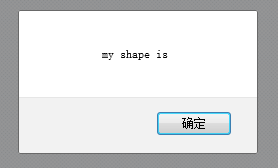
It was not passed in. I tried it with chrome, firefox and IE9, and the result was the same.
Solution 1:
<script type="text/javascript">
function shape(name) {
this.name = name;
this.timer = function(){alert('my shape is '+this.name)};
var _this = this;
setTimeout(function() {_this.timer.call(_this)}, 50);
}
new shape('rectangle');
</script>
Set a local variable _this, and then put it in the function variable of setTimeout. The timer executes call or apply to set the this value.
function can call the local variable _this, thanks to Javascript closures. It involves scope chain and other knowledge. If you are interested, you can learn about it yourself. I will not go into it here.
Solution 2:
This method is a bit fancy. Customized setTimeout and setInterval. It also extends the problem that lower versions of IE browsers do not support passing additional parameters to the delay function.
<script type="text/javascript">
//自定义setTimeout与setInterval
var __nativeST__ = window.setTimeout, __nativeSI__ = window.setInterval;
window.setTimeout = function (vCallback, nDelay /*, argumentToPass1, argumentToPass2, etc. */) {
var oThis = this, aArgs = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments, 2);
return __nativeST__(vCallback instanceof Function ? function () {
vCallback.apply(oThis, aArgs);
} : vCallback, nDelay);
};
window.setInterval = function (vCallback, nDelay /*, argumentToPass1, argumentToPass2, etc. */) {
var oThis = this, aArgs = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments, 2);
return __nativeSI__(vCallback instanceof Function ? function () {
vCallback.apply(oThis, aArgs);
} : vCallback, nDelay);
};
function shape(name) {
this.name = name;
this.timer = function(other){
alert('my shape is '+this.name);
alert('extra param is '+ other);
};
}
var rectangle = new shape('rectangle');
setTimeout.call(rectangle, rectangle.timer, 50, 'other');
</script>
1. Set local variables and assign values to native setTimeout and setInterval
2. Extend setTimeout and setInterval, aArgs obtains additional parameter arrays by splitting the arguments variable
3. Use vCallback instanceof Function to determine whether this is a function or code. If it is a function, use apply to execute it
4. SetTimeout is executed with call, and sets this object, as well as other func, delay and other parameters
5. By extending setTimeout, browsers with lower versions of IE can also execute additional parameters
3. The difference between setTimeout and setInterval
<script type="text/javascript">
setTimeout(function(){
/* Some long block of code... */
setTimeout(arguments.callee, 100);
}, 10);
setInterval(function(){
/* Some long block of code... */
}, 100);
</script>
看上去,两个功能是差不多的,但是里面其实是不一样的。
setTimeout回调函数的执行和上一次执行之间的间隔至少有100ms(可能会更多,但不会少于100ms)
setInterval的回调函数将尝试每隔100ms执行一次,不论上次是否执行完毕,时间间隔理论上是会<=delay的。
setInterval:
<script type="text/javascript">
function sleep(ms) {
var start = new Date();
while (new Date() - start <= ms) {}
}
var endTime = null;
var i = 0;
setInterval(count, 100);
function count() {
var elapsedTime = endTime ? (new Date() - endTime) : 100;
i++;
console.log('current count: ' + i + '.' + 'elapsed time: ' + elapsedTime + 'ms');
sleep(200);
endTime = new Date();
}
</script>
从firefox的firebug可以查看到,时间间隔很不规则。
情况大致是这样的:由于count函数的执行时间远大于setInterval的定时间隔,那么定时触发线程就会源源不断的产生异步定时事件,并放到任务队列尾而不管它们是否已被处理,但一旦一个定时事件任务处理完,这些排列中的剩余定时事件就依次不间断的被执行。
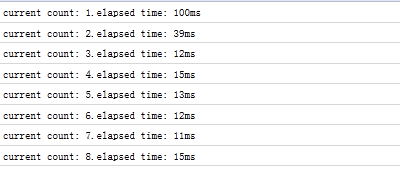
setTimeout:
<script type="text/javascript">
function sleep(ms) {
var start = new Date();
while (new Date() - start <= ms) {}
}
var endTime = null;
var i = 0;
setTimeout(count, 100);
function count() {
var elapsedTime = endTime ? (new Date() - endTime) : 100;
i++;
console.log('current count: ' + i + '.' + 'elapsed time: ' + elapsedTime + 'ms');
sleep(200);
endTime = new Date();
setTimeout(count, 100);
}
</script> 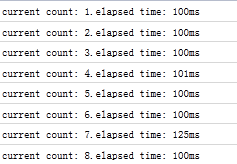
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家学习javascript定时器有所帮助。

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to implement an online speech recognition system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 pm 02:54 PM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system Introduction: With the continuous development of technology, speech recognition technology has become an important part of the field of artificial intelligence. The online speech recognition system based on WebSocket and JavaScript has the characteristics of low latency, real-time and cross-platform, and has become a widely used solution. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online speech recognition system.
 WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: key technologies for implementing real-time monitoring systems
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:30 PM
WebSocket and JavaScript: Key technologies for realizing real-time monitoring systems Introduction: With the rapid development of Internet technology, real-time monitoring systems have been widely used in various fields. One of the key technologies to achieve real-time monitoring is the combination of WebSocket and JavaScript. This article will introduce the application of WebSocket and JavaScript in real-time monitoring systems, give code examples, and explain their implementation principles in detail. 1. WebSocket technology
 How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
How to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
Introduction to how to use JavaScript and WebSocket to implement a real-time online ordering system: With the popularity of the Internet and the advancement of technology, more and more restaurants have begun to provide online ordering services. In order to implement a real-time online ordering system, we can use JavaScript and WebSocket technology. WebSocket is a full-duplex communication protocol based on the TCP protocol, which can realize real-time two-way communication between the client and the server. In the real-time online ordering system, when the user selects dishes and places an order
 How to implement an online reservation system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
How to implement an online reservation system using WebSocket and JavaScript
Dec 17, 2023 am 09:39 AM
How to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online reservation system. In today's digital era, more and more businesses and services need to provide online reservation functions. It is crucial to implement an efficient and real-time online reservation system. This article will introduce how to use WebSocket and JavaScript to implement an online reservation system, and provide specific code examples. 1. What is WebSocket? WebSocket is a full-duplex method on a single TCP connection.
 JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecasting system
Dec 17, 2023 pm 05:13 PM
JavaScript and WebSocket: Building an efficient real-time weather forecast system Introduction: Today, the accuracy of weather forecasts is of great significance to daily life and decision-making. As technology develops, we can provide more accurate and reliable weather forecasts by obtaining weather data in real time. In this article, we will learn how to use JavaScript and WebSocket technology to build an efficient real-time weather forecast system. This article will demonstrate the implementation process through specific code examples. We
 Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
Simple JavaScript Tutorial: How to Get HTTP Status Code
Jan 05, 2024 pm 06:08 PM
JavaScript tutorial: How to get HTTP status code, specific code examples are required. Preface: In web development, data interaction with the server is often involved. When communicating with the server, we often need to obtain the returned HTTP status code to determine whether the operation is successful, and perform corresponding processing based on different status codes. This article will teach you how to use JavaScript to obtain HTTP status codes and provide some practical code examples. Using XMLHttpRequest
 How to use insertBefore in javascript
Nov 24, 2023 am 11:56 AM
How to use insertBefore in javascript
Nov 24, 2023 am 11:56 AM
Usage: In JavaScript, the insertBefore() method is used to insert a new node in the DOM tree. This method requires two parameters: the new node to be inserted and the reference node (that is, the node where the new node will be inserted).
 What is java timer expression
Dec 27, 2023 pm 05:06 PM
What is java timer expression
Dec 27, 2023 pm 05:06 PM
The timer expression is used to define the execution plan of the task. The timer expression is based on the model of "execute a task after a given time interval". The expression usually consists of two parts: an initial delay and a time interval.





